This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
jin pushed a commit to branch main
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/main by this push:
new aa83ec2 fix(llm): align regex extraction of json to json format of
prompt (#211)
aa83ec2 is described below
commit aa83ec2a8596ff86ded04e154f32e38252de0574
Author: John <thesp...@qq.com>
AuthorDate: Tue Apr 22 11:25:02 2025 +0800
fix(llm): align regex extraction of json to json format of prompt (#211)
See #210
Main change of regex: matching `(\[.*])` -> matching `({.*})`.
tested models:
- qwen-max
- qwen-plus
- deepseek-v3
---------
Co-authored-by: imbajin <j...@apache.org>
---
.asf.yaml | 1 +
.github/workflows/hugegraph-python-client.yml | 2 +-
hugegraph-llm/README.md | 26 ++++-----
.../operators/llm_op/property_graph_extract.py | 61 ++++++++++++----------
4 files changed, 49 insertions(+), 41 deletions(-)
diff --git a/.asf.yaml b/.asf.yaml
index e92e30b..9fa40a0 100644
--- a/.asf.yaml
+++ b/.asf.yaml
@@ -58,6 +58,7 @@ github:
- HJ-Young
- afterimagex
- returnToInnocence
+ - Thespica
# refer
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/INFRA/Git+-+.asf.yaml+features#Git.asf.yamlfeatures-Notificationsettingsforrepositories
notifications:
diff --git a/.github/workflows/hugegraph-python-client.yml
b/.github/workflows/hugegraph-python-client.yml
index e05708a..60c84dd 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/hugegraph-python-client.yml
+++ b/.github/workflows/hugegraph-python-client.yml
@@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ jobs:
- name: Prepare HugeGraph Server Environment
run: |
docker run -d --name=graph -p 8080:8080 -e PASSWORD=admin
hugegraph/hugegraph:1.3.0
- sleep 5
+ sleep 10
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
diff --git a/hugegraph-llm/README.md b/hugegraph-llm/README.md
index 1714f08..0251f79 100644
--- a/hugegraph-llm/README.md
+++ b/hugegraph-llm/README.md
@@ -8,12 +8,12 @@ This project includes runnable demos, it can also be used as
a third-party libra
As we know, graph systems can help large models address challenges like
timeliness and hallucination,
while large models can help graph systems with cost-related issues.
-With this project, we aim to reduce the cost of using graph systems, and
decrease the complexity of
+With this project, we aim to reduce the cost of using graph systems and
decrease the complexity of
building knowledge graphs. This project will offer more applications and
integration solutions for
graph systems and large language models.
1. Construct knowledge graph by LLM + HugeGraph
2. Use natural language to operate graph databases (Gremlin/Cypher)
-3. Knowledge graph supplements answer context (GraphRAG -> Graph Agent)
+3. Knowledge graph supplements answer context (GraphRAG → Graph Agent)
## 2. Environment Requirements
> [!IMPORTANT]
@@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ graph systems and large language models.
## 3. Preparation
1. Start the HugeGraph database, you can run it via
[Docker](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hugegraph)/[Binary
Package](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/download/download/).
- Refer to detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)
for more guidance
+ Refer to a detailed
[doc](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-server/#31-use-docker-container-convenient-for-testdev)
for more guidance
2. Configuring the poetry environment, Use the official installer to install
Poetry, See the [poetry
documentation](https://poetry.pythonlang.cn/docs/#installing-with-pipx) for
other installation methods
```bash
@@ -32,11 +32,11 @@ graph systems and large language models.
curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 - # install the
latest version like 2.0+
```
-2. Clone this project
+3. Clone this project
```bash
git clone https://github.com/apache/incubator-hugegraph-ai.git
```
-3. Install [hugegraph-python-client](../hugegraph-python-client) and
[hugegraph_llm](src/hugegraph_llm), poetry officially recommends using virtual
environments
+4. Install [hugegraph-python-client](../hugegraph-python-client) and
[hugegraph_llm](src/hugegraph_llm), poetry officially recommends using virtual
environments
```bash
cd ./incubator-hugegraph-ai/hugegraph-llm
poetry config --list # List/check the current configuration (Optional)
@@ -48,11 +48,11 @@ graph systems and large language models.
