This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
luzhijing pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/doris-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new 7a5cbee5b4c Add two blogs (#262)
7a5cbee5b4c is described below
commit 7a5cbee5b4ca6f205f113a487a66fd53f0dcd7ef
Author: Hu Yanjun <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Fri Jul 14 17:52:04 2023 +0800
Add two blogs (#262)
---
blog/Moka.md | 104 ++++++++++++
blog/Tianyancha.md | 120 ++++++++++++++
i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Moka.md | 163 +++++++++++++++++++
.../docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Tianyancha.md | 175 +++++++++++++++++++++
4 files changed, 562 insertions(+)
diff --git a/blog/Moka.md b/blog/Moka.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..3222a610e8e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/Moka.md
@@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
+---
+{
+ 'title': 'Listen to That Poor BI Engineer: We Need Fast Joins',
+ 'summary': "JOIN queries are always a hassle, but yes, you can expect fast
joins from a relational database. Read this and learn how.",
+ 'date': '2023-07-10',
+ 'author': 'Baoming Zhang',
+ 'tags': ['Best Practice'],
+}
+
+
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+Business intelligence (BI) tool is often the last stop of a data processing
pipeline. It is where data is visualized for analysts who then extract insights
from it. From the standpoint of a SaaS BI provider, what are we looking for in
a database? In my job, we are in urgent need of support for fast join queries.
+
+## Why JOIN Query Matters
+
+I work as an engineer that supports a human resource management system. One
prominent selling point of our services is **self-service** **BI**. That means
we allow users to customize their own dashboards: they can choose the fields
they need and relate them to form the dataset as they want.
+
+
+
+Join query is a more efficient way to realize self-service BI. It allows
people to break down their data assets into many smaller tables instead of
putting it all in a flat table. This would make data updates much faster and
more cost-effective, because updating the whole flat table is not always the
optimal choice when you have plenty of new data flowing in and old data being
updated or deleted frequently, as is the case for most data input.
+
+In order to maximize the time value of data, we need data updates to be
executed really quickly. For this purpose, we looked into three OLAP databases
on the market. They are all fast in some way but there are some differences.
+
+
+
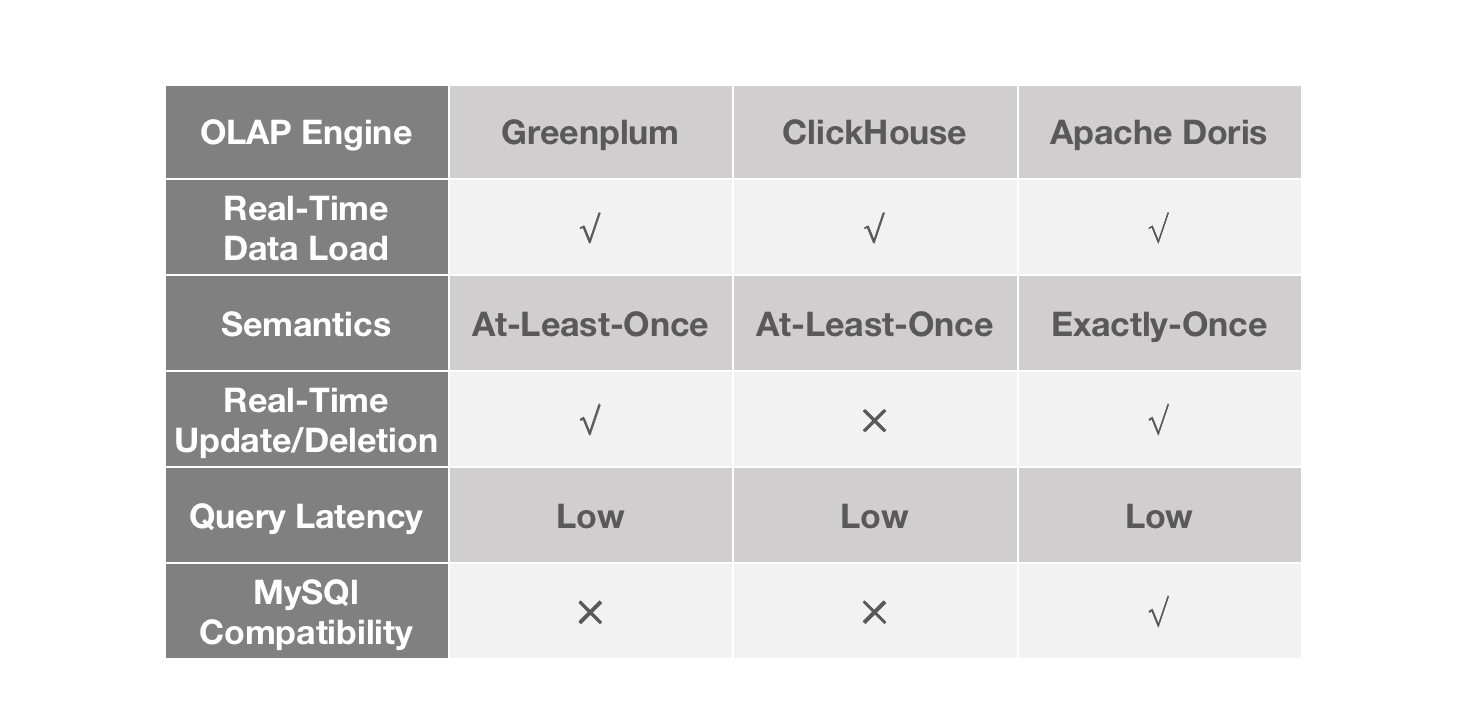
+Greenplum is really quick in data loading and batch DML processing, but it is
not good at handling high concurrency. There is a steep decline in performance
as query concurrency rises. This can be risky for a BI platform that tries to
ensure stable user experience. ClickHouse is mind-blowing in single-table
queries, but it only allows batch update and batch delete, so that's less
timely.
+
+## Welcome to JOIN Hell
+
+JOIN, my old friend JOIN, is always a hassle. Join queries are demanding for
both engineers and the database system. Firstly, engineers must have a thorough
grasp of the schema of all tables. Secondly, these queries are
resource-intensive, especially when they involve large tables. Some of the
reports on our platform entail join queries across up to 20 tables. Just
imagine the mess.
+
+We tested our candidate OLAP engines with our common join queries and our most
notorious slow queries.
+
+
+
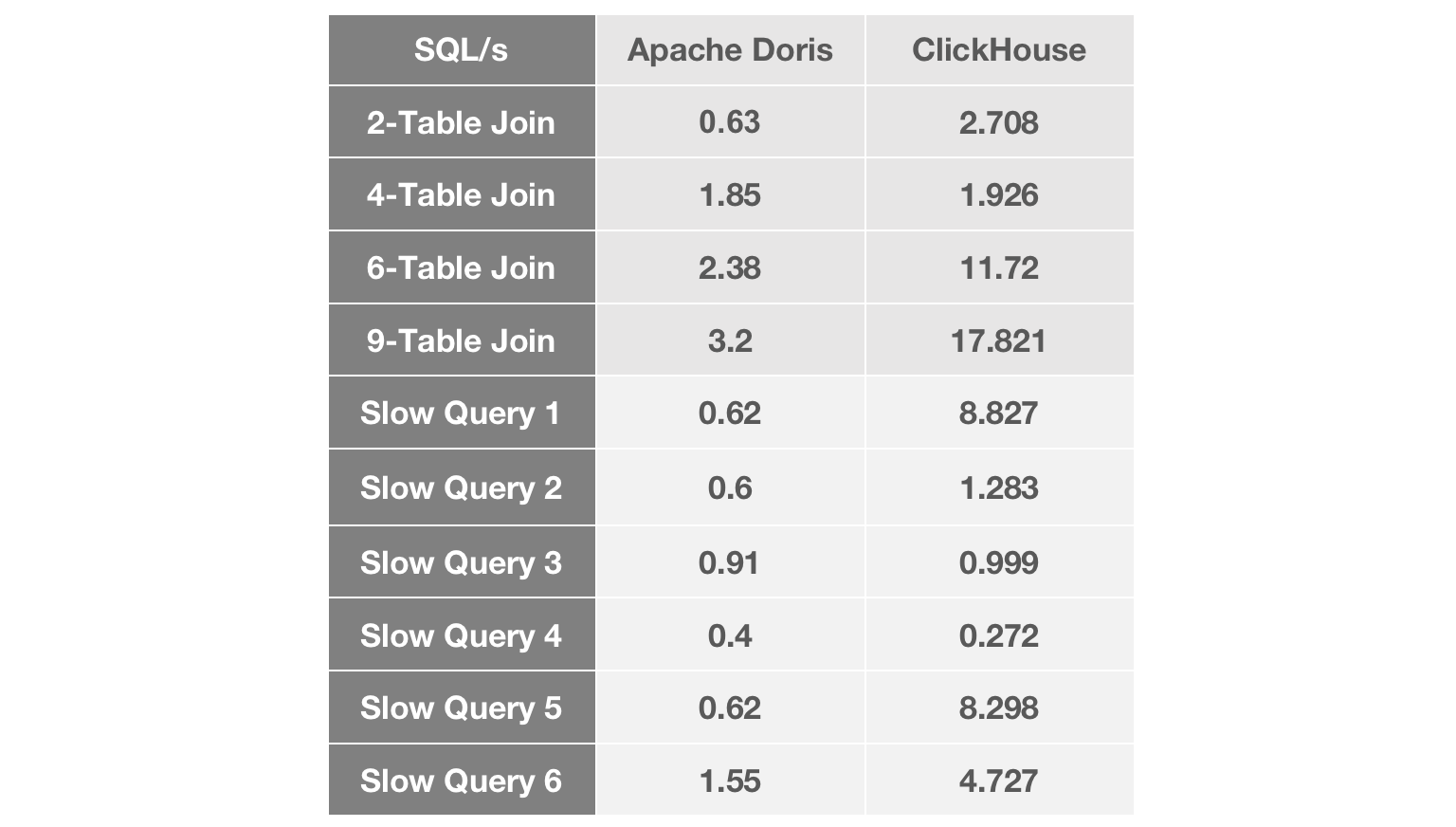
+As the number of tables joined grows, we witness a widening performance gap
between Apache Doris and ClickHouse. In most join queries, Apache Doris was
about 5 times faster than ClickHouse. In terms of slow queries, Apache Doris
responded to most of them within less than 1 second, while the performance of
ClickHouse fluctuated within a relatively large range.
+
+And just like that, we decided to upgrade our data architecture with Apache
Doris.
+
+## Architecture that Supports Our BI Services
+
+**Data Input:**
+
+Our business data flows into DBLE, a distributed middleware based on MySQL.
Then the DBLE binlogs are written into Flink, getting deduplicated, merged, and
then put into Kafka. Finally, Apache Doris reads data from Kafka via its
Routine Load approach. We apply the "delete" configuration in Routine Load to
enable real-time deletion. The combination of Apache Flink and the idempotent
write mechanism of Apache Doris is how we get exactly-once guarantee. We have a
data size of billions of ro [...]
+
+In addition, taking advantage of Apache Kafka and the Routine Load method, we
are able to shave the traffic peaks and maintain cluster stability. Kafka also
allows us to have multiple consumers of data and recompute intermediate data by
resetting the offsets.
+
+**Data Output**:
+
+As a self-service BI platform, we allow users to customize their own reports
by configuring the rows, columns, and filters as they need. This is supported
by Apache Doris with its capabilities in join queries.
+
+In total, we have 400 data tables, of which 50 has over 100 million rows. That
adds up to a data size measured in TB. We put all our data into two Doris
clusters on 40 servers.
+
+## No Longer Stalled by Privileged Access Queries
+
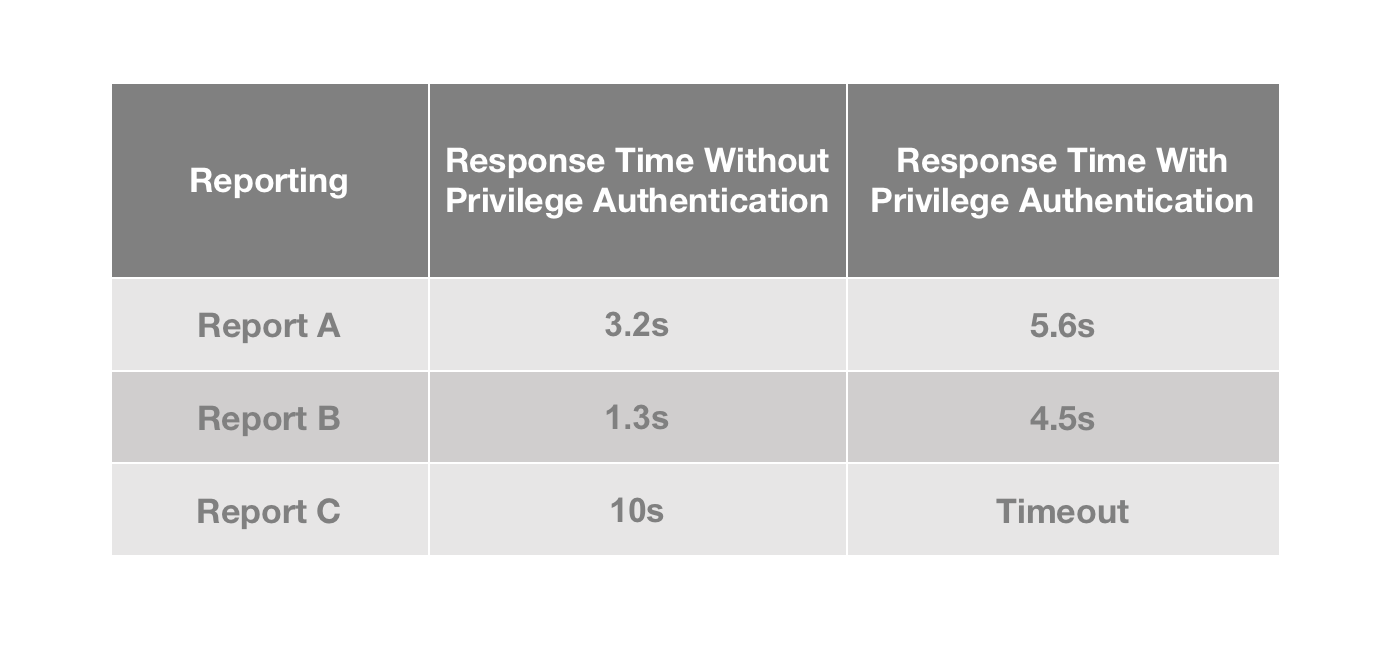
+On our BI platform, privileged queries are often much slower than
non-privileged queries. Timeout is often the case and even more so for queries
on large datasets.
+
+Human resource data is subject to very strict and fine-grained access control
policies. The role and position of users and the confidentiality level of data
determine who has access to what (the data granularity here is up to fields in
a table). Occasionally, we need to separately grant a certain privilege to a
particular person. On top of that, we need to ensure data isolation between the
multiple tenants on our platform.
+
+How does all this add to complexity in engineering? Any user who inputs a
query on our BI platform must go through multi-factor authentication, and the
authenticated information will all be inserted into the SQL via `in` and then
passed on to the OLAP engine. Therefore, the more fine-grained the privilege
controls are, the longer the SQL will be, and the more time the OLAP system
will spend on ID filtering. That's why our users are often tortured by high
latency.
+
+
+
+So how did we fix that? We use the [Bloom Filter
index](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/data-table/index/bloomfilter/) in
Apache Doris.
+
+
+
+By adding Bloom Filter indexes to the relevant ID fields, we improve the speed
of privileged queries by 30% and basically eliminate timeout errors.
