This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
guoqi pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/apisix-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new b8aba81aac1 docs: add api7-blogs-to-apisix.md (#1659)
b8aba81aac1 is described below
commit b8aba81aac17c1c22a3f44a4bc138386df314178
Author: Yilia <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Tue Aug 8 09:26:48 2023 +0800
docs: add api7-blogs-to-apisix.md (#1659)
---
.../2023/04/14/10-api-management-trends-2023.md | 161 ++++++++++++++
.../2023/05/04/apache-apisix-chaos-engineering.md | 127 +++++++++++
.../19/why-do-microservices-need-an-api-gateway.md | 105 +++++++++
blog/en/blog/2023/06/12/how-is-apisix-fast.md | 195 ++++++++++++++++
.../2023/07/09/apisix-integrates-with-vault.md | 246 +++++++++++++++++++++
5 files changed, 834 insertions(+)
diff --git a/blog/en/blog/2023/04/14/10-api-management-trends-2023.md
b/blog/en/blog/2023/04/14/10-api-management-trends-2023.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..7d0a1b41631
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2023/04/14/10-api-management-trends-2023.md
@@ -0,0 +1,161 @@
+---
+title: Top 10 API Management Trends for 2023
+authors:
+ - name: API7.ai
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/api7
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/61078451?s=200&v=4
+keywords:
+ - Apache APISIX
+ - API Management
+ - Microservices
+description: "10 major trends in API management: API security,
standardization, cloud-based API management solutions, low-code API platforms,
API marketplaces, emerging API protocols, AI and APIs, developer experience,
API analytics, and serverless architecture."
+tags: [Ecosystem]
+image:
https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/04/12/PtHsoEJS_top-10-trends.png
+---
+
+>This article introduces 10 significant trends in API management: API
security, standardization, cloud-based API management solutions, low-code API
platforms, API marketplaces, emerging API protocols, AI and APIs, developer
experience, API analytics, and serverless architecture.
+<!--truncate-->
+
+API management is increasingly crucial in digital transformation, accompanying
the challenges and opportunities.
+
+We focus on the ten major trends in API management, including API security,
standardization, cloud-based API management solutions, low-code API platforms,
API marketplaces, emerging API protocols, AI and APIs, developer experience,
API analytics, and serverless architecture.
+
+Let's dive into these trends, prepare for future challenges, capitalize on
opportunities, and achieve ongoing growth and innovation in their businesses.
+
+## What Is an API? What Is API Management?
+
+Recently, the application of AI-Generated Content (AIGC) has become
increasingly popular in various industries. AIGC service providers provide
their content generation capabilities to the outside world through APIs,
enabling users to easily access AIGC-related content. Obviously, APIs have
become an important pillar of AIGC applications. So, what exactly is an API?
+
+API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of predefined rules and
conventions for communication between different software applications. APIs
enable software applications (clients) to request functionality and data from
other software applications (servers), facilitating interaction and data
sharing between different systems. By leveraging APIs, developers can use the
functionality of other applications, allowing them to build and release new
applications more quickly.
+
+API management involves the processes of creating and publishing APIs,
formulating usage policies, controlling access rights, cultivating user
communities, collecting and analyzing usage statistics, and reporting
performance, typically including components such as an API gateway and a
developer portal. Among these, the API gateway, as a key component, is
responsible for handling and forwarding requests, as well as executing security
and performance policies, while the developer portal is [...]
+
+As enterprises increasingly rely on APIs to drive digital transformation, the
importance of API management has unprecedentedly risen. After a brief
introduction to the relevant concepts above, we will explore the top ten trends
in API management.
+
+### 1. API Security is Becoming Increasingly Important
+
+API security refers to the process of protecting the exchange of data and
functionality between applications and systems through APIs. The primary goal
of API security is to ensure the correctness, reliability, and confidentiality
of data and functionality, and to prevent unauthorized access and potential
malicious attacks. API security is critical for modern applications and
enterprise services, as they heavily rely on APIs for data exchange and
integration. The following are several im [...]
+
+1. **Data protection**: APIs are often used to transmit sensitive data, such
as user information, transaction details, and payment information. Ensuring API
security can prevent data leaks, tampering, and loss, protecting the
information security of users and enterprises.
+2. **System integrity**: Maintaining system integrity by ensuring that APIs
can only be accessed by authorized users and compliant applications can help
prevent malicious attackers from compromising or controlling the system through
APIs.
+3. **Trust and reputation**: A secure API is crucial in establishing user
trust in enterprise services and building a positive brand reputation.
Conversely, inadequate API security can harm the reputation of the enterprise
and result in loss of users.
+
+To ensure API security, API gateways are commonly used to manage security
features like identity authentication and access control, which protect APIs
from unauthorized access and attacks.
+
+There are numerous API gateways available on the market, one of which is
Apache APISIX. [Apache APISIX](https://api7.ai/apisix) is a cloud-native API
gateway under the Apache Software Foundation that boasts dynamic, real-time,
and high-performance capabilities. It provides a range of security features to
ensure API security, including authentication via plugins like `key-auth` and
`jwt-auth`, and access control via plugins like `consumer-restriction`. These
features help businesses preve [...]
+
+### 2. The Increasing Importance of API Standardization
+
+As APIs become increasingly prevalent, standardizing their design is of
growing importance. The following are several benefits of API standardization:
+
+1. **Facilitates collaboration and communication** within an organization by
ensuring that different teams and departments adhere to uniform design
principles and standards, thereby enhancing development efficiency and quality.
+2. **Enhances the security and stability** of APIs by defining clear
interfaces, data structures, and protocols, thereby mitigating the risks of
errors or misuse.
+3. **Improves the extensibility and interoperability** of APIs by adhering to
industry or community-recognized design guidelines or best practices, enabling
APIs to adapt to diverse scenarios and requirements.