poetry shell # use 'exit' to leave the shell
```
If `poetry install` fails or too slow due to network issues, it is
recommended to modify `tool.poetry.source` of `hugegraph-llm/pyproject.toml`
-4. Enter the project directory(`./incubator-hugegraph-ai/hugegraph-llm/src`)
+5. Enter the project directory(`./incubator-hugegraph-ai/hugegraph-llm/src`)
```bash
cd ./src
```
-5. Start the gradio interactive demo of **Graph RAG**, you can run with the
following command, and open http://127.0.0.1:8001 after starting
+6. Start the gradio interactive demo of **Graph RAG**, you can run with the
following command and open http://127.0.0.1:8001 after starting
```bash
python -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app # same as "poetry run xxx"
```
@@ -61,23 +61,23 @@ graph systems and large language models.
python -m hugegraph_llm.demo.rag_demo.app --host 127.0.0.1 --port 18001
```
-6. After running the web demo, the config file `.env` will be automatically
generated at the path `hugegraph-llm/.env`. Additionally, a prompt-related
configuration file `config_prompt.yaml` will also be generated at the path
`hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yaml`.
+7. After running the web demo, the config file `.env` will be automatically
generated at the path `hugegraph-llm/.env`. Additionally, a prompt-related
configuration file `config_prompt.yaml` will also be generated at the path
`hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/resources/demo/config_prompt.yaml`.
You can modify the content on the web page, and it will be automatically
saved to the configuration file after the corresponding feature is triggered.
You can also modify the file directly without restarting the web application;
refresh the page to load your latest changes.
(Optional)To regenerate the config file, you can use `config.generate`
with `-u` or `--update`.
```bash
python -m hugegraph_llm.config.generate --update
```
Note: `Litellm` support multi-LLM provider, refer
[litellm.ai](https://docs.litellm.ai/docs/providers) to config it
-7. (__Optional__) You could use
+8. (__Optional__) You could use
[hugegraph-hubble](https://hugegraph.apache.org/docs/quickstart/hugegraph-hubble/#21-use-docker-convenient-for-testdev)
to visit the graph data, could run it via
[Docker/Docker-Compose](https://hub.docker.com/r/hugegraph/hubble)
- for guidance. (Hubble is a graph-analysis dashboard include data
loading/schema management/graph traverser/display).
-8. (__Optional__) offline download NLTK stopwords
+ for guidance. (Hubble is a graph-analysis dashboard that includes data
loading/schema management/graph traverser/display).
+9. (__Optional__) offline download NLTK stopwords
```bash
python ./hugegraph_llm/operators/common_op/nltk_helper.py
```
> [!TIP]
-> You can also refer our [quick-start](./quick_start.md) doc to understand how
to use it & the basic query logic 🚧
+> You can also refer to our [quick-start](./quick_start.md) doc to understand
how to use it & the basic query logic 🚧
## 4 Examples
@@ -124,7 +124,7 @@ This can be obtained from the `LLMs` class.
