Boburmirzo commented on code in PR #1380: URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/1380#discussion_r1006704511
########## blog/en/blog/2022/10/27/ten-use-cases-api-gateway.md: ########## @@ -0,0 +1,180 @@ +--- +title: "10 most use cases of an API Gateway in API-Led architecture" +authors: + - name: Bobur Umurzokov + title: Author + url: https://github.com/Boburmirzo + image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607 +keywords: +- API Gateway +- Apache APISIX +- API +- Architecture +- Use-cases +- Microservices +description: This post elaborates on the 10 most common usages of an API Gateway such as Apache APISIX in architecting API-Led Connectivity. +tags: [Case Studies] +image: https://static.apiseven.com/2022/10/27/635a40e58b27a.png +--- + +> This post elaborates on the **10 most common usages** of an _API Gateway_ such as [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) in architecting [API-Led Connectivity](https://blogs.mulesoft.com/learn-apis/api-led-connectivity/what-is-api-led-connectivity/). We understand different solutions where you can make use of the API Gateway capabilities to design reliable, high-performance, and simple APIs for other developers. + +<!--truncate--> + +Here is the summary of 10 patterns that uses the API Gateway (but not all): + +1. API Resource routing. +2. API Content-based routing. +3. API Geo-routing. +4. API Aggregator. +5. API Centralized Authentication. +6. API Format Conversion. +7. API Observability. +8. API Caching. +9. API Fault handling. +10. Sidecar API Gateway. + +## API-Led Architecture + +First of all, let’s revise once again these 3 terms like: **API Gateway**, **API-Led architecture**, and **API-Led Connectivity**. + +[API Gateway](https://wikitech.wikimedia.org/wiki/API_Gateway) is a _pattern_ formed by adding a layer between the client and the server that acts as a reverse proxy forwarding request from the client to the server. It allows all clients to access the services they want to access with a single API Gateway layer. + +[API-led](https://dzone.com/articles/mulesoft-api-led-connectivity-architectural-and-de) is an _architectural approach_ that puts APIs at the heart of communications between applications and the business capabilities they need to access, in order to consistently deliver seamless functionality across all digital channels. + +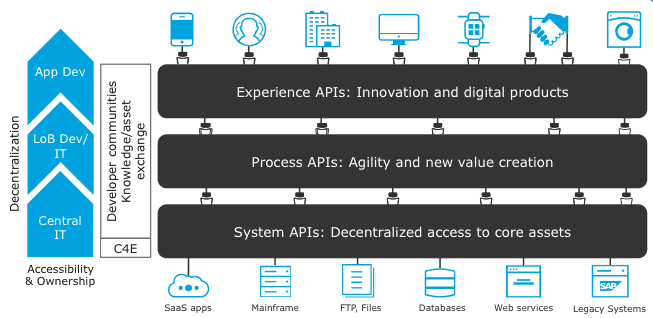 + +**API-led connectivity** refers to _the technique_ of using reusable and well-designed APIs to link data and applications which in turn it is based on **API-Led