+
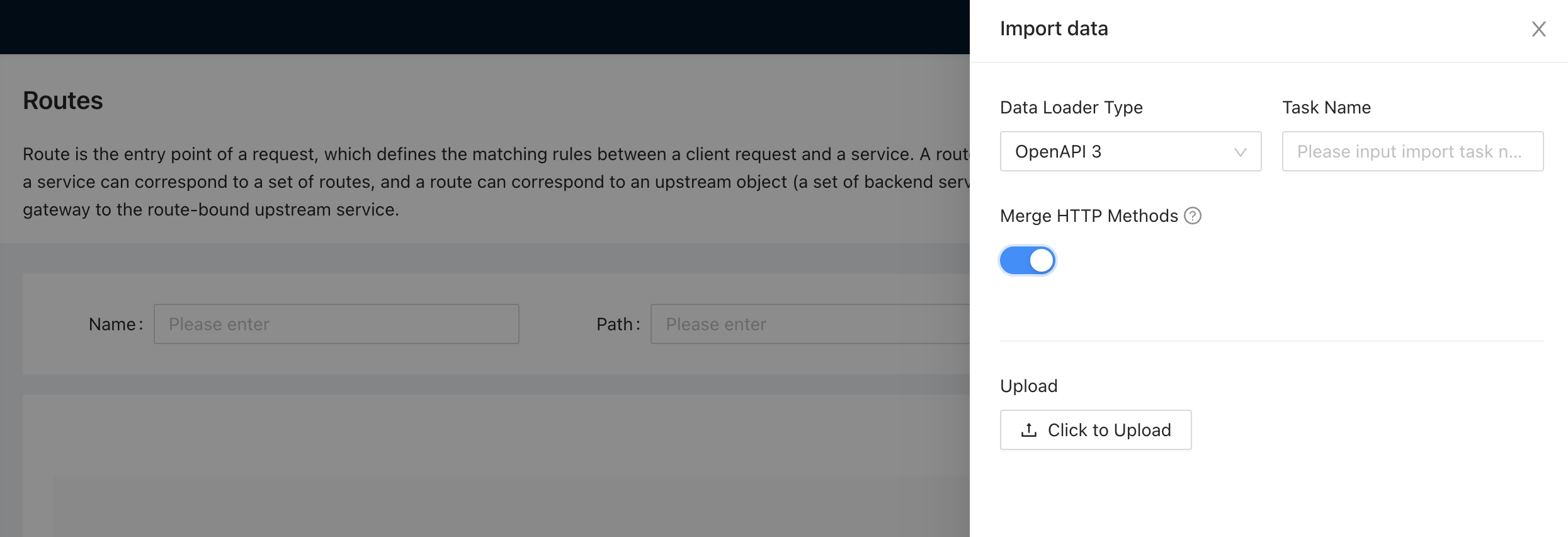
+In the process of API standardization, a common API standard specification is
the [OpenAPI Specfication](https://swagger.io/specification/). Many tools and
platforms support this specification to facilitate the import and management of
APIs. For example, the [Apache APISIX
Dashboard](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard) can import relevant
route data through OpenAPI documents.
+
+
+
+By using these standard specifications, teams can easily share and manage APIs
across different platforms and tools, further improving collaboration
efficiency and API maintainability.
+
+### 3. Popularization of Cloud-based API Management Solutions
+
+Traditional API management solutions typically focus on deploying and managing
APIs locally. This means that businesses need to purchase, deploy, and maintain
hardware and software resources to support API development, publishing, and
monitoring. However, with the development of businesses and the popularization
of cloud computing technology, traditional API management solutions face
challenges in scalability, cost-effectiveness, and cross-platform integration.
+
+Cloud-based API management solutions have emerged as a viable alternative to
traditional on-premises solutions. By leveraging the elasticity, pay-as-you-go,
and cross-platform capabilities of cloud computing, these solutions provide
businesses with a more flexible, efficient, and reliable way to manage their
APIs. Typically, cloud-based API management solutions comprise components such
as API gateways, security features, monitoring, and analytics, enabling
businesses to achieve unified m [...]
+
+Cloud-based API management solutions offer several advantages over traditional
API management solutions, including:
+
+1. **High availability**: Cloud-based API management solutions provide elastic
load balancing and auto-scaling features, as well as automated failover and
disaster recovery capabilities, which result in increased availability.
+2. **Cost-effectiveness**: By reducing the costs of API development,
deployment, and maintenance, cloud-based API management solutions allow
businesses to focus on innovation instead of infrastructure management.
+3. **Cross-platform support**: Cloud-based API management solutions support
hybrid and multi-cloud environments, enabling businesses to seamlessly
integrate and manage their APIs across different cloud vendors, and easily
migrate and scale them as needed.
+
+It's worth mentioning that [API7 Cloud](https://api7.ai/cloud), based on
Apache APISIX, is a cloud-based API management solution that provides a modern
cloud architecture to help enterprises manage APIs deployed on hybrid cloud and
multi-cloud environments. It efficiently and reliably connects them. Compared
to traditional API management solutions, API7 Cloud offers more advantages and
flexibility.
+
+### 4. Utilizing Low-Code API Platforms for Easy API Creation and Deployment
+
+Low-code API platforms are tools that enable users to create, publish, and
manage APIs using a simple graphical interface and pre-built modules. These
platforms are designed to streamline the API development process, reduce
development barriers, and increase development efficiency.
+
+An excellent example is [Apache APISIX
Dashboard](https://github.com/apache/apisix-dashboard), which enables users to
create routes without the need to manually write code. By using drag-and-drop
functionality, users can easily arrange and combine different plugins.
+
+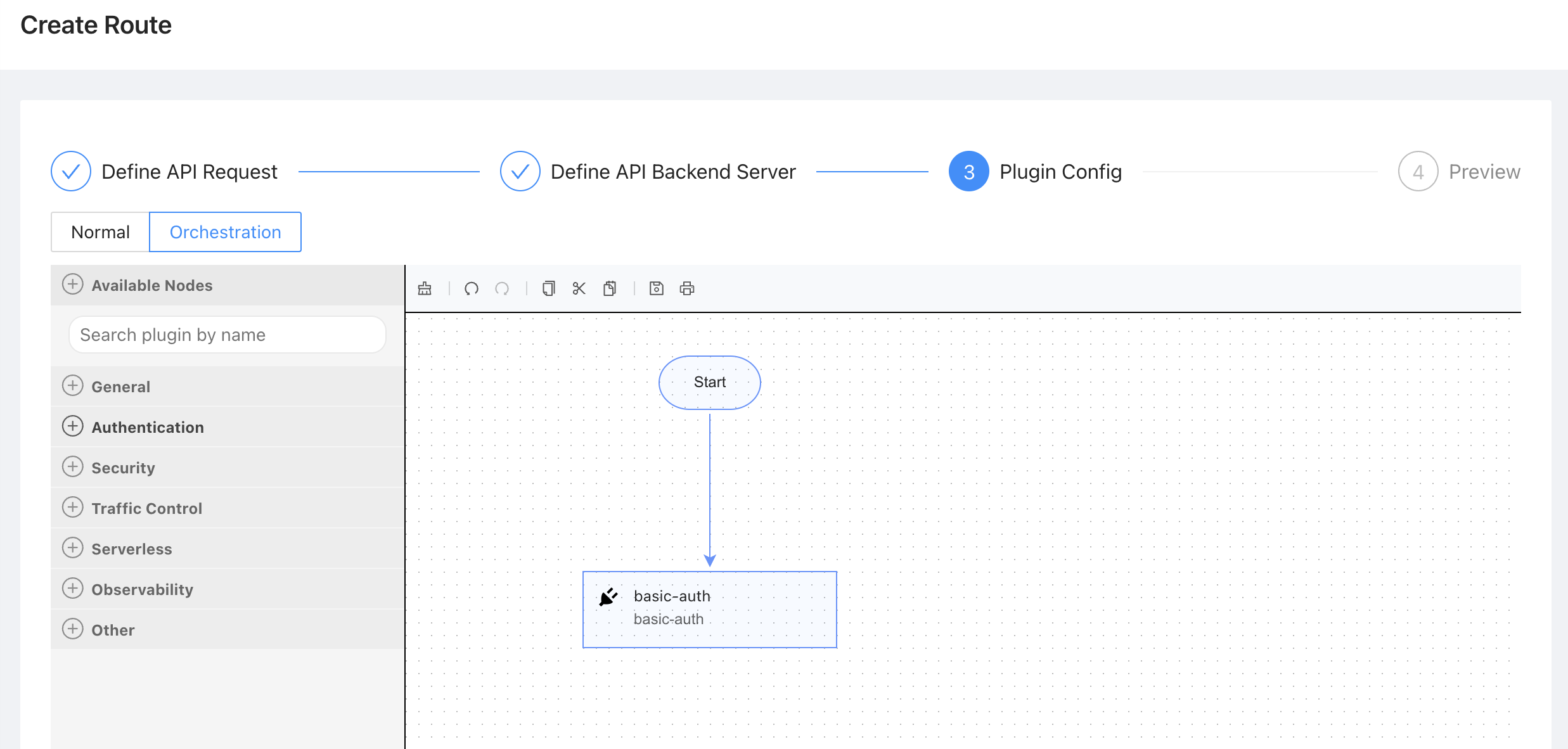
+
+### 5. The Development of the API Marketplace
+
+With the popularity of APIs, the API marketplace has gradually become a way
for enterprises to discover, evaluate, and purchase APIs from various vendors.