)
```
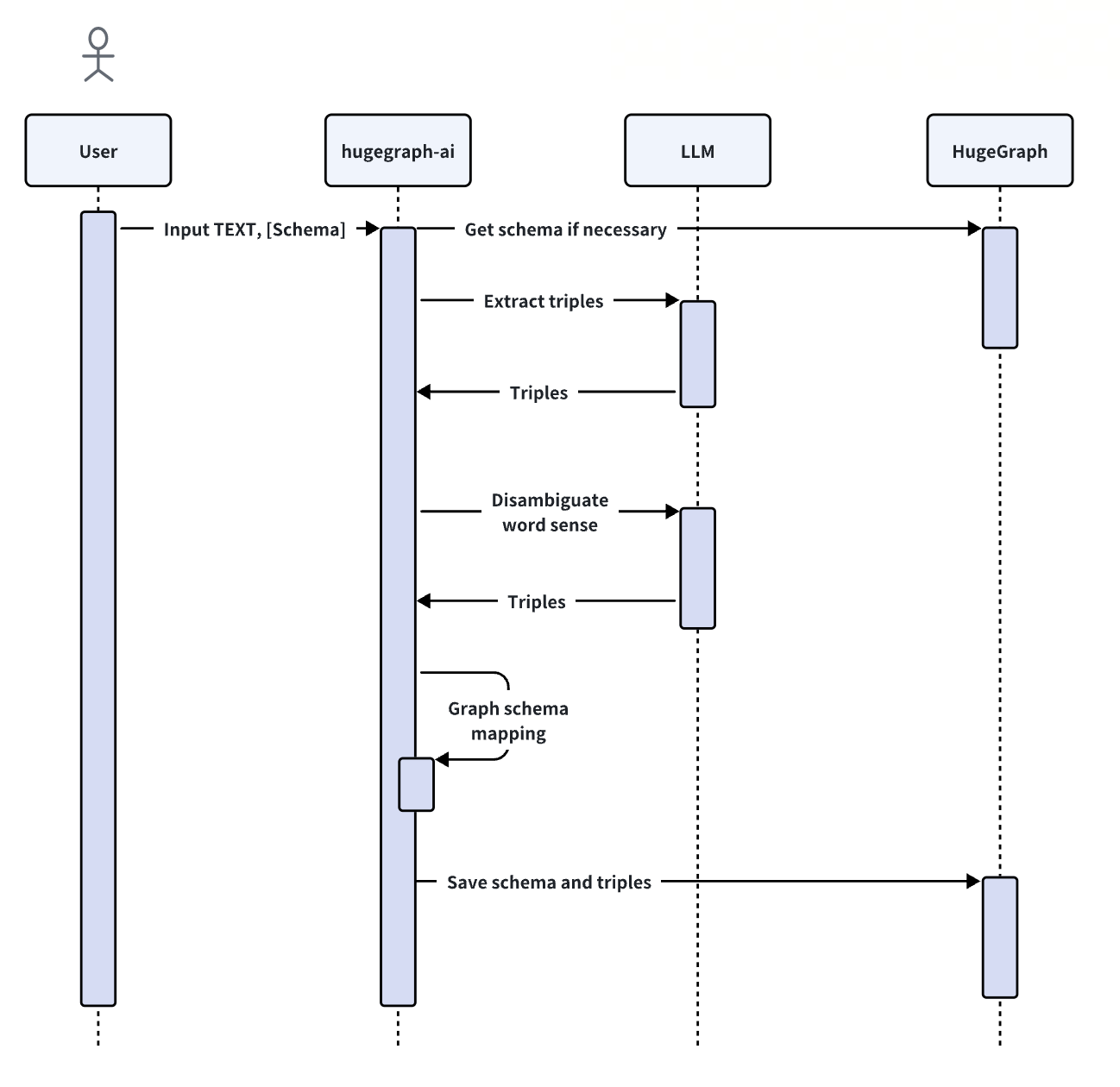
-2. **Import Schema**: The `import_schema` method is used to import a schema
from a source. The source can be a HugeGraph instance, a user-defined schema or
an extraction result. The method `print_result` can be chained to print the
result.
+2. **Import Schema**: The `import_schema` method is used to import a schema
from a source. The source can be a HugeGraph instance, a user-defined schema,
or an extraction result. The method `print_result` can be chained to print the
result.