+
+
+
+Tips on when you should use the Bloom Filter index:
+
+- For non-prefix filtering
+- For `in` and `=` filters on a particular column
+- For filtering on high-cardinality columns, such as UserID. In essence, the
Bloom Filter index is used to check if a certain value exists in a dataset.
There is no point in using the Bloom Filter index for a low-cardinality column,
like "gender", for example, because almost every data block contains all the
gender values.
+
+## To All BI Engineers
+
+We believe self-service BI is the future in the BI landscape, just like AGI is
the future for artificial intelligence. Fast join queries is the way towards
it, and the foregoing architectural upgrade is part of our ongoing effort to
empower that. May there be less painful JOINs in the BI world. Cheers.
+
+
+
+Find the Apache Doris developers on [Slack](https://t.co/ZxJuNJHXb2)
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/blog/Tianyancha.md b/blog/Tianyancha.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..22e52fd08c5
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/Tianyancha.md
@@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
+---
+{
+ 'title': 'Replacing Apache Hive, Elasticsearch and PostgreSQL with Apache
Doris',
+ 'summary': "How does a data service company build its data warehouse?
Simplicity is the best policy. See how a due diligence platform increased data
writing efficiency by 75%.",
+ 'date': '2023-07-01',
+ 'author': 'Tao Wang',
+ 'tags': ['Best Practice'],
+}
+
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+How does a data service company build its data warehouse? I worked as a
real-time computing engineer for a due diligence platform, which is designed to
allow users to search for a company's business data, financial, and legal
details. It has collected information of over 300 million entities in more than
300 dimensions. The duty of my colleagues and I is to ensure real-time updates
of such data so we can provide up-to-date information for our registered users.
That's the customer-facing [...]
+
+Our old data warehouse consisted of the most popular components of the time,
including **Apache** **Hive**, **MySQL**, **Elasticsearch**, and
**PostgreSQL**. They support the data computing and data storage layers of our
data warehouse:
+
+- **Data Computing**: Apache Hive serves as the computation engine.
+- **Data Storage**: **MySQL** provides data for DataBank, Tableau, and our
customer-facing applications. **Elasticsearch** and **PostgreSQL** serve for
our DMP user segmentation system: the former stores user profiling data, and
the latter stores user group data packets.
+
+As you can imagine, a long and complicated data pipeline is high-maintenance
and detrimental to development efficiency. Moreover, they are not capable of
ad-hoc queries. So as an upgrade to our data warehouse, we replaced most of
these components with [Apache Doris](https://github.com/apache/doris), a
unified analytic database.
+
+
+
+
+
+## Data Flow
+
+This is a lateral view of our data warehouse, from which you can see how the
data flows.
+
+
+
+For starters, binlogs from MySQL will be ingested into Kafka via Canal, while
user activity logs will be transferred to Kafka via Apache Flume. In Kafka,
data will be cleaned and organized into flat tables, which will be later turned
into aggregated tables. Then, data will be passed from Kafka to Apache Doris,
which serves as the storage and computing engine.
+
+We adopt different data models in Apache Doris for different scenarios: data
from MySQL will be arranged in the [Unique
model](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/data-table/data-model/#unique-model),
log data will be put in the [Duplicate
model](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/data-table/data-model/#duplicate-model),
while data in the DWS layer will be merged in the [Aggregate
model](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/data-table/data-model/#aggregate-model).
+
+This is how Apache Doris replaces the roles of Hive, Elasticsearch, and
PostgreSQL in our datawarehouse. Such transformation has saved us lots of
efforts in development and maintenance. It also made ad-hoc queries possible
and our user segmentation more efficient.
+
+## Ad-Hoc Queries
+
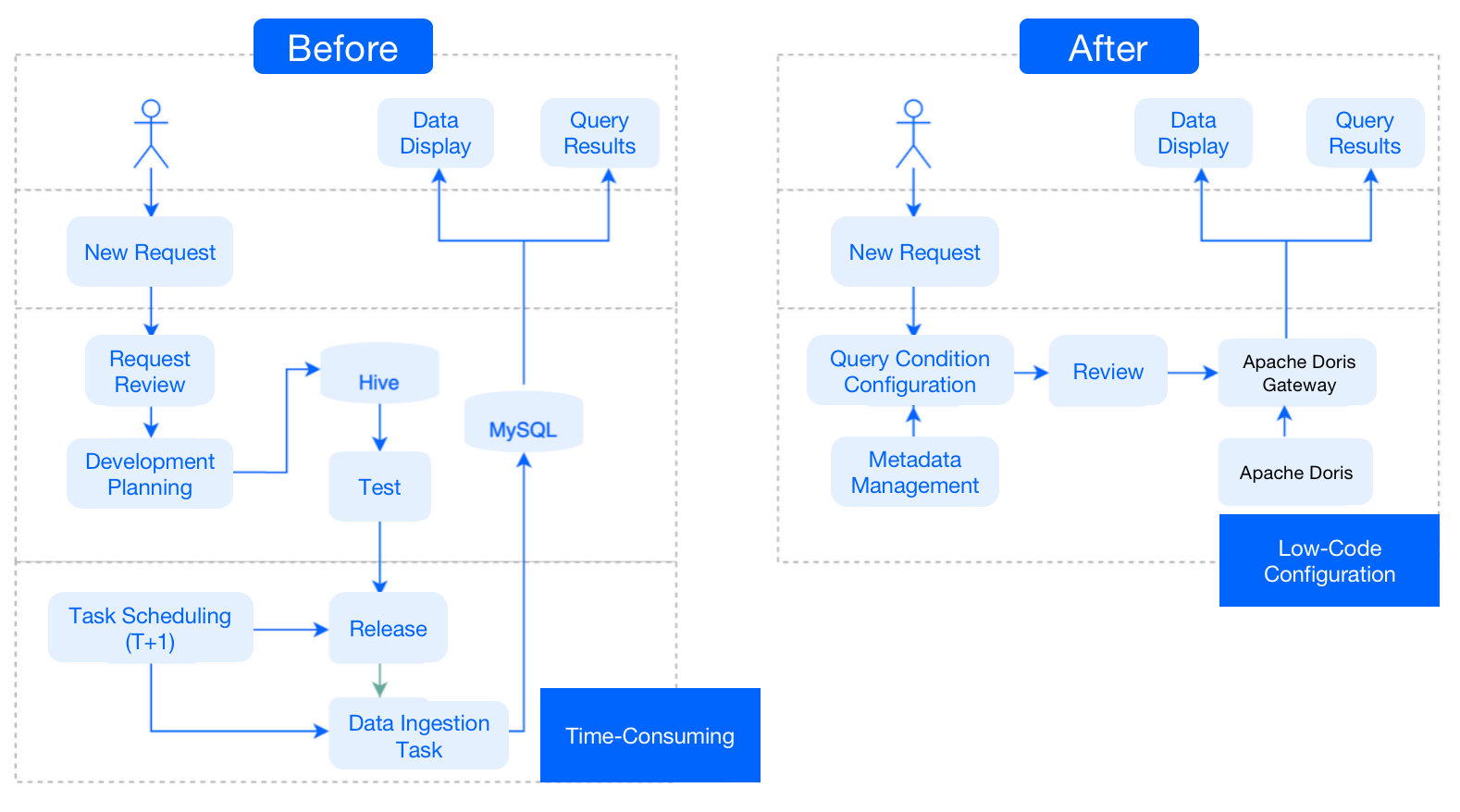
+**Before**: Every time a new request was raised, we developed and tested the
data model in Hive, and wrote the scheduling task in MySQL so that our
customer-facing application platforms could read results from MySQL. It was a
complicated process that took a lot of time and development work.
+
+**After**: Since Apache Doris has all the itemized data, whenever it is faced
with a new request, it can simply pull the metadata and configure the query
conditions. Then it is ready for ad-hoc queries. In short, it only requires
low-code configuration to respond to new requests.
+
+
+
+## User Segmentation
+
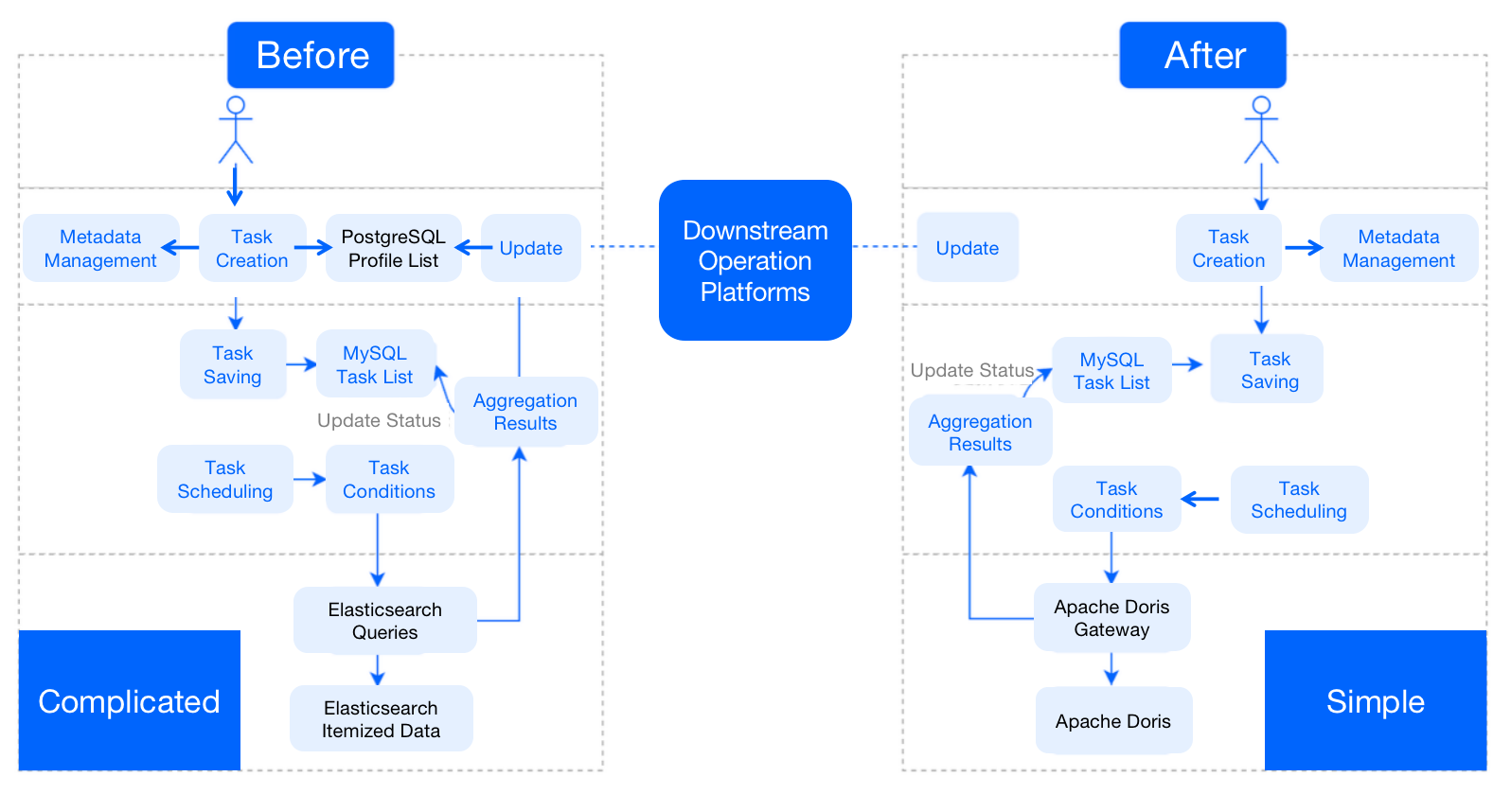
+**Before**: After a user segmentation task was created based on metadata, the
relevant user IDs would be written into the PostgreSQL profile list and the
MySQL task list. Meanwhile, Elasticsearch would execute the query according to
the task conditions; after the results are produced, it would update status in
the task list and write the user group bitmap package into PostgreSQL. (The
PostgreSQL plug-in is capable of computing the intersection, union, and
difference set of bitmap.) Then [...]
+
+Tables in Elasticsearch and PostgreSQL were unreusable, making this
architecture cost-ineffective. Plus, we had to pre-define the user tags before
we could execute a new type of query. That slowed things down.
+
+**After**: The user IDs will only be written into the MySQL task list. For
first-time segmentation, Apache Doris will execute the **ad-hoc query** based
on the task conditions. In subsequent segmentation tasks, Apache Doris will
perform **micro-batch rolling** and compute the difference set compared with
the previously produced user group packet, and notify downstream platforms of
any updates. (This is realized by the [bitmap
functions](https://doris.apache.org/docs/dev/sql-manual/sql-fu [...]
+
+In this Doris-centered user segmentation process, we don't have to pre-define
new tags. Instead, tags can be auto-generated based on the task conditions. The
processing pipeline has the flexibility that can make our user-group-based A/B
testing easier. Also, as both the itemized data and user group packets are in
Apache Doris, we don't have to attend to the read and write complexity between
multiple components.
+
+
+
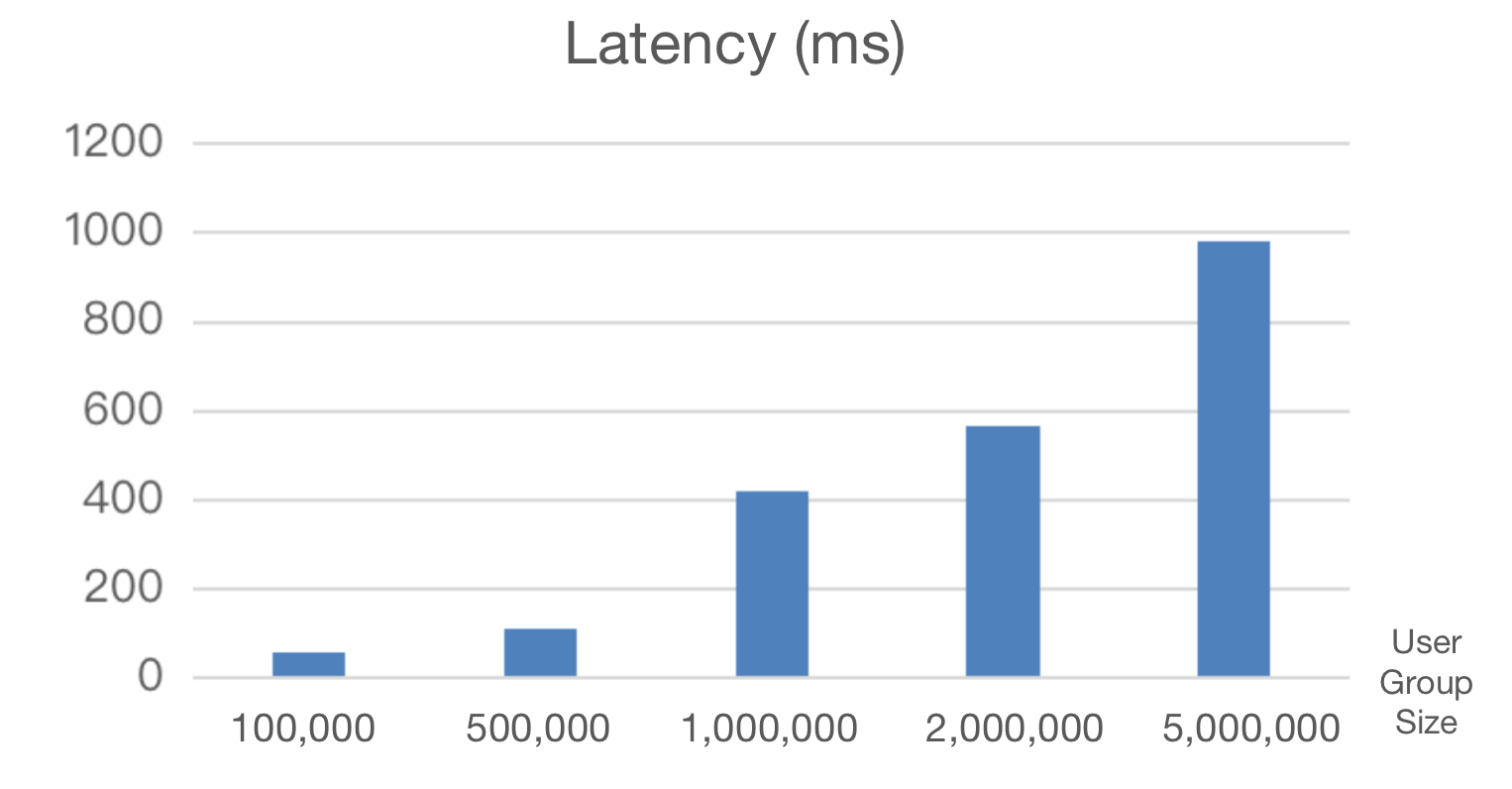
+## Trick to Speed up User Segmentation by 70%
+
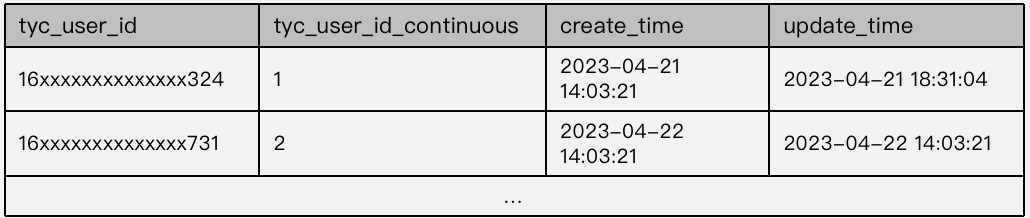
+Due to risk aversion reasons, random generation of `user_id` is the choice for
many companies, but that produces sparse and non-consecutive user IDs in user
group packets. Using these IDs in user segmentation, we had to endure a long
waiting time for bitmaps to be generated.