architecture**. It’s _a modern approach_ that looks at the best ways of reusing APIs to boost your innovation and move quickly in the market. At the most basic level, API-led architecture should address things like: + +- Securing APIs from unauthorized access and significant security threats. +- Ensuring that consuming applications can always find the right API endpoint. +- Throttling and/or limiting the number of calls made to an API to ensure continuous availability. +- Supporting capabilities such as API design, testing, continuous integration, life cycle management, monitoring, and operations, to name a few. +- Error handling and preventing error propagation across the stack. +- Real-time monitoring of APIs with rich analytics and insight. +- An approach for implementing scalable and flexible business capabilities, for example, in support of microservices architectures. + +Let’s describe in subsequent sections each usage of an API Gateway to address common requirements/challenges that arise when adopting API-led architectures. + +--- + +## API resource routing + +The first in the list is the **API resource routing** method which uses an API Gateway to route incoming calls based on unique resource identifiers (URIs). Implementing an API gateway as the single entry point to all services means that API consumers only have to be aware of one URL domain. In this way, it becomes the API gateway's responsibility to route the traffic to the corresponding service endpoints and also enforce any applied policies as it is depicted in the below diagram. + +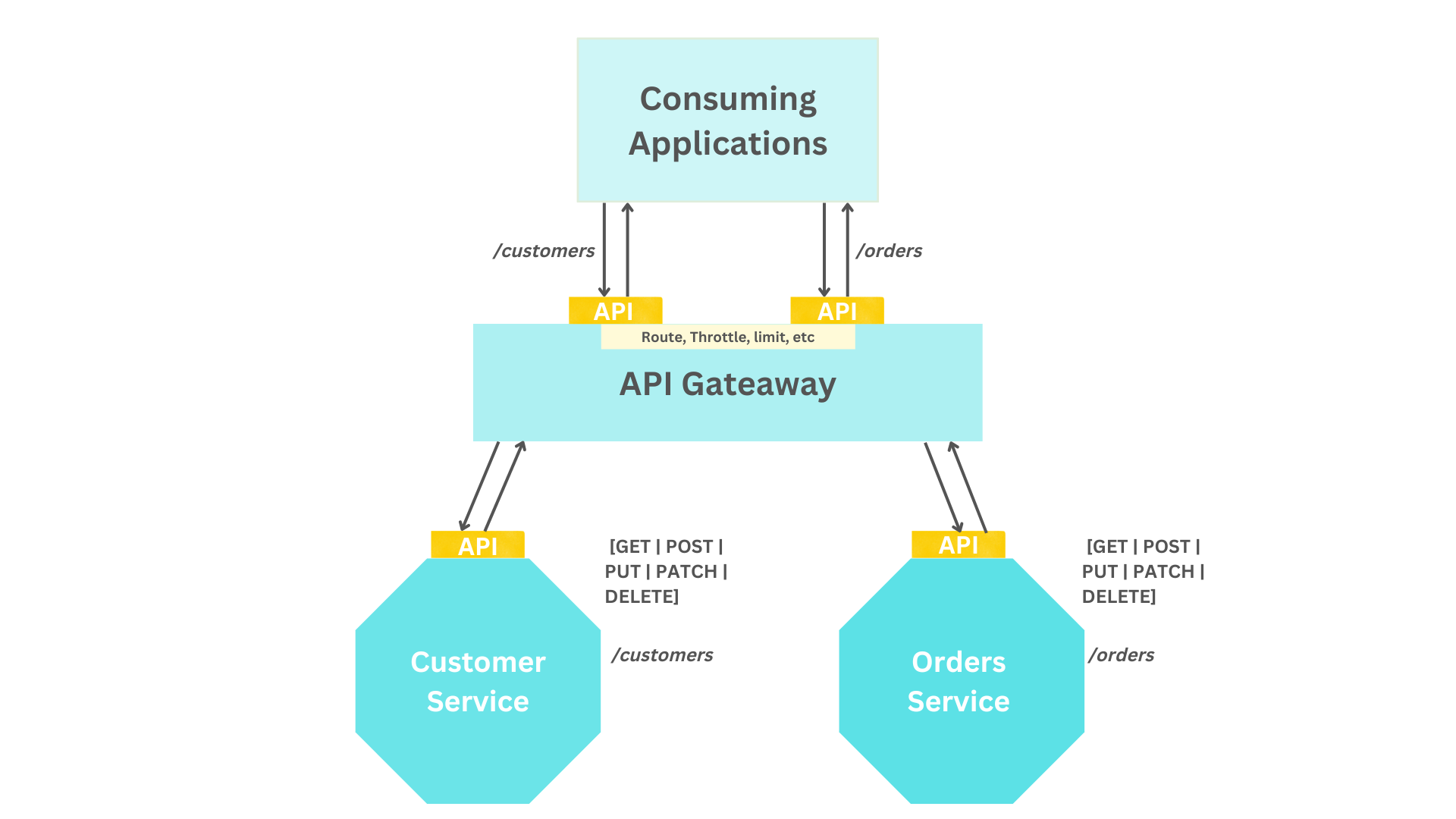 + +It reduces complexity on the API consumer side because they do not need to track and consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints in case there are many services in the system. Also, no need to implement all cross-cutting concerns, such as authentication/authorization, throttling, and rate limiting separately for each service. Most API Gateways like [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/terminology/api-gateway/) has already these core features. Review Comment: > I don't know what it means It means "the client applications do not need to consume functionality from multiple HTTP endpoints" I will rephrase it. -- This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service. To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the URL above to go to the specific comment. To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected] For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at: [email protected]