```python
# Import schema from a HugeGraph instance
builder.import_schema(from_hugegraph="xxx").print_result()
diff --git
a/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/operators/llm_op/property_graph_extract.py
b/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/operators/llm_op/property_graph_extract.py
index 945fd30..faff1c6 100644
--- a/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/operators/llm_op/property_graph_extract.py
+++ b/hugegraph-llm/src/hugegraph_llm/operators/llm_op/property_graph_extract.py
@@ -26,7 +26,6 @@ from hugegraph_llm.document.chunk_split import ChunkSplitter
from hugegraph_llm.models.llms.base import BaseLLM
from hugegraph_llm.utils.log import log
-
"""
TODO: It is not clear whether there is any other dependence on the
SCHEMA_EXAMPLE_PROMPT variable.
Because the SCHEMA_EXAMPLE_PROMPT variable will no longer change based on
@@ -88,9 +87,9 @@ def filter_item(schema, items) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
class PropertyGraphExtract:
def __init__(
- self,
- llm: BaseLLM,
- example_prompt: str = prompt.extract_graph_prompt
+ self,
+ llm: BaseLLM,
+ example_prompt: str = prompt.extract_graph_prompt
) -> None:
self.llm = llm
self.example_prompt = example_prompt
@@ -125,33 +124,41 @@ class PropertyGraphExtract:
return self.llm.generate(prompt=prompt)
def _extract_and_filter_label(self, schema, text) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
- # analyze llm generated text to JSON
- json_strings = re.findall(r'(\[.*?])', text, re.DOTALL)
- longest_json = max(json_strings, key=lambda x: len(''.join(x)),
default=('', ''))
-
- longest_json_str = ''.join(longest_json).strip()
+ # Use regex to extract a JSON object with curly braces
+ json_match = re.search(r'({.*})', text, re.DOTALL)
+ if not json_match:
+ log.critical("Invalid property graph! No JSON object found, "
+ "please check the output format example in prompt.")
+ return []
+ json_str = json_match.group(1).strip()
items = []
try:
- property_graph = json.loads(longest_json_str)
+ property_graph = json.loads(json_str)
+ # Expect property_graph to be a dict with keys "vertices" and
"edges"
+ if not (isinstance(property_graph, dict) and "vertices" in
property_graph and "edges" in property_graph):
+ log.critical("Invalid property graph format; expecting
'vertices' and 'edges'.")
+ return items
+
+ # Create sets for valid vertex and edge labels based on the schema
vertex_label_set = {vertex["name"] for vertex in
schema["vertexlabels"]}
edge_label_set = {edge["name"] for edge in schema["edgelabels"]}
- for item in property_graph:
- if not isinstance(item, dict):
- log.warning("Invalid property graph item type '%s'.",
type(item))
- continue
- if not self.NECESSARY_ITEM_KEYS.issubset(item.keys()):
- log.warning("Invalid item keys '%s'.", item.keys())
- continue
- if item["type"] == "vertex" or item["type"] == "edge":
- if (item["label"] not in vertex_label_set
- and item["label"] not in edge_label_set):
- log.warning("Invalid '%s' label '%s' has been
ignored.", item["type"], item["label"])
- else:
- items.append(item)
- else:
- log.warning("Invalid item type '%s' has been ignored.",
item["type"])
- except json.JSONDecodeError:
- log.critical("Invalid property graph! Please check the extracted
JSON data carefully")
+ def process_items(item_list, valid_labels, item_type):
+ for item in item_list:
+ if not isinstance(item, dict):
+ log.warning("Invalid property graph item type '%s'.",
type(item))
+ continue
+ if not self.NECESSARY_ITEM_KEYS.issubset(item.keys()):
+ log.warning("Invalid item keys '%s'.", item.keys())
+ continue
+ if item["label"] not in valid_labels:
+ log.warning("Invalid %s label '%s' has been ignored.",
item_type, item["label"])
+ continue
+ items.append(item)
+
+ process_items(property_graph["vertices"], vertex_label_set,
"vertex")
+ process_items(property_graph["edges"], edge_label_set, "edge")
+ except json.JSONDecodeError:
+ log.critical("Invalid property graph JSON! Please check the
extracted JSON data carefully")
return items