+
+To solve that, we created consecutive and dense mappings for these user IDs.
**In this way, we decreased our user segmentation latency by 70%.**
+
+
+
+
+
+### Example
+
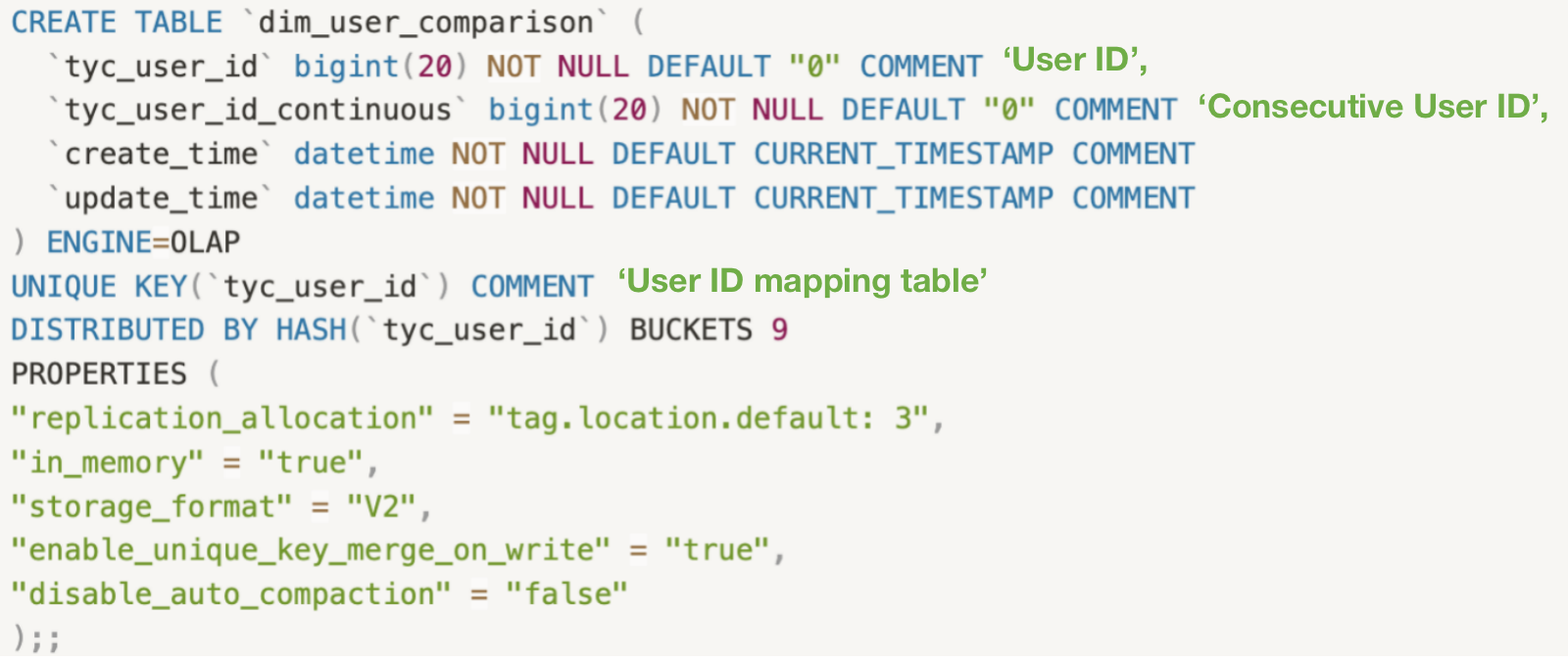
+**Step 1: Create a user ID mapping table:**
+
+We adopt the Unique model for user ID mapping tables, where the user ID is the
unique key. The mapped consecutive IDs usually start from 1 and are strictly
increasing.
+
+
+
+**Step 2: Create a user group table:**
+
+We adopt the Aggregate model for user group tables, where user tags serve as
the aggregation keys.
+
+
+
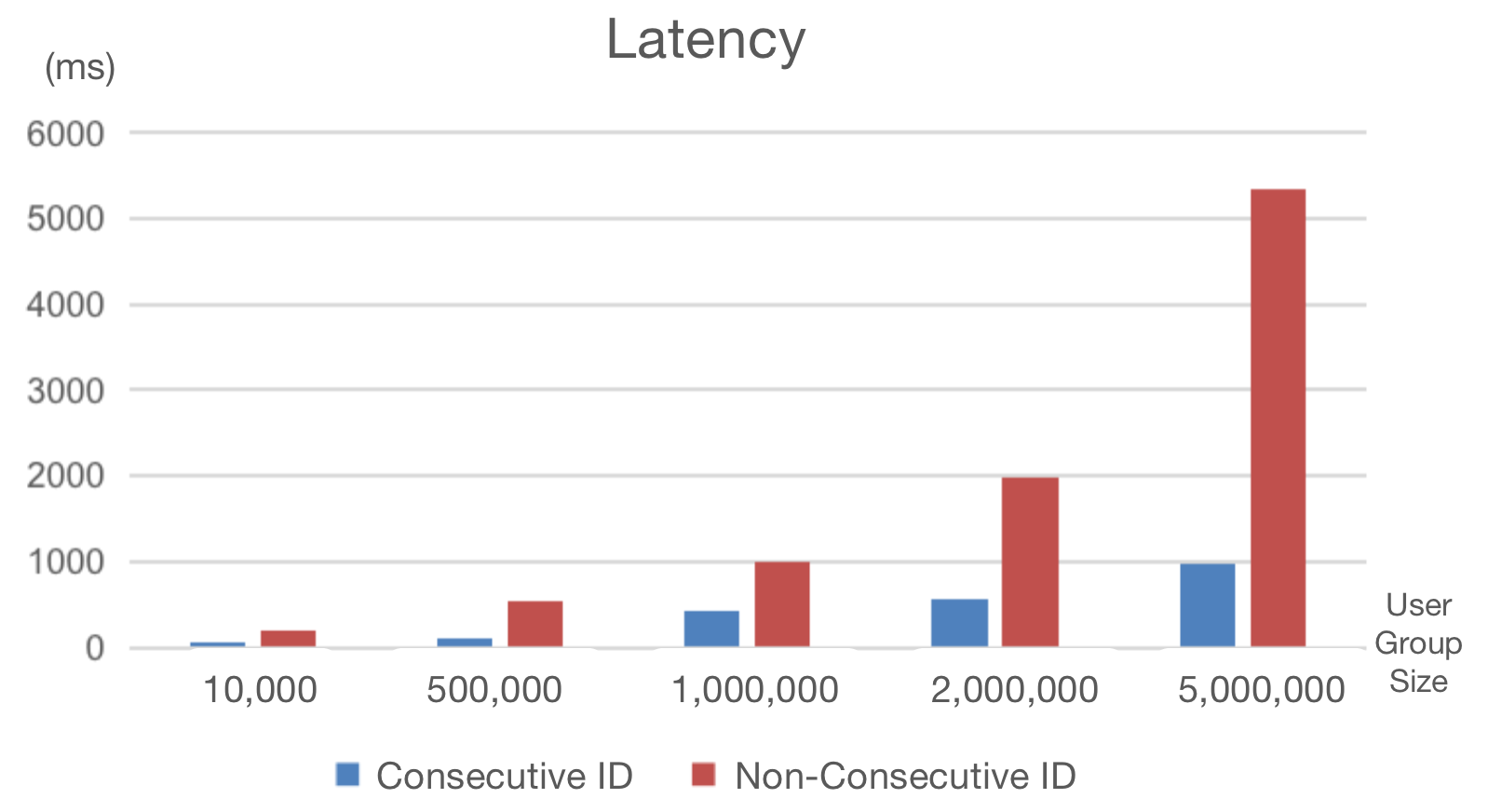
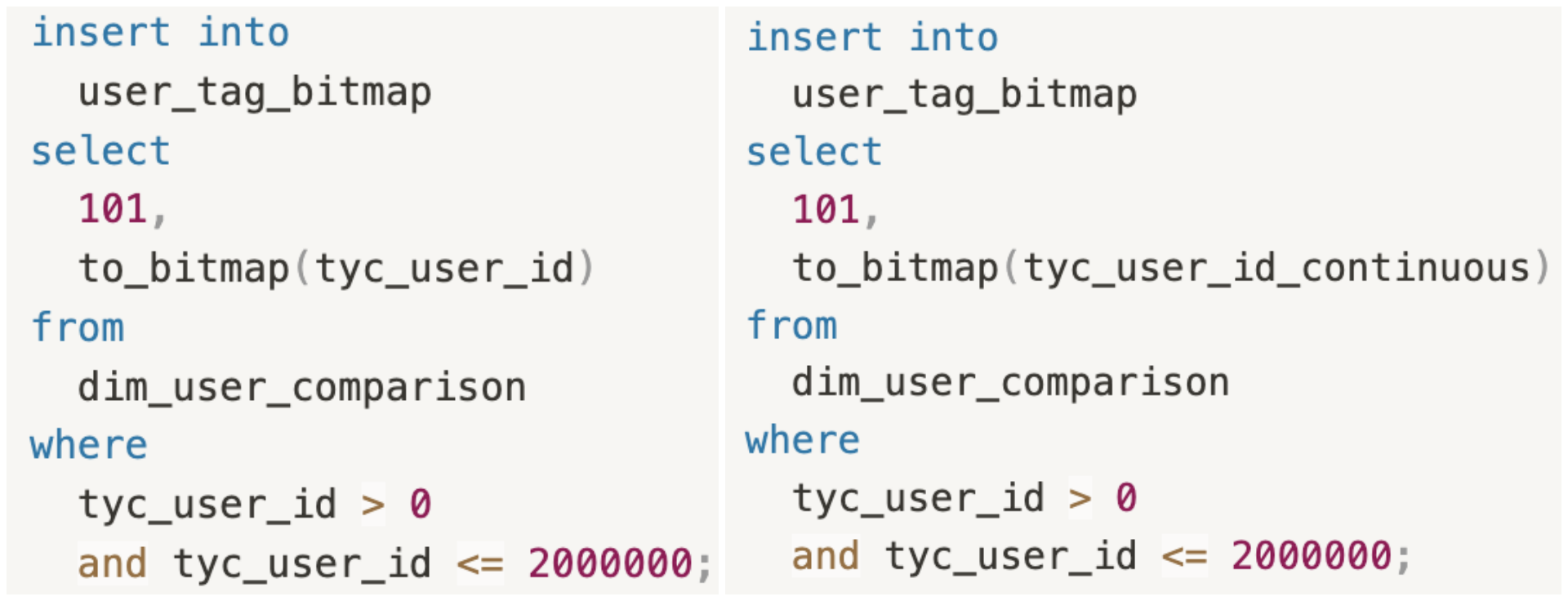
+Supposing that we need to pick out the users whose IDs are between 0 and
2000000.
+
+The following snippets use non-consecutive (`tyc_user_id`) and consecutive
(`tyc_user_id_continuous`) user IDs for user segmentation, respectively. There
is a big gap between their **response time:**
+
+- Non-Consecutive User IDs: **1843ms**
+- Consecutive User IDs: **543ms**
+
+
+
+## Conclusion
+
+We have 2 clusters in Apache Doris accommodating tens of TBs of data, with
almost a billion new rows flowing in every day. We used to witness a steep
decline in data ingestion speed as data volume expanded. But after upgrading
our data warehouse with Apache Doris, we increased our data writing efficiency
by 75%. Also, in user segmentation with a result set of less than 5 million, it
is able to respond within milliseconds. Most importantly, our data warehouse
has been simpler and friendli [...]
+
+
+
+Lastly, I would like to share with you something that interested us most when
we first talked to the [Apache Doris community](https://t.co/KcxAtAJZjZ):
+
+- Apache Doris supports data ingestion transactions so it can ensure data is
written **exactly once**.
+- It is well-integrated with the data ecosystem and can smoothly interface
with most data sources and data formats.
+- It allows us to implement elastic scaling of clusters using the command line
interface.