The API marketplace can help enterprises accelerate innovation and reduce
development costs.
+
+1. For API suppliers, the API marketplace can increase the visibility and
attractiveness of their APIs, increase their revenue and customer base, and
utilize market analysis to optimize their API strategy and design.
+2. For API consumers, the API marketplace can provide a convenient one-stop
service that enables them to easily find and use various high-quality APIs to
meet their business needs, and saves them time and resources in developing or
maintaining these APIs themselves.
+3. For the API ecosystem, the API marketplace can foster collaboration and
innovation, inspiring new use cases and generating value by bringing together
API suppliers and consumers.
+
+### 6. Rise of More API Protocols
+
+With the rise of next-generation API protocols such as
[GraphQL](https://api7.ai/blog/what-is-graphql) and
[gRPC](https://api7.ai/blog/what-is-grpc-and-how-to-work-with-apisix), which
are competing with the current dominant but gradually declining [REST
API](https://api7.ai/blog/understanding-and-using-restful-apis), more and more
API protocols are being widely used.
+
+GraphQL is a data query and manipulation language developed by Facebook. It
allows clients to explicitly request the required data based on their needs and
obtain multiple resources in a single request, reducing data transmission and
improving performance. Compared to REST API, GraphQL has the following
advantages:
+
+1. **Flexible data requests**: Clients can specify the data they need,
avoiding excessive or insufficient data transmission.
+2. **More efficient request processing**: Retrieving multiple resources with a
single request helps to reduce network round trips.
+3. **Real-time data updates**: GraphQL supports real-time data updates and can
respond promptly to clients' data change needs.
+
+[gRPC](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GRPC) is a high-performance, open-source
remote procedure call (RPC) framework developed by Google. It allows clients to
call server-side methods as if they were calling local methods. gRPC uses
Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) as the interface definition language and data
serialization format, enabling efficient data transmission. Compared to REST
API, gRPC has several advantages:
+
+1. gRPC uses Protobuf for data serialization, which offers higher performance
and smaller data size than JSON format.
+2. gRPC is based on the HTTP/2 protocol, supporting bidirectional streaming,
multiplexing, and built-in TLS security. This makes it faster, more flexible,
and more secure than REST API based on the HTTP/1.1 protocol's one-way
request-response mode.
+3. gRPC defines APIs based on Protobuf and provides native code generation
functionality. It can automatically generate client and server-side code in
multiple programming languages, making it more convenient and consistent than
REST API, which requires third-party tools like Swagger to generate code.
+
+In order to accommodate the needs of emerging protocols, Apache APISIX offers
a range of plugins designed to support the processing of different protocols.
+
+In Apache APISIX, the following plugins can handle these emerging API
protocols:
+
+-
[grpc-transcode](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-transcode/):
grpc-transcode facilitates conversion between HTTP and gRPC requests.
+- [grpc-web](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/grpc-web/):
grpc-web is a proxy plugin that processes gRPC Web requests from JavaScript
clients to a gRPC service.
+- [degraphql](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/degraphql/):
degraphql is a plugin that supports the decoding of RESTful APIs into GraphQL.
+
+### 7. Artificial Intelligence and APIs
+
+API management platforms are leveraging machine learning and artificial
intelligence to automate tasks such as API discovery, threat detection, and
anomaly detection. This can help enterprises reduce the burden on their IT
teams and improve the efficiency and accuracy of their API management processes.
+
+1. **Threat detection**: Machine learning and artificial intelligence can
assist API management platforms in real-time monitoring and analyzing API
traffic to detect and prevent any malicious or abnormal requests.
+2. **Anomaly detection**: Machine learning and artificial intelligence can
help API management platforms predict and diagnose any potential issues that
may affect API performance or availability, facilitating timely repair and
optimization.
+
+### 8. Greater Focus on Developer Experience
+
+As APIs become increasingly central to business operations, developer
experience has become increasingly important. API management platforms are
adding more developer-friendly features, such as documentation, testing tools,
and SDKs, to make it easier for developers to use APIs.
+
+1. **Documentation**: Documentation is the primary way for developers to
understand and learn about an API, so it should describe the API's functions,
parameters, examples, error codes, and other information clearly, completely,
accurately, and in a timely manner. Documentation should also provide
interactive consoles or sandboxes that allow developers to quickly test and
debug APIs.
+2. **Testing tools**: Testing tools are an essential means for developers to
verify and optimize APIs, so they should support a variety of testing scenarios
and requirements in a convenient, reliable, and flexible manner. Testing tools
should also provide real-time feedback and reports so that developers can
identify and resolve issues in a timely manner.
+3. **SDKs**: SDKs are a convenient way for developers to integrate and use
APIs, so they should cover a variety of mainstream programming languages and
platforms and stay in sync with API updates. SDKs should also follow best
practices and standards to make it easy for developers to understand and call
APIs.