+- It outperforms ClickHouse in **join queries**.
diff --git a/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Moka.md
b/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Moka.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..733c5bd64f8
--- /dev/null
+++ b/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Moka.md
@@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
+---
+{
+ 'title': '查询提速 20 倍,Apache Doris 在 Moka BI SaaS 服务场景下的应用实践',
+ 'summary': "为了提供更完备的数据支持,助力企业提升招聘竞争力,MOKA 引入性能强悍的 Apache Doris
对早期架构进行升级转型,成就了 Moka BI 强大的性能与优秀的用户体验。",
+ 'date': '2023-07-10',
+ 'author': '张宝铭',
+ 'tags': ['最佳实践'],
+}
+
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+**导读:** MOKA 主要有两大业务线 MOKA 招聘(智能化招聘管理系统)和 MOKA People(智能化人力资源管理系统),MOKA BI
通过全方位数据统计和可灵活配置的实时报表,赋能于智能化招聘管理系统和人力资源管理系统。为了提供更完备的数据支持,助力企业提升招聘竞争力,MOKA
引入性能强悍的 [Apache Doris](https://github.com/apache/doris) 对早期架构进行升级转型,成就了 Moka BI
强大的性能与优秀的用户体验。
+
+
+
+作者**|**Moka 数据架构师 张宝铭
+
+
+# 业务需求
+
+MOKA 主要有两大业务线 MOKA 招聘(智能化招聘管理系统)和 MOKA People(智能化人力资源管理系统)。
+
+- MOKA 招聘系统覆盖社招、校招、内推、猎头管理等场景,让 HR
获得更高效的招聘体验,更便捷的协作体验,让管理者获得招聘数据洞见,让招聘降本增效的同时,树立企业在候选人心目中的专业形象。
+- MOKA People 覆盖企业所需要的组织人事、假期考勤、薪酬、绩效、审批等高频业务场景,打通从招聘到人力资源管理的全流程,为 HR
工作提效赋能。通过多维度数据洞见,助力管理者高效科学决策。全生态对接,更加注重全员体验,是一款工作体验更愉悦的人力资源管理系统。
+
+而 MOKA BI 通过全方位数据统计和可灵活配置的实时报表,赋能于智能化招聘管理系统和人力资源管理系统。通过 PC
端和移动端的多样化报表展示,为企业改善招聘业务提供数据支持,全面提升招聘竞争力,从而助力科学决策。
+
+
+
+# MOKA BI 早期架构
+
+
+
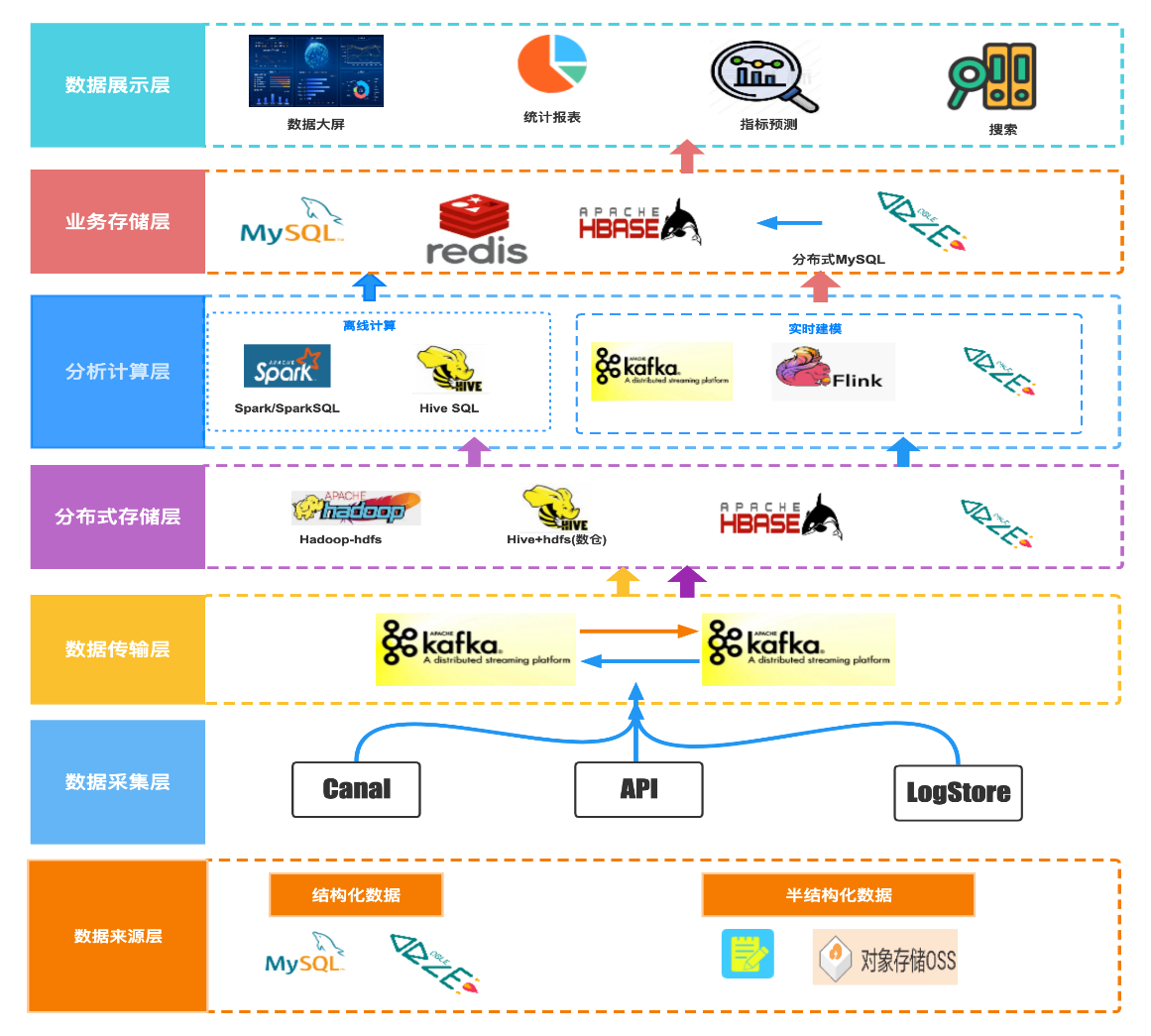
+Moka BI 数仓早期架构是类 Lambda 架构,实时处理和离线处理并存。
+
+- 实时部分数据主要来源为结构化的数据,Canal 采集 MySQL 或 DBLE(基于 MySQL 的分布式中间件)的 Binlog 输出至
Kafka 中;未建模的数据按照公司分库,存储在业务 DBLE 中,通过 Flink 进行实时建模,将计算后的数据实时写入业务 DBLE 库,通过 DBLE
提供报表查询能力,支持数据大屏和实时报表统计。
+- 离线部分涵盖了实时部分数据,其结构化数据来源于 DBLE 的 Binlog,明细数据在 Hbase 中实时更新,并映射成 Hive
表,非结构化数据通过 ETL 流程,存储至 Hive 中,通过 Spark 进行进行离线部分建模计算,离线数仓 ADS 层数据输出至 MySQL 和
Redis 支持离线报表统计,明细数据又为指标预测和搜索等外部应用提供数据支持。
+
+
+
+
+## **现状与问题**
+
+在早期数仓架构中,为了实现实时建模以及实时报表查询功能,就必须要求底层数据库能够承载业务数据的频繁插入、更新及删除操作,并要求支持标准
SQL,因此当时我们选择 DBLE 作为数据存储、建模、查询的底层库。早期 Moka BI 灰度期用户较少,业务数据量以及报表的使用量都比较低,DBLE
尚能满足业务需求,但随着 Moka BI 逐渐面向所有用户开放,DBLE 逐渐无法适应 BI
报表的查询分析性能要求,同时实时与离线架构分离、存储成本高且数据不易维护,亟需进行升级转型。
+
+
+
+
+# 技术选型
+
+为匹配业务飞速增长的要求、满足更复杂的查询需求,我们决定引入一款性能突出的 OLAP 引擎对 Moka BI
进行升级改造。同时出于多样化分析场景的考虑,我们希望其能够支撑更广泛的应用场景。调研的主要方向包括 报表的实时查询能力、数据的更新能力、标准的查询 SQL
以及数据库的可维护性、扩展性、稳定性等。
+
+
+
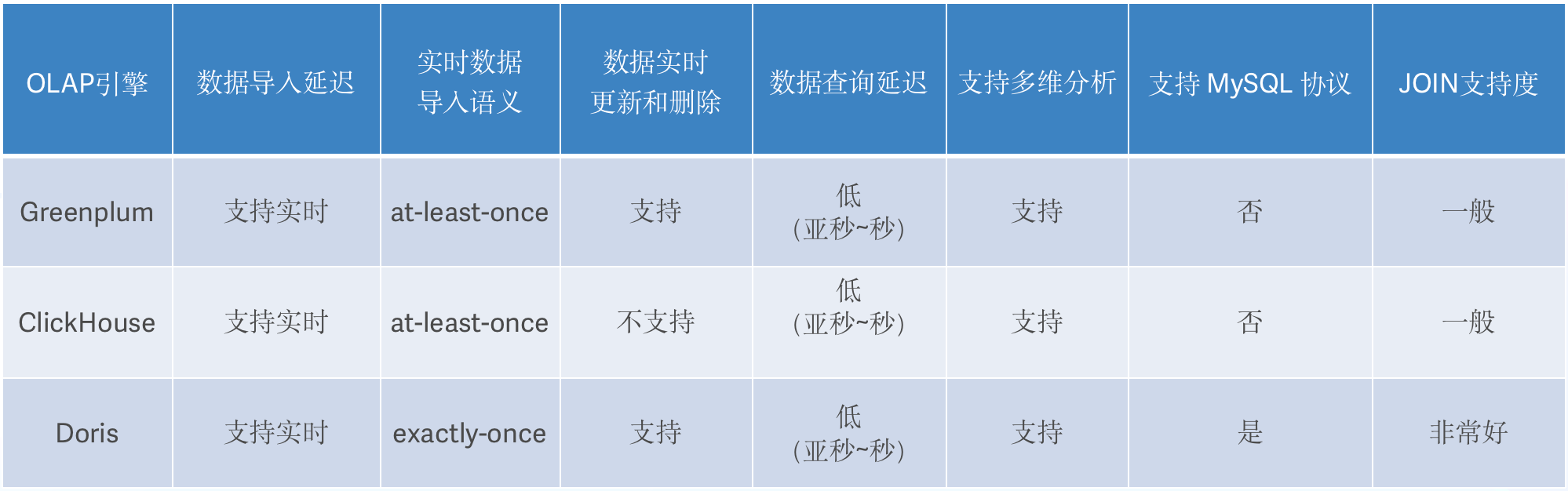
+确定调研方向后,我们首先对 Greenplum 展开了调研,其特点主要是数据加载和批量 DML
处理快,但受限于主从双层架构设计、存在性能瓶颈,且并发能力很有限、性能随着并发量增加而快速下降,同时其使用的是 PG 语法、不支持 MySQL
语法,在进行引擎切换时成本较高,因此在基本功能调研结束后便不再考虑使用。
+
+随后我们对 ClickHouse 进行了调研,ClickHouse 在单表查询场景下性能表现非常优异的,但是在多表 Join 场景中性能表现不尽如人意,另外
ClickHouse 缺少数据实时更新和删除的能力,仅适用于批量删除或修改数据,同时 ClickHouse 对 SQL
的支持也比较有限,使用起来需要一定的学习成本。
+
+紧接着我们对近几年势如破竹的 Apache Doris 进行了调研,在调研中发现,Doris 支持实时导入,同时也支持数据的实时更新与删除,可以实现
Exactly-Once 语义;其次,在实时查询方面,Doris 可以实现秒级查询,且在多表 Join 能力的支持上更加强劲;除此之外,Doris
简单易用,部署只需两个进程,不依赖其他系统,兼容 MySQL 协议,并且使用标准 SQL ,可快速上手,部署及学习成本投入均比较低。
+
+## **Benchmark**
+
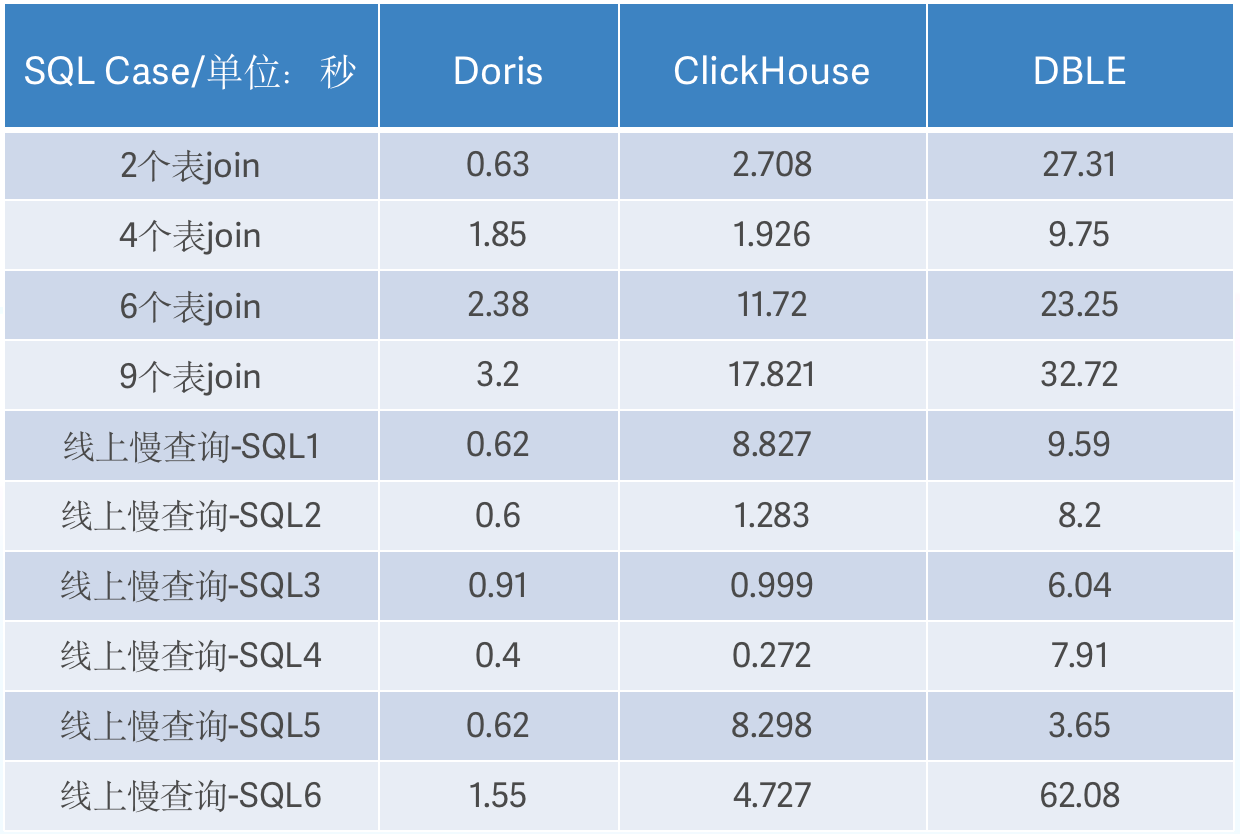
+在初步调研的基础之上,我们进一步将 Apache Doris 、Clickhouse 与当下使用的 DBLE 在查询性能上进行了多轮测试对比,查询耗时如下:
+
+
+
+- **多表 Join**:随着 SQL Join 数量的增多,Doris 和 ClickHouse 性能表现差距越来越大,Doris
的查询延迟相对比较稳定,最长耗时仅为 3.2s;而 ClickHouse 的查询延迟呈现指数增长,最长耗时甚至达到 17.8s,二者性能最高相差 5
倍,DBLE 的查询性能则远不如这两款产品。
+- **慢查询:** 在线上慢查询 SQL 的对比测试中,Doris 的性能同样非常稳定,不同的 SQL 查询基本都能在 1s
内返回查询结果,ClickHouse 与之对比查询延迟波动较大、性能表现很不稳定,二者相同 SQL 性能差距最大超过 10 余倍。
+
+
+
+
+**通过以上调研对比,可以看出 Apache Doris 不管是在基本功能上、还是查询性能上表现都更胜一筹,因此我们将目标锁定了 Doris,并决定尽快引入
Apache Doris 作为 Moka** **BI** **新一代** **数仓** **架构的查询引擎。**
+
+
+
+
+# 新版架构
+
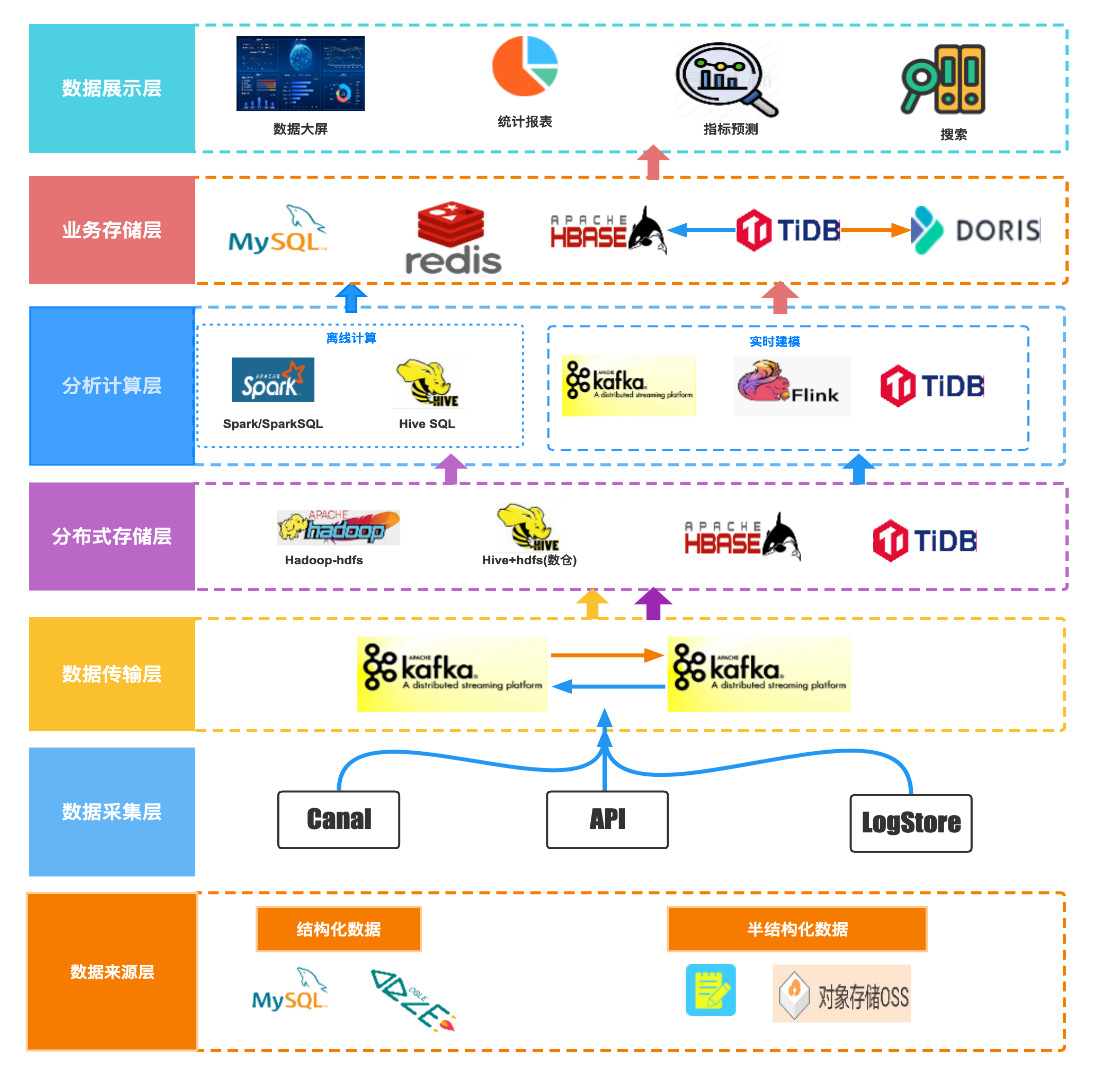
+
+
+在引入 Doris 之后,Moka BI 数仓架构的主要变化是将 OLAP 和 OLTP 进行分离,即使用 DBLE 支持数据的实时建模,数据来源于
Moka 系统的业务数据,包含了结构化和半结构化的数据,通过 Flink 读取 DBLE Binlog,完成数据去重、合并后写入 Kafka,Doris 通过
Routine Load 读取 Kafka 完成数据写入,此时 DBLE 仅作为数据建模合成使用,由 Doris 提供报表查询能力。
+
+
+
+
+基于 Doris 列存储、高并发、高性能等特性,Moka BI
报表采用自助方式构建完成,支撑客户根据需求灵活配置行、列、筛选的场景。与传统报表按需求定制开发方式对比,这种自助式报表构建非常灵活,平台开发与需求开发完全独立,需求完成速度得到极大的提升。
+
+
+
+数据导入方面,数据通过 Routine Load 定期批量导入到 Doris
数据仓库中,保证了数据的准实时同步。通过对系统数据收集与建模,及时向客户提供最新的业务数据,以帮助客户快速了解招聘情况,并做出有效的调整。
+
+数据更新方面,Doris 在大数据量(单表几十亿)的场景下,表现出了突出的数据更新和删除能力,Moka BI 读取的是业务库的 Binlog
数据,其中有大量的更新以及删除操作,Doris 可以通过 Routine Load 的 Delete 配置实现实时删除,根据 Key 实现幂等性写入,配合
Flink 可以做到真正的 Exactly-Once。在架构中增加了 Routine Load 后,数仓可以实现 1 分钟级别的准实时 **,** 同时结合
Routine load + Kafka 可以实现流量的削峰,保证集群稳定,并且可以通过重置 Kafka 偏移量来实现间数据重写,通过 Kafka
实现多点消费等。
+
+数据查询方面,充分利用 Doris 的多表 Join
能力,使得系统能够实现实时查询。我们将不同的数据表按照关联字段进行连接,形成一个完整的数据集,基于数据集可进行各种数据分析和可视化操作,同时可高效应对任意条件组合的查询场景以及需要灵活定制需求的查询分析场景,**在某些报表中,需要
Join 的表可能达到几十张,Doris 强大的 Join 性能,使 Moka** **BI** **的报表查询可以达到秒级响应。**
+
+运维管理方面,Doris 部署运维简单方便,不依赖第三方组件,无损弹性扩缩容,自动数据均衡,集群高可用。Doris 集群仅有 FE 和 BE
两个组件,不依赖 Zookeeper 等组件即可实现高可用,部署、运维方便,相比传统的 Hadoop
组件,非常友好,支持弹性扩容,只需简单配置即可实现无损扩容,并且可以自动负载数据到扩容的节点,大大降低了我们引入新技术栈的难度和运维压力。
+
+
+
+
+# 调优实践
+
+新架构实际的落地使用中,我们总结了一些调优的经验,在此分享给大家。
+
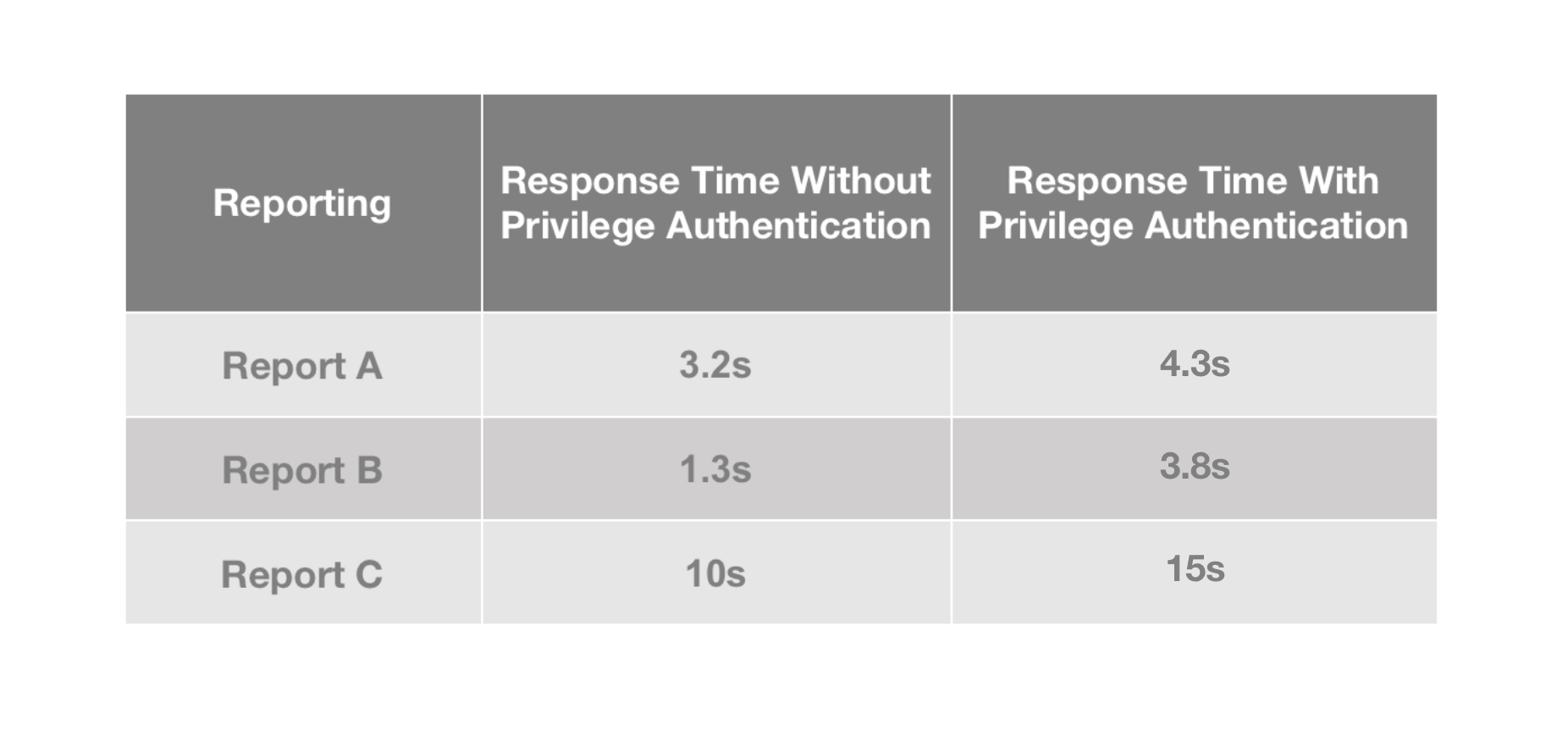
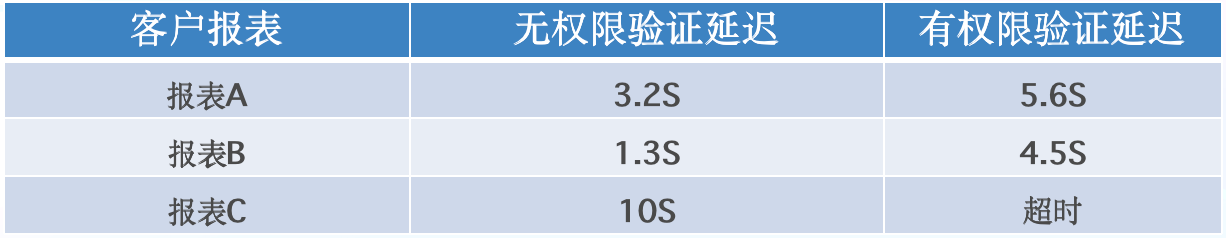
+在 Moka BI 报表查询权限场景中,同样配置的报表,**有权限认证**时查询速度比**没有权限认证**时慢 30%
左右,甚至出现查询超时,而**超管权限**查询时则正常,这一现象在数据量较大的客户报表中尤为明显。
+
+人力资源管理业务的数据权限有着极为严格和精细的管控需求,除了 SaaS
业务自身对于不同租户间的数据隔离要求外,还需要针对业务人员的身份角色、管理部门范畴以及被管理人员的信息敏感程度对可见数据的范围进行进一步细分,因此在 Moka
BI 权限功能模块的设计之时就考虑并实现了极为灵活的自定义配置化方案。例如 HRBP 与 PayRoll、HRIS
等角色的可见字段不同、不同职级或部门但角色一致用户的可见数据区间不同,同时针对部分敏感的人员信息还需要做数据过滤,或者出于管理授权的需求临时开通某一权限,甚至以上权限要求还会进行多重的交叉组合,以保证每一用户可查看的数据、报表、信息均被限制在权限范围以内。
+
+因此当用户需要对数据报表进行查询时,会先在 Moka BI 的权限管理模块进行多重验证,验证信息会通过` in `的方式拼接在查询 SQL 中并传递给
OLAP 系统。随着客户业务体量的增大,对于权限管控的要求越精细、最终所产生的 SQL
就越复杂,部分业务规模比较大的客户报表会出现上千甚至更多的权限限制,因此造成 OLAP 系统的 id
过滤时间变长,导致报表查询延迟增加,给大客户造成了体验不佳。
+
+
+
+**解决方案:**
+
+为适配该业务场景,我们通过查看官方的文档发现 Doris Bloom Filter 索引的特性可以很好的解决该问题
+
+
+
+Doris BloomFilter 索引使用场景:
+
+- BloomFilter 适用于非前缀过滤。
+- 查询会根据该列高频过滤,而且查询条件大多是` in `和` = `过滤。
+- 不同于 Bitmap,BloomFilter 适用于高基数列,比如 UserID。因为如果创建在低基数的列上,比如 “性别” 列,则每个 Block
几乎都会包含所有取值,导致 BloomFilter 索引失去意义。
+
+
+
+经过验证,可以通过上方对比报表看到,**将相关 ID 字段增加 BloomFilter 索引后** **,权限验证场景查询速度提升约 30%
,有权限验证的报表超时的问题也得到了改善。**
+
+
+
+
+# 收益与总结
+
+**目前 Moka** **BI** **Doris 有两个集群,** **共 40 台服务器,** **数仓** **共维护了 400 多张表**
**,其中 50 多张表数据量超过 1 亿,总数据量为 T** **B** **级别。**
+
+引入 Apache Doris 改造了新的数据仓库之后,满足了日益增长的分析需求以及对数据实时性的要求,总体收益包含以下几点:
+
+1. **高性能数据查询:** Doris 基于列存储技术,能够快速处理大量的数据,并支持高并发的在线查询,解决了关系型数据库无法支持的复杂查询问题,复杂
SQL 查询的速度上升了一个数据量级。
+1. **数据仓库** **的可扩展性:** Doris
采用分布式集群架构,可以通过增加节点来线性提升存储和查询瓶颈,打破了关系型数据库数据单点限制问题,查询性能得以显著提升。
+1. **更广泛的应用:** 基于 Doris 构建了统一的数据查询平台,应用不再局限于报表服务,对于离线的查询也有很好的支撑,可以说 Doris
的引入是构建数仓一体化的前奏。
+1. **实现自助式分析:** 基于 Doris 强大的查询能力,我们引入了全新的报表构建方式,通过用户自助构建报表方式,能够快速满足用户的各种灵活需求。
+
+在使用 Doris 的两年多时间里,Moka BI 与 Apache Doris 共同成长、共同进步,可以说 Doris 成就了 Moka BI
强大的性能与优秀的用户体验;也正是 Moka BI 特殊的使用场景,也丰富了 Doris 的优化方向,我们提的很多 Issue
与建议,经过版本更新迭代后使其更具竞争力。在未来的时间里,Moka BI 也会紧跟社区脚步,不断优化、回馈社区,希望 [Apache
Doris](https://github.com/apache/doris) 和 [SelectDB](https://cn.selectdb.com/)
发展越来越好、越来越强大。
\ No newline at end of file
diff --git a/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Tianyancha.md
b/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Tianyancha.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..15244d407d9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/i18n/zh-CN/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/Tianyancha.md
@@ -0,0 +1,175 @@
+---
+{
+ 'title': '秒级数据写入,毫秒查询响应,天眼查基于 Apache Doris 构建统一实时数仓',
+ 'summary': "天眼查引入 Apache Doris 对数仓架构进行升级改造,实现了数据门户的统一,大大缩短了数据处理链路,数据导入速率提升
75 %,500 万及以下人群圈选可以实现毫秒级响应,收获了公司内部数据部门、业务方的一致好评",
+ 'date': '2023-07-01',
+ 'author': '王涛',
+ 'tags': ['最佳实践'],
+}
+---
+
+<!--
+Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
+or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
+distributed with this work for additional information
+regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
+to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
+"License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
+with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
+
+ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
+
+Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing,
+software distributed under the License is distributed on an
+"AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY
+KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
+specific language governing permissions and limitations
+under the License.