+
+### 9. The Rise of API Analytics
+
+API Analytics is a technology used to collect, analyze, and interpret data on
API usage. With the growing popularity of APIs in the software and internet
industries, API Analytics has emerged as a critical tool for management and
optimization. Here are a few reasons for the rise of API Analytics:
+
+1. With the development of technologies such as cloud computing, big data, and
the Internet of Things (IoT), APIs have become an important tool for exchanging
data and functionality between enterprises and developers. This has led to a
growing need for API Analytics to better understand and optimize API
performance.
+2. Modern software development increasingly adopts a microservices
architecture, which decomposes complex applications into multiple independent
and scalable services. These services communicate with each other via APIs,
making the need for API Analytics more apparent in this architecture.
+3. API Analytics can help detect potential security vulnerabilities and
violations of compliance, thereby reducing risk.
+
+### 10. More APIs Are Provided Through Serverless Architecture
+
+Serverless architecture is a cloud computing model that allows developers to
deploy and run applications without managing servers.
+
+To provide API services through serverless architecture, you only need to
follow a few steps:
+
+1. Choose a serverless platform, and write your API logic code using the
programming languages and frameworks provided by the serverless platform.
+2. Configure your API triggers on the platform, such as HTTP requests, timers,
events, etc.
+3. Deploy your API code to the serverless platform using the relevant tools
provided by the platform and test its functionality and performance.
+
+Using serverless architecture has the following advantages:
+
+1. Serverless architecture allows API developers to focus on business logic
without worrying about infrastructure, deployment, scaling, etc.
+
+2. Serverless architecture can automatically allocate resources according to
API request volume, avoiding resource waste or shortages.
+
+3. Serverless architecture can improve API response speed and reliability by
leveraging distributed edge computing nodes to process requests.
+
+Apache APISIX also supports this area, including plugins such as
[serverless](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/serverless/) and
[openfunction](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/openfunction/).
+
+## Summary
+
+API management is an integral part of successful digital transformation, and
as such, it brings both challenges and opportunities. As companies strive to
stay ahead in the rapidly evolving digital landscape, it is crucial to keep up
with the ten major trends in API management. By doing so, businesses can
position themselves to meet future challenges, leverage new opportunities, and
foster continuous growth and innovation.
diff --git a/blog/en/blog/2023/05/04/apache-apisix-chaos-engineering.md
b/blog/en/blog/2023/05/04/apache-apisix-chaos-engineering.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..b5df1dad65c
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2023/05/04/apache-apisix-chaos-engineering.md
@@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
+---
+title: Building a More Robust Apache APISIX Ingress Controller With Litmus
Chaos
+authors:
+ - name: API7.ai
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/api7
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/61078451?s=200&v=4
+keywords:
+ - Apache APISIX
+ - Chaos Engineering
+ - APISIX Ingress Controller
+description: Chaos engineering is a powerful tool for ensuring system
reliability and performance, and its application in designing Chaos experiments
for Ingress Controllers can help organizations identify weaknesses in their
applications and infrastructure.
+tags: [Ecosystem]
+image:
https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/04/20/yeuKN9nu_Building%20a%20More%20Robust%20Apache%20APISIX%20Ingress%20Controller%20With%20Litmus%20Chaos.png
+---
+
+>Chaos engineering is a powerful tool for ensuring system reliability and
performance, and its application in designing Chaos experiments for Ingress
Controllers can help organizations identify weaknesses in their applications
and infrastructure.
+<!--truncate-->
+
+## Overview
+
+[Chaos Engineering](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chaos_engineering) plays a
crucial role in assessing and enhancing the resilience and reliability of
software systems. By simulating disruptive events, organizations can identify
vulnerabilities and improve the system's design and architecture. In this
article, we will discuss the importance of Chaos Engineering and its specific
application in designing Chaos experiments for Ingress Controllers.
+
+## Why We Need Chaos Engineering?
+
+Chaos Engineering is the process of evaluating software systems by simulating
destructive events, such as server network outages or API throttling. By
introducing chaos or faults within the system, we can test the system's
resilience and reliability in unstable and unexpected conditions.
+
+Chaos Engineering helps teams identify hidden risks, monitor vulnerabilities,
and identify performance bottlenecks in distributed systems by simulating
real-world scenarios in a secure control environment. This approach effectively
prevents system downtime or production interruptions.
+
+Netflix's approach to handling systems inspired us to adopt a more scientific
approach, which drove the birth and development of Chaos Engineering.
+
+**1. Introduction of Disruptive Events**
+
+Chaos Engineering involves introducing disruptive events, such as network
partitions, service degradation, and resource constraints, to simulate
real-world scenarios and test the system's ability to handle unexpected
conditions. The purpose is to identify vulnerabilities or weaknesses and
improve the system's design and architecture to make it more robust and
resilient.
+
+**2. Testing System Resilience**
+
+In today's constantly evolving and fast-paced technology landscape, testing
system resilience is crucial to ensure that systems are robust, scalable, and
capable of handling unexpected challenges and conditions. Chaos Engineering is
an effective way to achieve this by introducing disruptive events to observe
the system's response and measure its ability to handle unexpected conditions.
+
+Organizations can monitor system logs, performance metrics, and user
experience to measure the impact of disruptive events on system resilience.
Tracking these metrics provides a better understanding of the system's
behavior, allowing organizations to identify areas for improvement.
+
+**3. Discovering Hidden Problems**
+
+Distributed systems are prone to hidden issues, such as data loss, performance
bottlenecks, and communication errors, which can be challenging to detect, as
they may only become visible when the system is under pressure. Chaos
Engineering can help uncover these hidden issues by introducing disruptive
events. This information can then be used to improve the system's design and
architecture, making it more resilient and reliable.
+
+Proactively identifying and resolving these problems enhances the reliability
and performance of systems, preventing downtime, reducing the risk of data
loss, and ensuring the system runs smoothly.
+
+**4. What It's Worth and Why We Need It?**
+
+Distributed systems are complex and inherently chaotic, which can lead to
failure. The use of cloud and
[microservices](https://api7.ai/blog/what-are-microservices) architecture
provides many advantages but also comes with complexity and chaos. Engineers
are responsible for making the system as reliable as possible.
+
+Without testing, there is no confidence to use the project in the production
environment. In addition to conventional unit tests and end-to-end tests,
introducing chaos tests makes the system more robust.
+
+When an error occurs, repairing it takes time and can cause immeasurable
losses, with long-term effects in the future. During the repair process,
various factors need consideration, including the system's complexity, the type
of error, and possible new problems, to ensure effective final repair.
+
+Furthermore, when an open-source project brings serious faults to users in the
production environment, many users may switch to other products.
+
+## How to Design Chaos Experiments for an Ingress Controller?
+
+**1. What Is Ingress?**
+
+Ingress is a Kubernetes resource object that contains rules for how external
clients can access services within the cluster. These rules dictate which
clients can access which services, how client requests are routed to the
appropriate services, and how client requests are handled.
+
+**2. What Is an Ingress Controller?**
+
+An Ingress resource requires an Ingress Controller to process it. The
controller translates the Ingress rules into configurations on a proxy,
allowing external clients to access services within the cluster. In a
production environment, Ingress Controllers need to have complex capabilities,
such as limiting access sources and request methods,
[authentication](https://api7.ai/blog/api-gateway-authentication), and
authorization. Most Ingress Controllers extend the semantics of Ingress throu
[...]
+
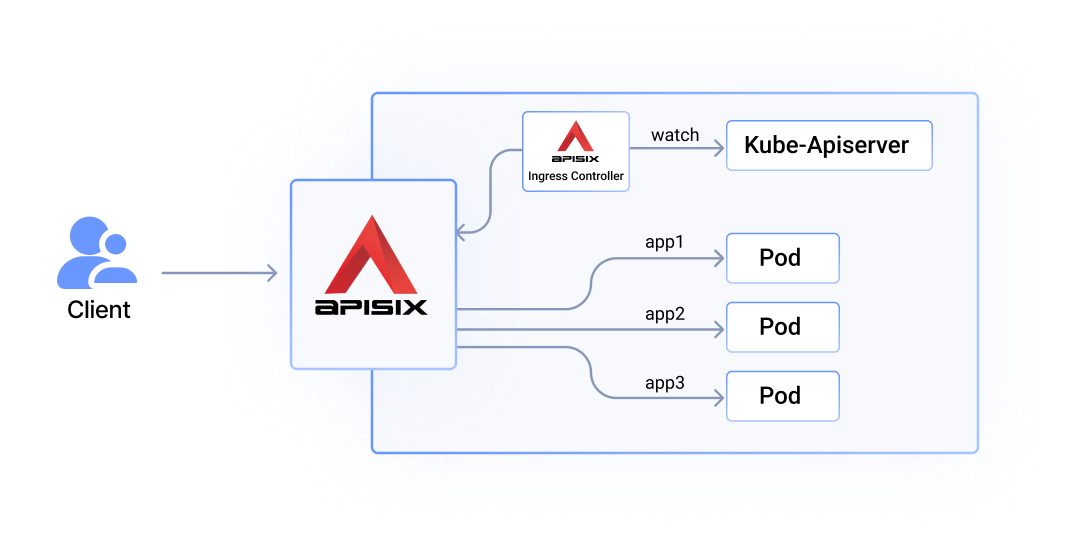
+**3. What Is Apache APISIX Ingress Controller?**
+
+Apache APISIX Ingress Controller is a specialized type of load balancer that
helps administrators manage and control Ingress traffic. It uses APISIX as a
data plane to provide users with [dynamic
routing](https://api7.ai/blog/dynamic-routing-based-on-user-credentials), load
balancing, elastic scaling, security policies, and other features to improve
network control and ensure higher availability and security for their business.
APISIX Ingress Controller supports three configuration modes [...]
+
+
+
+**4. What Is Litmus Chaos?**
+
+[Litmus Chaos](https://litmuschaos.io/) is an open-source Chaos Engineering
framework that provides an infrastructure experimental framework to validate
the stability of controllers and microservices architectures. It can simulate
various environments, such as container-level and application-level
environments, natural disasters, faults, and upgrades, to understand how the
system responds to these changes. The framework can also explore the behavior
changes between controllers and applic [...]
+
+**5. How to Design Chaos Experiments?**
+
+Here is a general procedure for designing chaos experiments in any scenario:
+
+- **Define the system under test:** Identify the specific components of the
system you want to experiment on and develop clear and measurable objectives
for the experiment. This includes creating a comprehensive list of the
components, such as hardware and software, that will be tested, as well as
defining the scope of the experiment and the expected outcomes.
+
+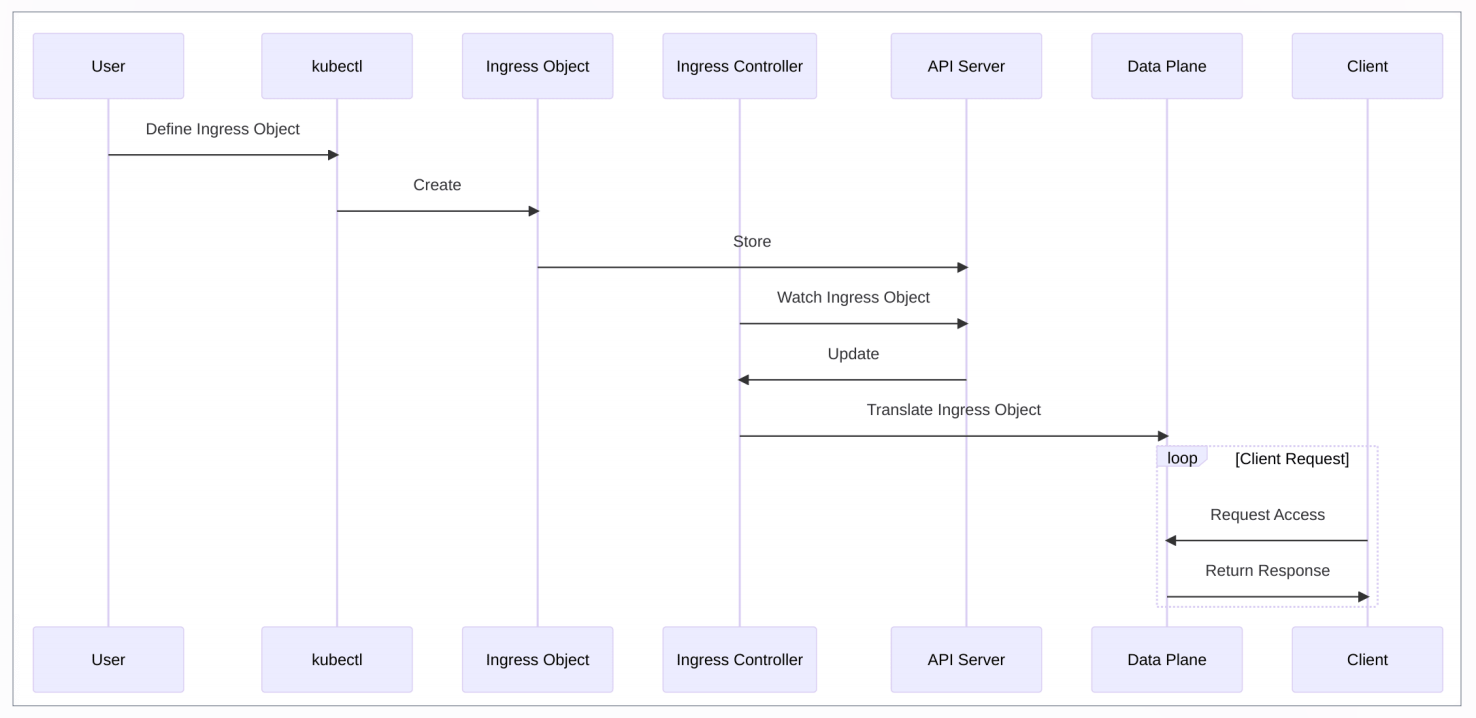
+
+>kube-apiserver: if an exception occurs, the Ingress resource write failed.