+-->
+
+**导读:**
随着天眼查近年来对产品的持续深耕和迭代,用户数量也在不断攀升,业务的突破更加依赖于数据赋能,精细化的用户/客户运营也成为提升体验、促进消费的重要动力。在这样的背景下正式引入
Apache Doris 对数仓架构进行升级改造,实现了数据门户的统一,大大缩短了数据处理链路,数据导入速率提升 75 %,500
万及以下人群圈选可以实现毫秒级响应,收获了公司内部数据部门、业务方的一致好评。
+
+**作者:** 王涛,天眼查实时计算负责人
+
+# 业务需求
+
+天眼查的数据仓库主要服务于三个业务场景,每个场景都有其特点和需求,具体如下:
+
+1. **亿级用户人群圈选:** 人群圈选场景中目前有 100+ 人群包,我们需要根据 SQL
条件圈选人群包,来支持人群包的交并差、人群包实时圈选和人群包更新通知下游等需求。例如:圈选出下单未支付超过 5
分钟的用户,我们通过用户标签可以直观掌握用户支付状态,为运营 & 营销团队提供更精细化的人群管理服务,从而提高转化率。
+1. **多元活动支撑的精准营销:** 该场景目前支持了 1000
多个指标,可支持即席查询,根据活动效果及时调整运营策略。例如在“开工季”活动中,需要为数据分析 & 运营团队提供数据支持,从而生成可视化的活动驾驶舱。
+1. **高并发的 C 端分析数据:** 该场景承载了 3 亿+实体(多种维度)的数据体量,同时要求实时更新,以供用户进行数据分析。
+
+# 原有架构及痛点
+
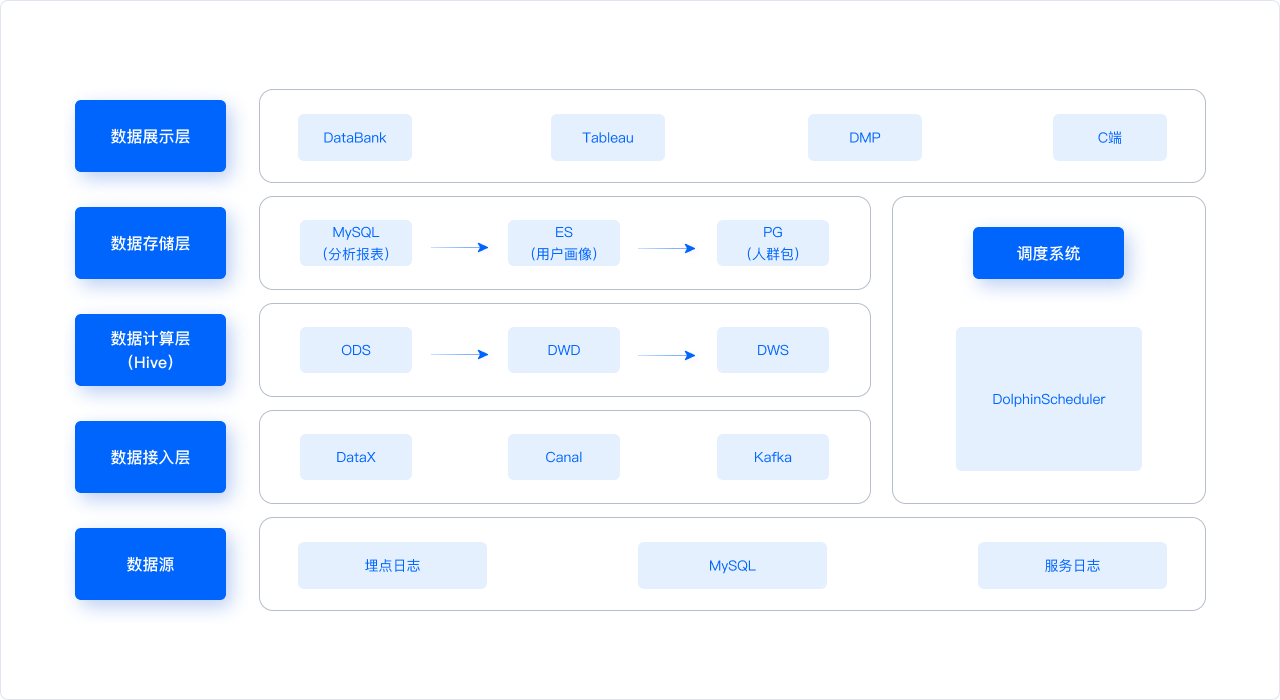
+为满足各业务场景提出的需求,我们开始搭建第一代数据仓库,即原有数仓:
+
+
+
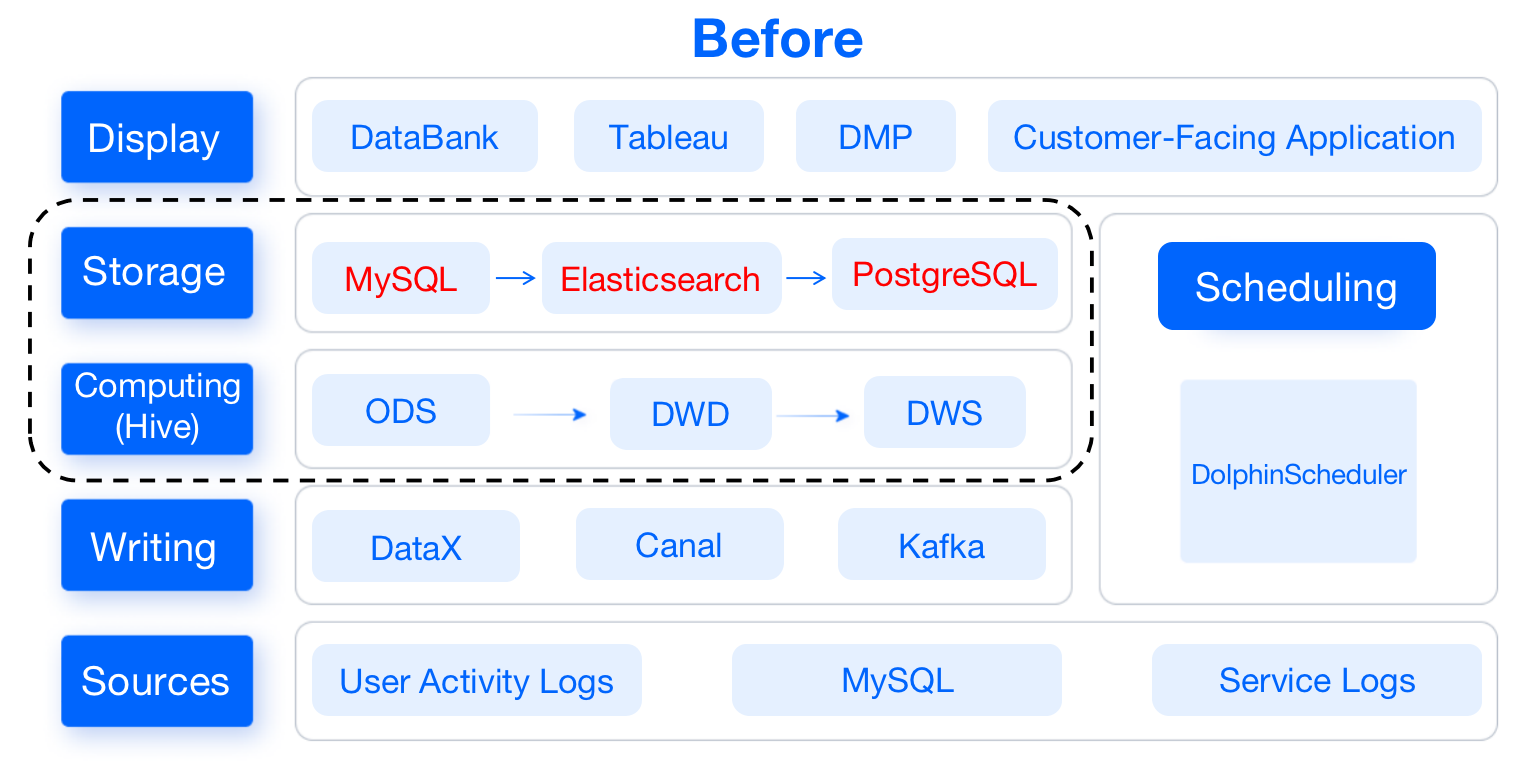
+在原有数仓架构中, Hive 作为数据计算层,MySQL、ES、PG 作为数据存储层,我们简单介绍一下架构的运行原理:
+
+- **数据源层和数据接入层:** MySQL 通过 Canal 将 BinLog 接入 Kafka、埋点日志通过 Flume 接入 Kafka,最后由
DataX 把 Kafka 中的数据接入数据计算层 Hive 中;
+- **数据计算层:** 该层使用 Hive 中的传统的数仓模型,并利用海豚调度使数据通过 ODS -> DWD -> DWS 分层,最后通过
DataX 将 T+1 把数据导入到数据存储层的 MySQL 和 ES 中。
+- **数据存储层:** MySQL 主要为 DataBank、Tableau、C 端提供分析数据,ES 用于存储用户画像数据,PG
用于人群包的存储(PG 安装的插件具有 Bitmap 交并差功能),ES、PG 两者均服务于 DMP人群圈选系统。
+
+**问题与挑战:**
+
+依托于原有架构的投入使用,初步解决了业务方的需求,但随着天眼查近年来对产品的持续深耕和迭代,用户数量也在不断攀升,业务的突破更加依赖于数据赋能。精细化的用户/客户运营也成为提升体验、促进消费的重要动力。在这样的背景下,原有架构的缺点逐渐暴露:
+
+1. 开发流程冗长:体现在数据处理链路上,比如当面对一个简单的开发需求,需要先拉取数据,再经过 Hive 计算,然后通过
T+1更新导入数据等,数据处理链路较长且复杂,非常影响开发效率。
+1. 不支持即席查询:体现在报表服务和人群圈选场景中,所用的指标无法根据条件直接查询,必须提前进行定义和开发。
+1. T+1 更新延迟高:T+1 数据时效性已经无法提供精确的线索,主要体现在报表和人群圈选场景上。
+1. 运维难度高:原有架构具有多条数据处理链路、多组件耦合的特点,运维和管理难度都很高。
+
+# 理想架构
+
+基于以上问题,我们决定对架构进行升级改进,在正式升级之前,我们希望未来的架构可以做到以下几点:
+
+- 原架构涉及 MySQL 、PG、ES 等多个组件,并为不同应用提供服务;我们希望未来的架构可以兼容 MySQL
协议,实现低成本替换、无缝衔接以上组件。
+-
支持即席查询且性能优异,即席查询能够给业务方提供更灵活的表达方式,业务方可以从多个角度、多个维度对数据进行查询和分析,更好地发现数据的规律和趋势,帮助业务方更精准备地做出决策。
+- 支持实时聚合,以减轻开发负担并保证计算结果的准确性。
+- 统一数据出口,原架构中数据出口不唯一,我们希望未来的架构能更统一数据出口,缩短链路维护成本,提升数据的可复用性。
+- 支持高并发, C 端的实时分析数据需要较高的并发能力,我们希望未来的架构可以高并发性能优异。
+
+# 技术选型
+
+考虑到和需求的匹配度,我们重点对 OLAP 引擎进行了调研,并快速定位到 ClickHouse 和 [Apache
Doris](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/) 这两款产品,在深入调研中发现 Doris
在以下几个方面优势明显,更符合我们的诉求:
+
+- 标准 SQL:ClickHouse 对标准 SQL 支持有限,使用中需要对多表 Join 语法进行改写;而 Doris 兼容 MySQL
协议,支持标准 SQL ,可以直接运行,同时 Doris 的 Join 性能远优于 ClickHouse。
+- 降本增效:Doris 部署简单,只有 FE 和 BE
两个组件,不依赖其他系统;生态内导数功能较为完备,可针对数据源/数据格式选择导入方式;还可以直接使用命令行操作弹性伸缩,无需额外投入人力;运维简单,问题排查难度低。相比之下,ClickHouse
需要投入较多的开发人力来实现类似的功能,使用难度高;同时 ClickHouse 运维难度很高,需要研发一个运维系统来支持处理大部分的日常运维工作。
+- 并发能力:ClickHouse 的并发能力较弱是一个潜在风险,而 Doris 并发能力更占优势,并且刚刚发布的 2.0