+>Ingress-controller: Network interruption, Crash, Podfaults, I/O
+>data-plane: Network interruption, Crash, Podfaults, I/O
+
+- **Choose the right experiment:** Select an experiment that is aligned with
the objectives you have set and closely mimics a real-world scenario. This will
help ensure that the experiment produces meaningful results and accurately
reflects the behavior of the system.
+- **Establish a hypothesis:** Establish a hypothesis about how the system will
behave during the experiment and what outcomes you anticipate. This should be
based on experience or research, and it should be reasonable and testable.
+- **Run the experiment:** Run the experiment in a controlled environment, such
as a staging environment, to limit the potential for harm to the production
system. Collect all relevant data during the experiment and store it securely.
There may be differing opinions on whether the experiment should take place
directly in the production environment. However, for most scenarios, we need to
ensure the Service Level Objective (SLO) of the system is met.
+- **Evaluate the results:** Evaluate the results of the experiment and compare
them to your hypothesis. Analyze the data collected and document any
observations or findings. This includes identifying any unexpected results or
discrepancies and determining how they might affect the system. Additionally,
consider how the results of the experiment can be used to improve the system.
+
+## Main Usage Scenarios of Ingress Controller
+
+The most important capability of an Ingress Controller is to proxy traffic,
and all other functions are based on this core function. Therefore, when
conducting Chaos Engineering, normal proxy traffic is the key metric.
+
+To define the system under test for APISIX Ingress Controller, users need to
create route configurations, such as Ingress, Gateway API, or CRD, and apply
them to the Kubernetes cluster via Kubectl. This process goes through
kube-apiserver for authentication, authorization, admission and other related
procedures, and is then stored in etcd.
+
+The APISIX Ingress Controller continuously watches for changes in Kubernetes
resources. These configurations are then converted to configurations on the
data plane. When a client requests the data plane, it accesses the upstream
service according to the routing rules.
+
+If kube-apiserver has an exception, it will prevent the configuration from
being created, or the Ingress Controller from getting the correct
configuration. Similarly, if there is an exception in the data plane, such as a
network interruption or Pod killed, it will also not be able to do normal
traffic proxy.
+
+The scope of our experiment is mainly the impact on system availability if the
Ingress Controller has an exception.
+
+**1. Detailed Operation Steps**
+
+- Choose the right experiment: We can cover many scenarios of incorrect
configuration through end-to-end tests. Mainly through Chaos Engineering, we
can verify whether the data plane can still proxy traffic normally when the
Ingress Controller encounters an exception, such as DNS errors, network
interruptions, or Pod killed.
+- Establish a hypothesis: For each scenario, we can create a hypothesis such
as "When the Ingress-controller Pod gets `X?`, the client's request can still
get a normal response."
+- Run the experiment: The experiment and variables have been determined, so
all that's left is to experiment.
+Litmus Chaos provides various ways to conduct experiments. We can do this
through the Litmus Portal. To do this, we need to create a Chaos scenario,
select the application to be experimented on, and these steps are relatively
straightforward. However, we must pay attention to the fact that Litmus Chaos
includes a Probes resource.
+
+Probes are pluggable checks that can be defined within the ChaosEngine for any
Chaos Experiment. The experiment pods execute these checks based on the mode
they are defined in and factor their success as necessary conditions in
determining the verdict of the experiment, in addition to the standard in-built
checks.
+At the same time, we can also schedule experiments, which is a very valuable
function.
+
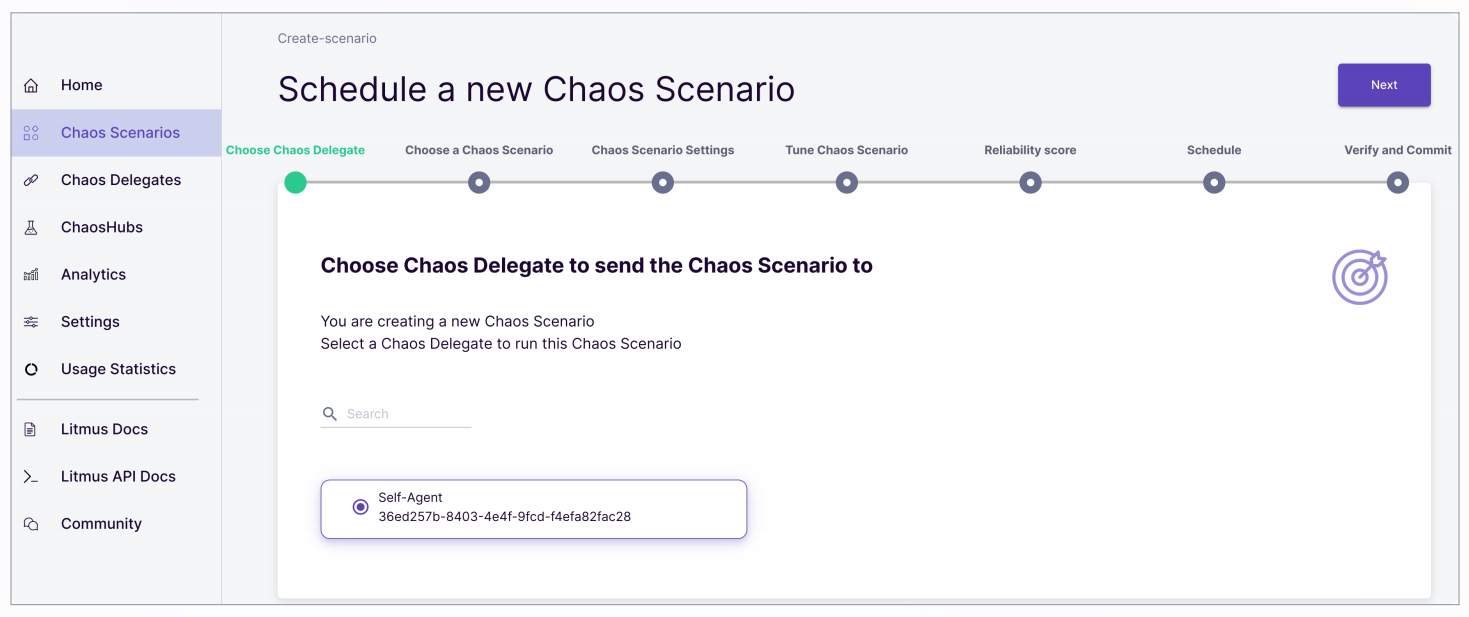
+Additionally, Litmus Chaos also supports running experiments by submitting
YAML manifests.