版本支持了[更高并发的点查](https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=Mzg3Njc2NDAwOA==&mid=2247516978&idx=1&sn=eb3f1f74eedd2306ca0180b8076fe773&chksm=cf2f8d35f85804238fd680c18b7ab2bc4c53d62adfa271cb31811bd6139404cc8d2222b9d561&token=699376670&lang=zh_CN#rd)。
+- 导入事务:ClickHouse 的数据导入没有事务支持,无法实现 Exactly Once 语义,如导数失败需要删除重导,流程比较复杂;而
Doris 导入数据支持事务,可以保证一批次内的数据原子生效,不会出现部分数据写入的情况,降低了判断的成本。
+- 丰富的使用场景:ClickHouse 支持场景单一,Doris 支持场景更加丰富,用户基于 Doris 可以构建用户行为分析、AB
实验平台、日志检索分析、用户画像分析、订单分析等应用。
+- 丰富的数据模型:Doris 提供了Unique、Duplicate、Aggregate 三种数据模型,可以针对不同场景灵活应用不同的数据模型。
+- 社区响应速度快:Doris 社区的响应速度是其独有特色,SelectDB
为社区组建了一直完备的社区支持团队,社区的快速响应让我们少走了很多歪路,帮助我们解决了许多问题。
+
+# 新数仓架构
+
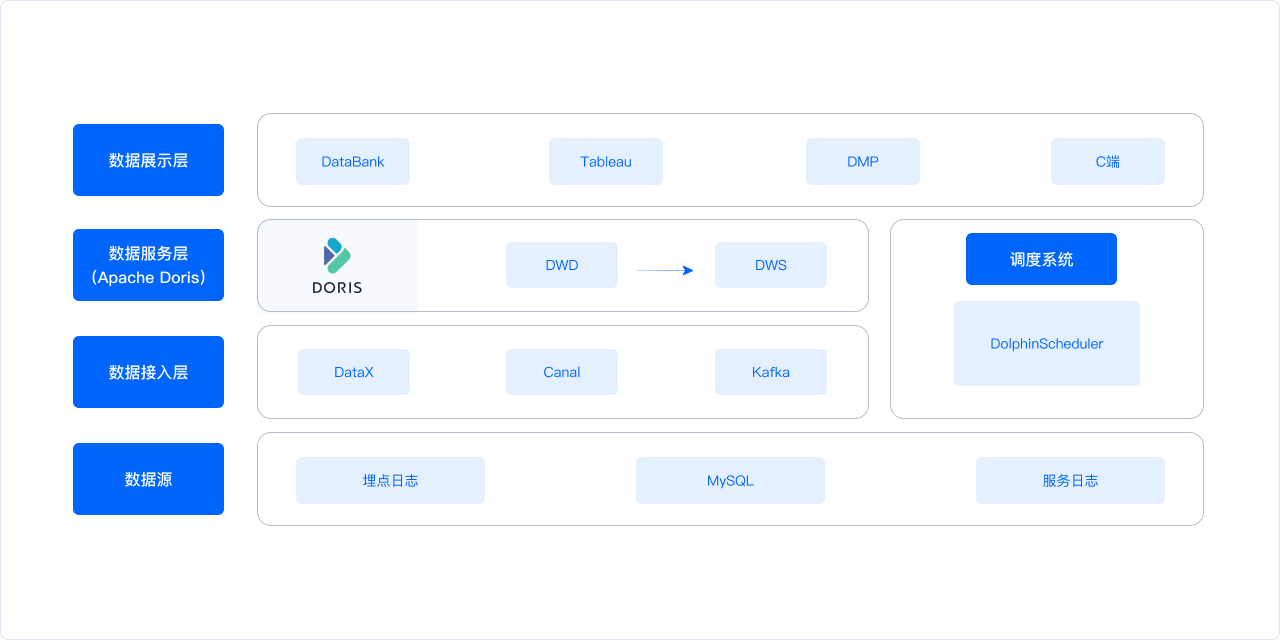
+经过对 Doris 进行综合评估,我们最终决定采用 Doris 对原有架构进行升级优化,并在架构层级进行了压缩。新的架构图如下所示:
+
+
+
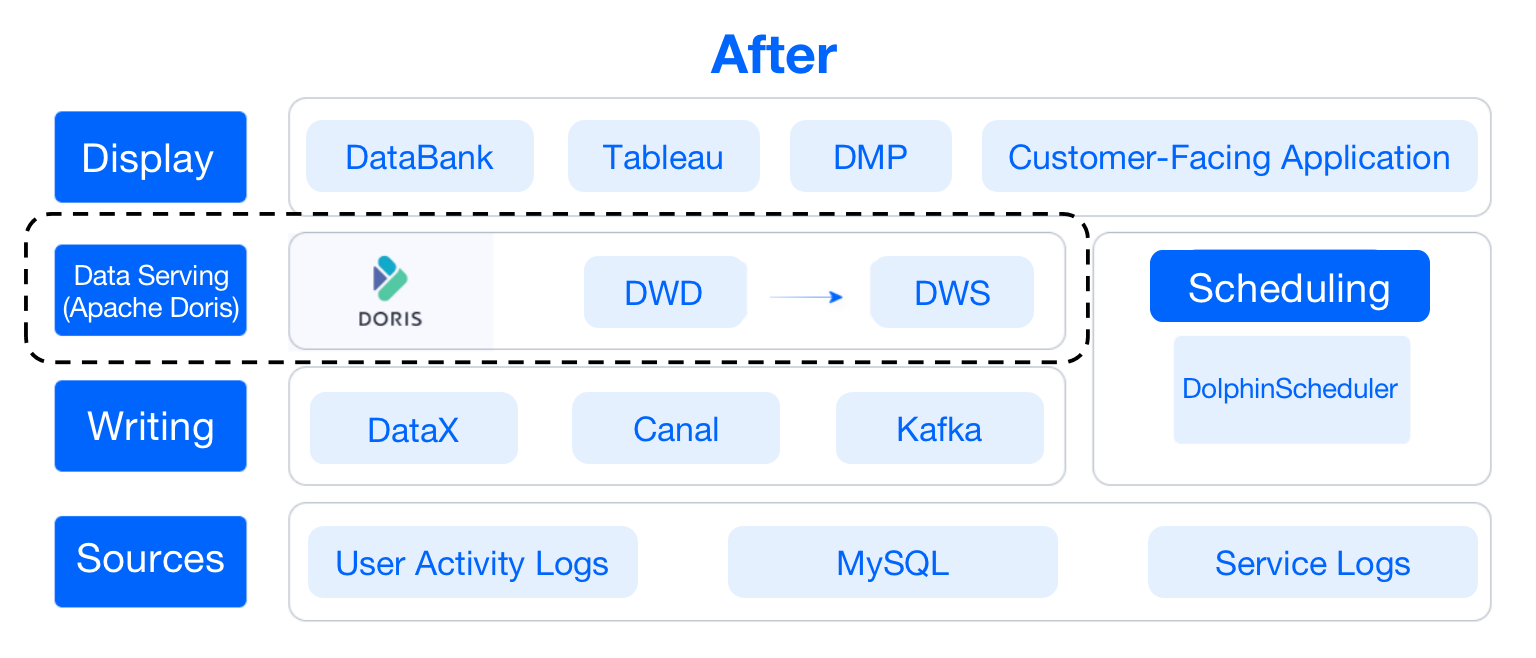
+在新架构中,数据源层和数据接入层与原有架构保持一致,**主要变化是将 Doris
作为新架构的数据服务层,统一了原有架构中的数据计算层和存储层,这样实现了数据门户的统一,大大缩短了数据处理链路,解决了开发流程冗长的问题。** 同时,基于
Doris 的高性能,实现了即席查询能力,提高了数据查询效率。另外,Flink 与 Doris 的结合实现了实时数据快速写入,解决了 T+1
数据更新延迟较高的问题。除此之外,借助于 Doris 精简的架构,大幅降低了架构维护的难度。
+
+**数据流图**
+
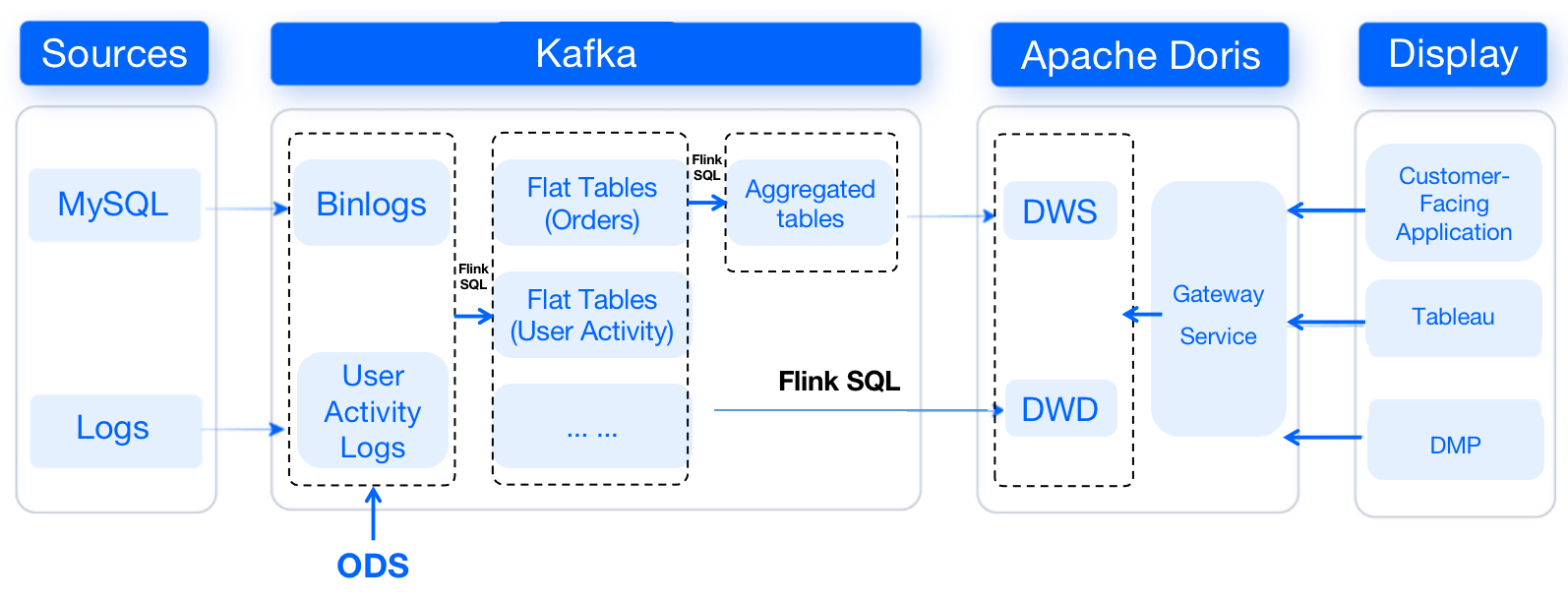
+缩短数据处理链路直接或间接地带来了许多收益。接下来,我们将具体介绍引入 Doris 后的数据流图。
+
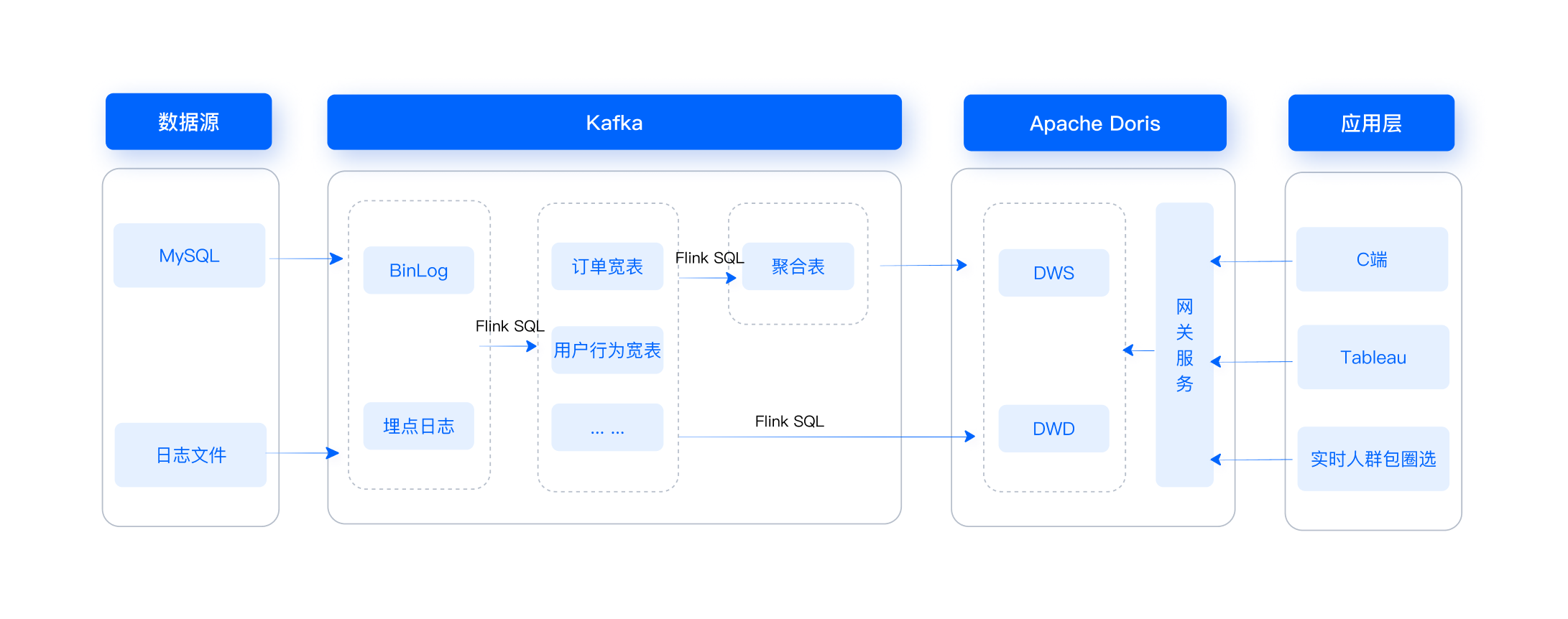
+
+
+总体而言,数据源由 MySQL 和日志文件组成,数据在 Kafka 中进行分层操作(ODS、DWD、DWS),Apache Doris
作为数据终点统一进行存储和计算。应用层包含 C 端、Tableau 和 DMP 系统,通过网关服务从 Doris 中获取相应的数据。
+
+具体来看,MySQL 通过 Canal 把 Binlog 接入 Kafka,日志文件通过 Flume 接入 Kafka 作为 ODS 层。然后经过
Flink SQL 进行清洗、关联维表,形成 DWD 层的宽表,并生成聚合表。为了节省空间,我们将 ODS 层存储在 Kafka 中,DWD 层和 DWS
层主要与 Doris 进行交互。DWD 层的数据一般通过 Flink SQL 写入
Doris。针对不同的场景,我们应用了不同的数据模型进行数据导入。MySQL 数据使用 Unique 模型,日志数据使用 Duplicate 模型,DWS
层采用 Aggregate 模型,可进行实时聚合,从而减少开发成本。
+
+# 应用场景优化
+
+在应用新的架构之后,我们必须对业务场景的数据处理流程进行优化以匹配新架构,从而达到最佳应用效果。接下来我们以人群圈选、C端分析数据及精准营销线索为主要场景,分享相关场景流程优化的实践与经验。
+
+## 人群圈选
+
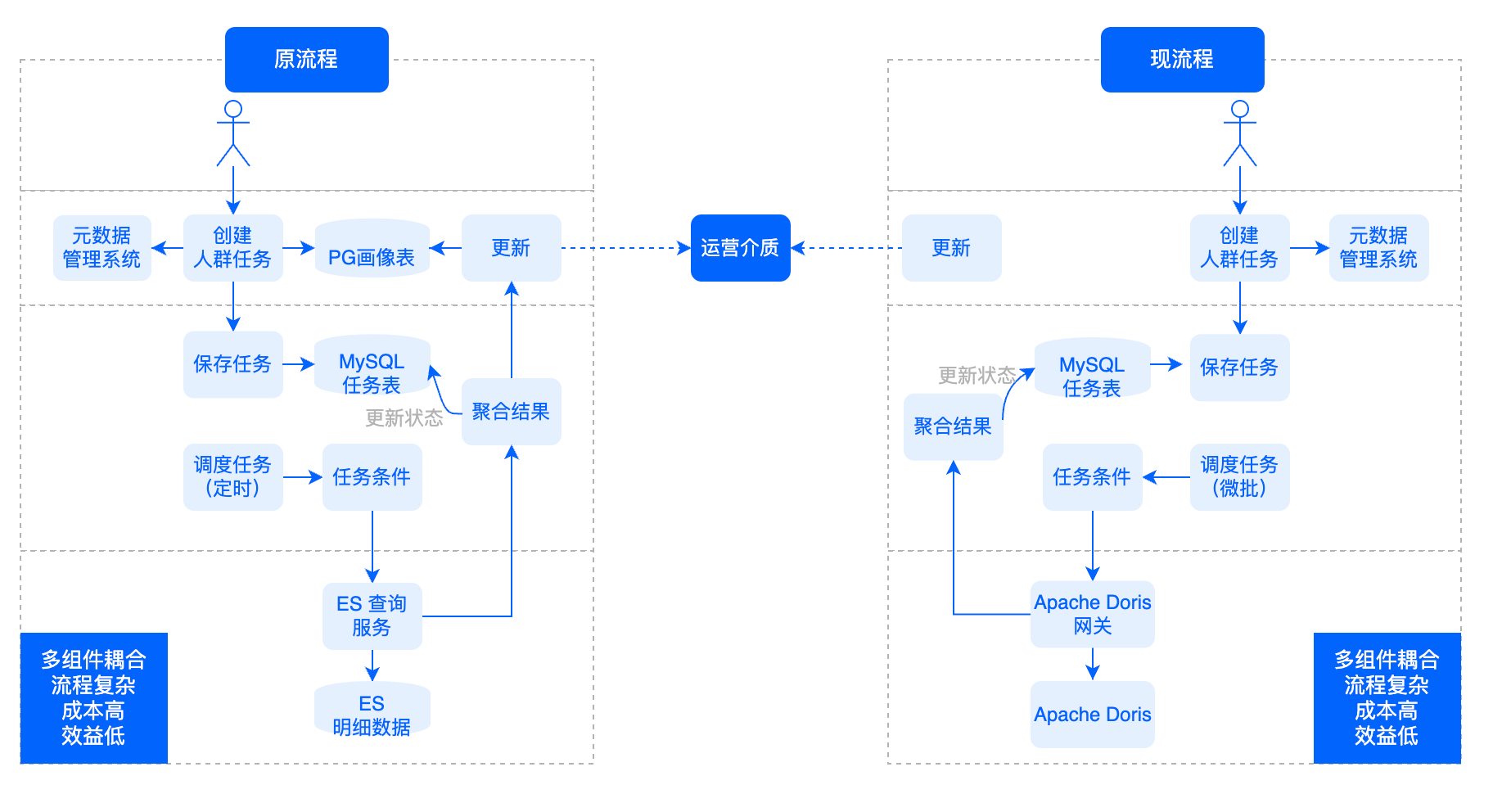
+
+
+**原流程(左)中**,业务人员在画像平台页面上利用表的元数据创建人群圈选任务,任务创建后进行人群 ID 分配,写入到 PG 画像表和 MySQL
任务表中。接着根据任务条件定时在 ES 中查询结果,获取结果后更新任务表的状态,并把 Bitmap 人群包写入 PG。利用 PG 插件提供的 Bitmap
交并差能力操作人群包,最后下游运营介质从 PG 取相应人群包。
+
+然而,该流程处理方式非常复杂,ES 和 PG 中的表无法复用,造成成本高、效益低。同时,原流程中的数据为 T+1
更新,标签必须提前进行定义及计算,这非常影响查询效率。
+
+**现流程(右)中**,业务人员在画像平台创建人群圈选任务,后台分配人群 ID,并将其写入 MySQL 任务表中。首次圈选时,根据任务条件在 Doris
中进行即席查询,获取结果后对任务表状态进行更新,并将人群包写入 Doris。后续根据时间进行微批轮询,利用 Doris Bitmap
函数提供的交并差功能与上一次的人群包做差集,如果有人群包更新会主动通知下游。
+
+引入 Doris 后,原有流程的问题得到了解决,新流程以 Doris
为核心构建了人群圈选服务,支持人群包实时更新,新标签无需提前定义,可通过条件配置自助生成,减少了开发时间。新流程表达方式更加灵活,为人群包 AB
实验提供了便捷的条件。流程中采用 Doris 统一了明细数据和人群包的存储介质,实现业务聚焦,无需处理多组件数据之间的读写问题,达到了降本增效的终极目标。