+
+
+
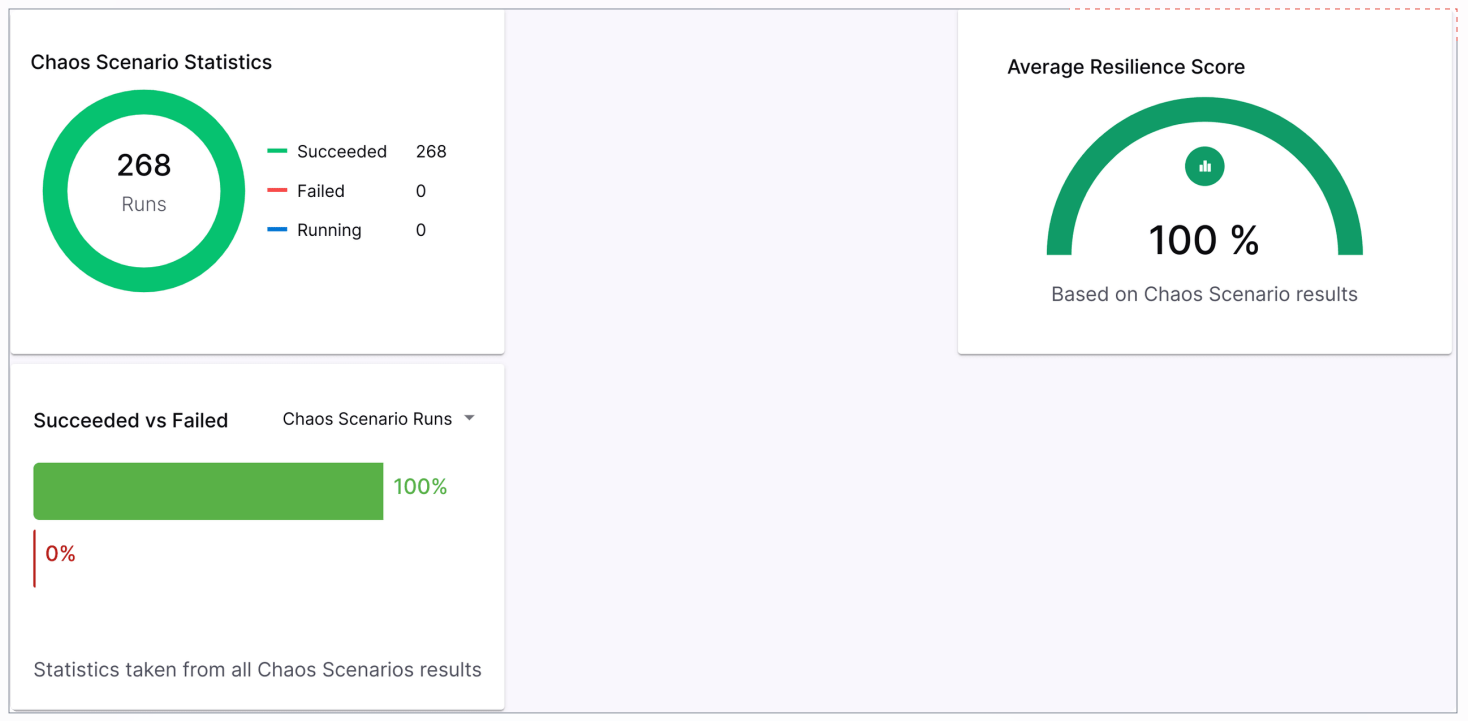
+- Evaluate the results: Litmus Chaos has built-in statistical reports, and it
can be integrated with [Prometheus and
Grafana](https://apisix.apache.org/blog/2021/12/13/monitor-apisix-ingress-controller-with-prometheus/#installing-prometheus-and-grafana)
to provide a unified dashboard for integration.
+
+
+
+**2. Benefits and Future**
+
+Through rigorous end-to-end testing and the power of Chaos Engineering, we're
confident in the stability and reliability of the delivered APISIX Ingress
Controller. Chaos Engineering has also helped us to identify and fix bugs.
We're constantly working to improve and evolve this amazing project, and we
invite you to join our community.
diff --git
a/blog/en/blog/2023/05/19/why-do-microservices-need-an-api-gateway.md
b/blog/en/blog/2023/05/19/why-do-microservices-need-an-api-gateway.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..6d053708ff6
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2023/05/19/why-do-microservices-need-an-api-gateway.md
@@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
+---
+title: Why Do Microservices Need an API Gateway
+authors:
+ - name: API7.ai
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/api7
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/61078451?s=200&v=4
+keywords:
+ - Apache APISIX
+ - Microservices
+ - Alternatives to Kong
+description: Let's learn the importance of API gateway in the microservices
architecture, and compare common API gateways.
+tags: [Ecosystem]
+image:
https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/02/16/CHqaC3Xw_Ecosystem%20%E6%A8%A1%E6%9D%BF1.png
+---
+
+>The microservices architecture has been widely adopted by many companies. As
the data and API quantity of microservices increases, it is crucial to choose
an excellent API gateway for high-traffic governance: APISIX.
+<!--truncate-->
+
+## What Are Microservices
+
+Microservice architecture, usually referred to as
[microservices](https://api7.ai/blog/what-are-microservices), is a type of
architecture used to develop applications. With microservices, large
applications can be broken down into multiple independent components, each with
its own responsibilities. When processing a user request, an application based
on microservices may call many internal microservices to generate its response
jointly. Microservices are a result of internet development, [...]
+
+Overall, the architecture of systems has roughly evolved from monolithic
architecture to SOA architecture to microservice architecture. The specific
progression and pros/cons of each architecture are outlined in the table below.
+
+| Architecture Type | Description
|
Advantages
| Disadvantages
|
+|----|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| Monolithic Application Architecture | Pack all functional code into a
single service. | 1. Simple architecture with low project development and
maintenance costs.
| Coupling all modules together is beneficial for developing and maintaining
small projects, but it can create issues for large projects, including <br/> 1.
The modules in the pr [...]
+| [SOA
Architecture](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Service-oriented_architecture)
| The term stands for "service-oriented architecture," which typically
involves multiple services. <br/>A service typically exists independently in an
operating system process, and communication between services is achieved
through dependencies or communication mechanisms, <br/> Ultimately, it provides
a series of functions.
[...]
+| Microservice Architecture | Microservices are the
sublimation of SOA. One of the key emphases of the microservices architecture
is "the need to thoroughly componentize and serviceize business", <br/>The
original single business system will be split into multiple parts that can be
developed, designed, and deployed independently.<br/>These parts will run as
small, independent applications. Each application will collaborate and
communicate with the others to achieve integ [...]