+
+## C端分析数据及精准营销线索场景
+
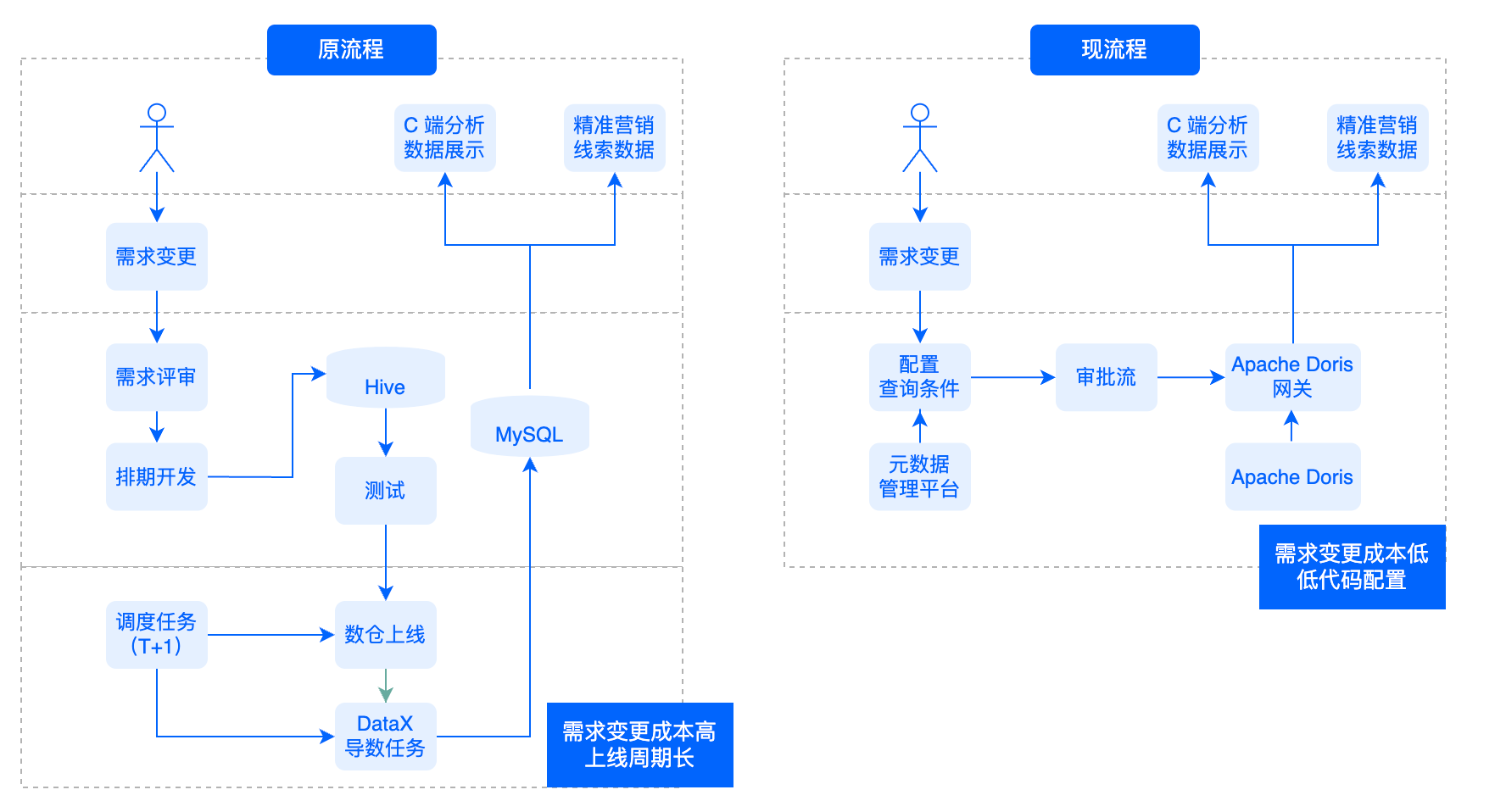
+
+
+**原流程:** 在原流程中,如果业务提出新需求,需要先发起需求变更,再经过评审、排期开发,然后开始对 Hive
中的数据模型进行开发并进行测试,测试完成后进行数仓上线,配置 T+1 调度任务写入 MySQL,最后 C端和精准营销系统对 MySQL
数据进行读取。原流程链路复杂,主要体现在流程长、成本高、上线周期长。
+
+**现流程:** 当前明细数据已经在 Doris 上线,当业务方发起需求变更时,只需要拉取元数据管理平台元数据信息,配置查询条件,审批完成后即可上线,上线
SQL 可直接在 Doris 中进行即席查询。相比原流程,现在的流程大幅缩短了需求变更流程,只需进行低代码配置,成功降低了开发成本,缩短了上线周期。
+
+# 优化经验
+
+为了规避风险,许多公司的人群包`user_id`是随机生成的,这些`user_id`相差很大且是非连续的。然而,使用非连续的`user_id`进行人群圈选时,会导致
Bitmap 生成速度较慢。因此,我们生成了映射表,并生成了连续稠密的`user_id`。当使用连续 `user_id` 圈选人群时,**速度较之前提升了
70%** 。
+
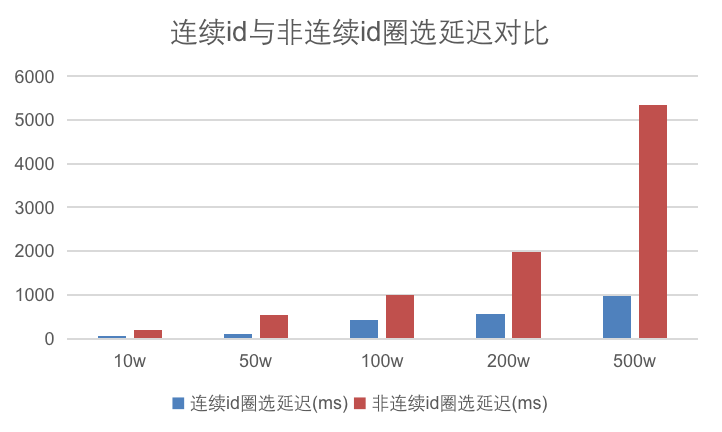
+
+
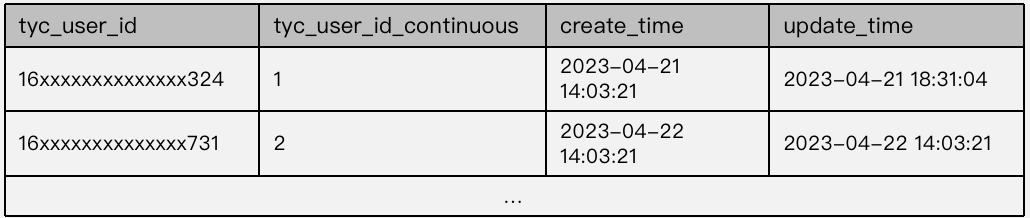
+用户 ID 映射表样例数据:从图可知原始用户 ID 由多位数字组合,并且 ID 很稀疏(用户 ID 间相差很大),而连续用户 ID 则 从1开始,且 ID
很稠密。
+
+
+
+**案例展示:**
+
+1. 用户 ID 映射表:
+
+用户 ID 映射表将用户 ID 作为唯一键模型,而连续用户 ID 则通过用户 ID 来生成,一般从 1
开始,严格保持单调递增。需要注意的是,因为该表使用频繁,因此将 `in_memory` 设置为`true`,直接将其缓存在内存中:
+
+
+
+2. 人群包表
+
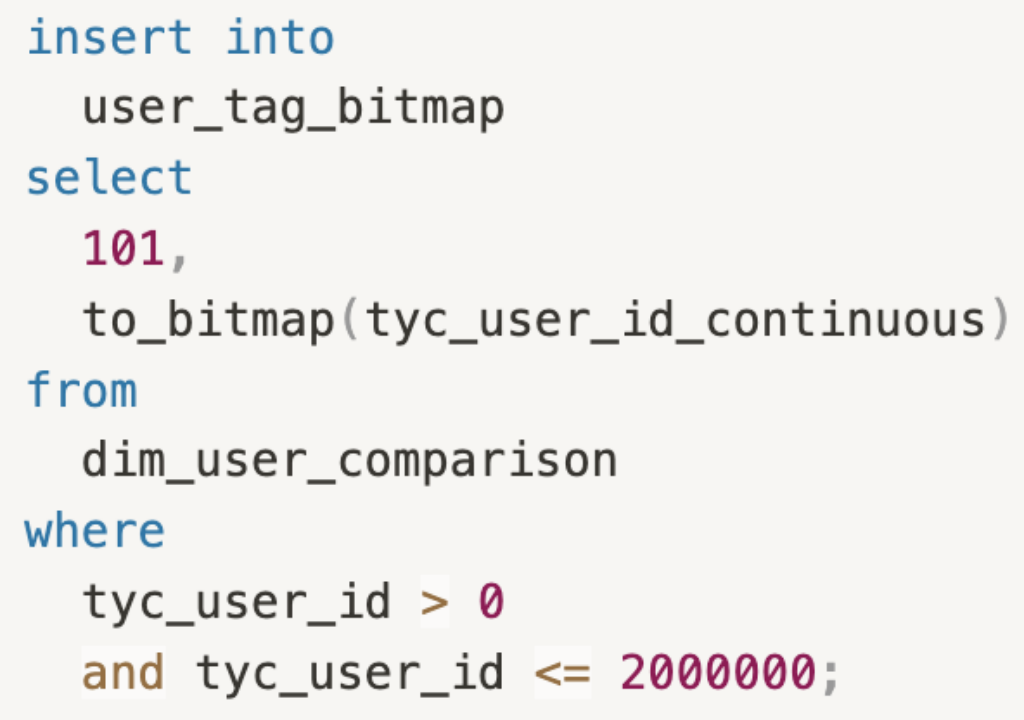
+人群包表是以用户标签作聚合键的模型,假设以 `user_id` 大于 0、小于 2000000 作为圈选条件,使用原始 `user_id`
进行圈选耗费的时间远远远大于连续稠密 `user_id` 圈选所耗时间。
+
+
+
+如下图所示,左侧使用
`tyc_user_id`圈选生成人群包响应时间:1843ms,右侧使用使`tyc_user_id_continuous`圈选生成人群包响应时间:543ms。消耗时间大幅缩短
+
+
+
+# 规模与收益:
+
+引入 Doris 后,我们已经搭建了 2
个集群,承载的数据规模正随着迁移的推进而持续增大。目前,**我们已经处理的数据总量已经达到了数十TB,单日新增数据量已经达到了
数亿条**,而数据体量还在持续增长中。此外,我们在 Doris 上运行的指标和人群包数量已经超过了 500,分别涵盖了商查、搜索、运营、用户和营收五大类指标。
+
+Doris 的引入满足了业务上的新需求,解决了原有架构的痛点问题,具体表现为以下几点:
+
+- **降本增效:** Doris 统一了数据的门户,实现了存储和计算的统一,提高了数据/表的复用率,降低了资源消耗。同时,新架构优化了数据到
MySQL、ES 的流程,开发效率得到有效提升。
+- **导入速率提升:** 原有数据流程中,数据处理流程过长,数据的导入速度随着业务体量的增长和数据量的不断上升而急剧下降。引入 Doris
后,我们依赖 Broker Load 优秀的写入能力,使得**导入速率提升了 75%以上**。
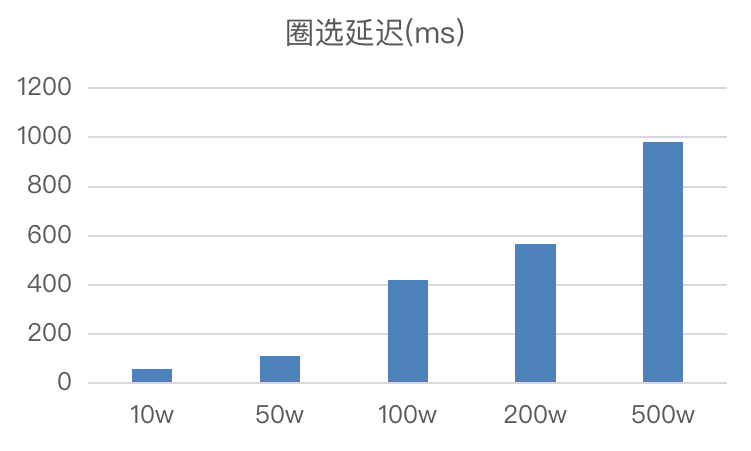
+- **响应速度**:Doris 的使用提高了各业务场景中的查询响应速度。例如,在人群圈选场景中,对于 **500
万及以下的人群包进行圈选时,能够做到毫秒级响应**。
+
+
+
+# 未来规划
+
+正如前文所讲,Apache Doris
的引入解决了许多架构及业务上的难题,初见成效,同时也收获了公司内部数据部门、业务方的一致好评,未来我们将继续探索,基于 Doris
展开更深度的应用,不久的将来,我们将重点推进以下几个方面工作:
+
+- 离线指标实时化:将更多的指标从离线转为实时,提供更及时的数据服务。
+- 搭建数据血缘系统:将代码中的血缘关系重新定义为可视,全面构建数据血缘关系,为问题排查、链路报警等提供有效支持。
+- 探索批流一体路线:从使用者的角度思考设计,实现语义开发层的统一,使数据开发更便捷、更低门槛、更高效率。
+
+在此特别感谢 [SelectDB 团队](https://cn.selectdb.com/),作为基于 [Apache
Doris](https://doris.apache.org/zh-CN/)
的商业化公司,为社区投入了大量的研发和用户支持力量,在使用过程中遇到任何问题都能及时响应,为我们降低了许多试错成本。未来,我们也会更积极参与社区贡献及活动中来,与社区共同进步和成长,欢迎大家选择和使用
Doris,相信 Doris 一定不会让你失望。
\ No newline at end of file
---------------------------------------------------------------------
To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected]
For additional commands, e-mail: [email protected]