+
+Therefore, microservices are an inevitable result of Internet development, and
the system architecture of many traditional companies is gradually becoming
microservice-oriented.
+
+However, with Internet business development, the number of APIs is also
increasing dramatically, and gateways for unified API management will also face
challenges. Choosing a more robust API gateway can effectively enhance the
system's capabilities in monitoring, disaster recovery, authentication, and
rate limiting.
+
+## What Is an API Gateway?
+
+API gateway provides a unified interface for interactions between clients and
service systems and serves as a central point for managing requests and
responses. Choosing a suitable API gateway can simplify development and improve
system operation and management efficiency.
+
+In a microservices architecture, an API gateway serves as a solution for
system design by integrating various microservices from different modules and
coordinating services in a unified manner.
+
+As a system access aspect, the API gateway provides a unified entry point for
clients, hides the implementation details of the system architecture, and makes
microservices more user-friendly. It also integrates some common features such
as [authentication](https://api7.ai/blog/api-gateway-authentication), [rate
limiting](https://api7.ai/blog/rate-limiting-in-api-management), and circuit
breaking to avoid individual development of each microservice, improve
efficiency, and standardize the [...]
+
+## Why Do Microservices Need an API Gateway?
+
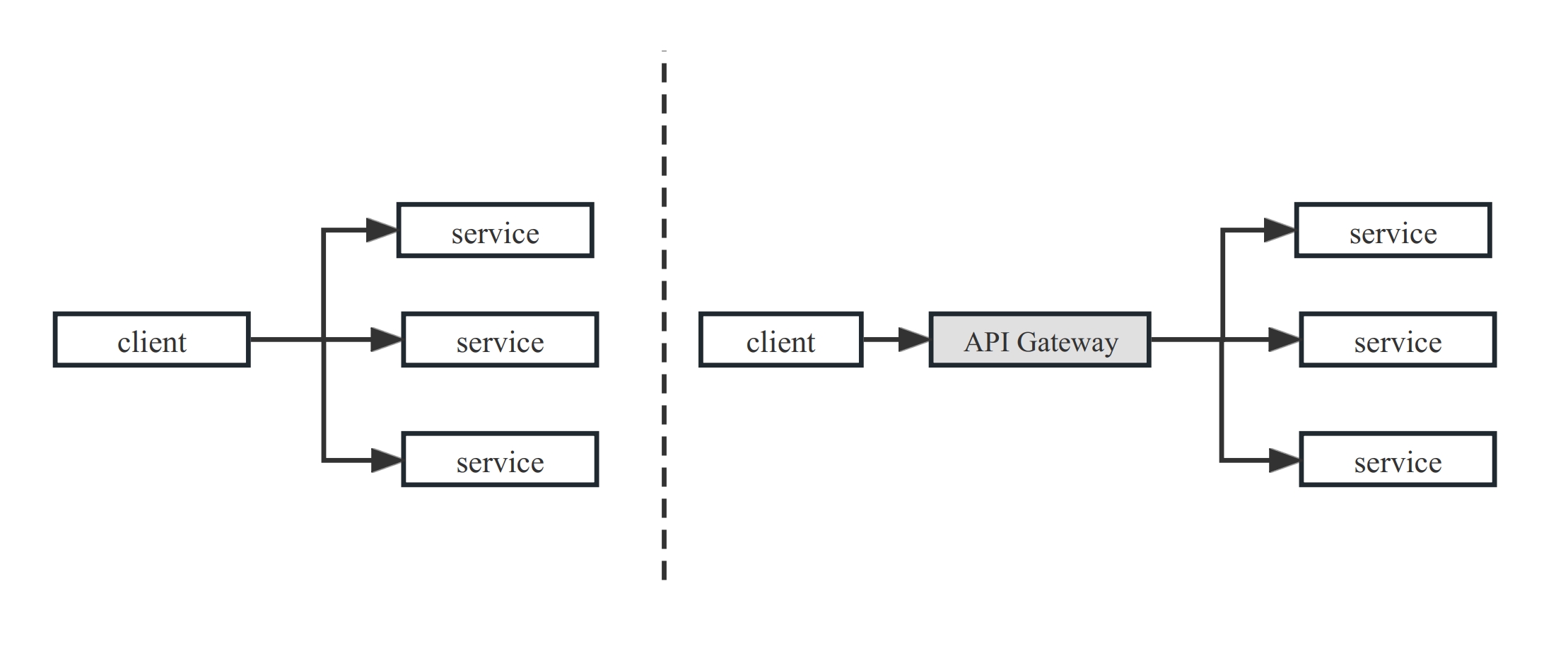
+
+
+As shown in the above diagram, the API gateway serves as an intermediate layer
between the client and microservices. It can provide microservices to the
outside world at a unified address and route the traffic to the correct service
nodes within the internal cluster based on appropriate rules.
+
+Without an API gateway, the inlets and outlets of the traffic are not unified,
and the client needs to know the access information of all services. The
significance of microservices will not exist. Therefore, a microservices
gateway is necessary for a microservice architecture. Additionally, the API
gateway plays a vital role in system observability, identity authentication,
stability, and [service
discovery](https://api7.ai/blog/what-is-service-discovery-in-microservices).
+
+### Challenges Faced by Microservices
+
+The microservices gateway should first have API routing capabilities. As the
number of microservices increases, so does the number of APIs. The gateway can
also be used as a traffic filter in specific scenarios to provide certain
optional features. Therefore, higher demands are placed on the microservices
API gateway, such as:
+
+- Observability: In the past, troubleshooting in monolithic applications was
often done by checking logs for error messages and exception stacks. However,
in a microservices architecture with many services, problem diagnosis becomes
very difficult. Therefore, how to monitor the operation of microservices and
provide rapid alarms when anomalies occur poses a great challenge to developers.
+- Authentication and Authorization: In a microservices architecture, an
application is divided into several micro-applications, which need to
authenticate access and be aware of the current user and their permissions.The
[authentication](https://api7.ai/blog/understanding-microservices-authentication-services)
method in monolithic application architecture is unsuitable, especially when
access is not only from a browser but also from other service calls. In a
microservices architecture, v [...]
+- System stability: If the number of requests exceeds the processing capacity
of a microservice, it may overwhelm the service, even causing a cascading
effect that affects the system's overall stability.
+- Service discovery: The decentralized management of microservices also
presents challenges for implementing load balancing.
+
+### Solutions
+
+API gateway, as the intermediate bridge between the client and the server,
provides a unified management mechanism for the microservices system. In
addition to basic functions such as request distribution, API management, and
conditional routing, it also includes identity authentication, monitoring and
alarm, tracing analysis, load balancing, rate limiting, isolation, and circuit
breaking.
+
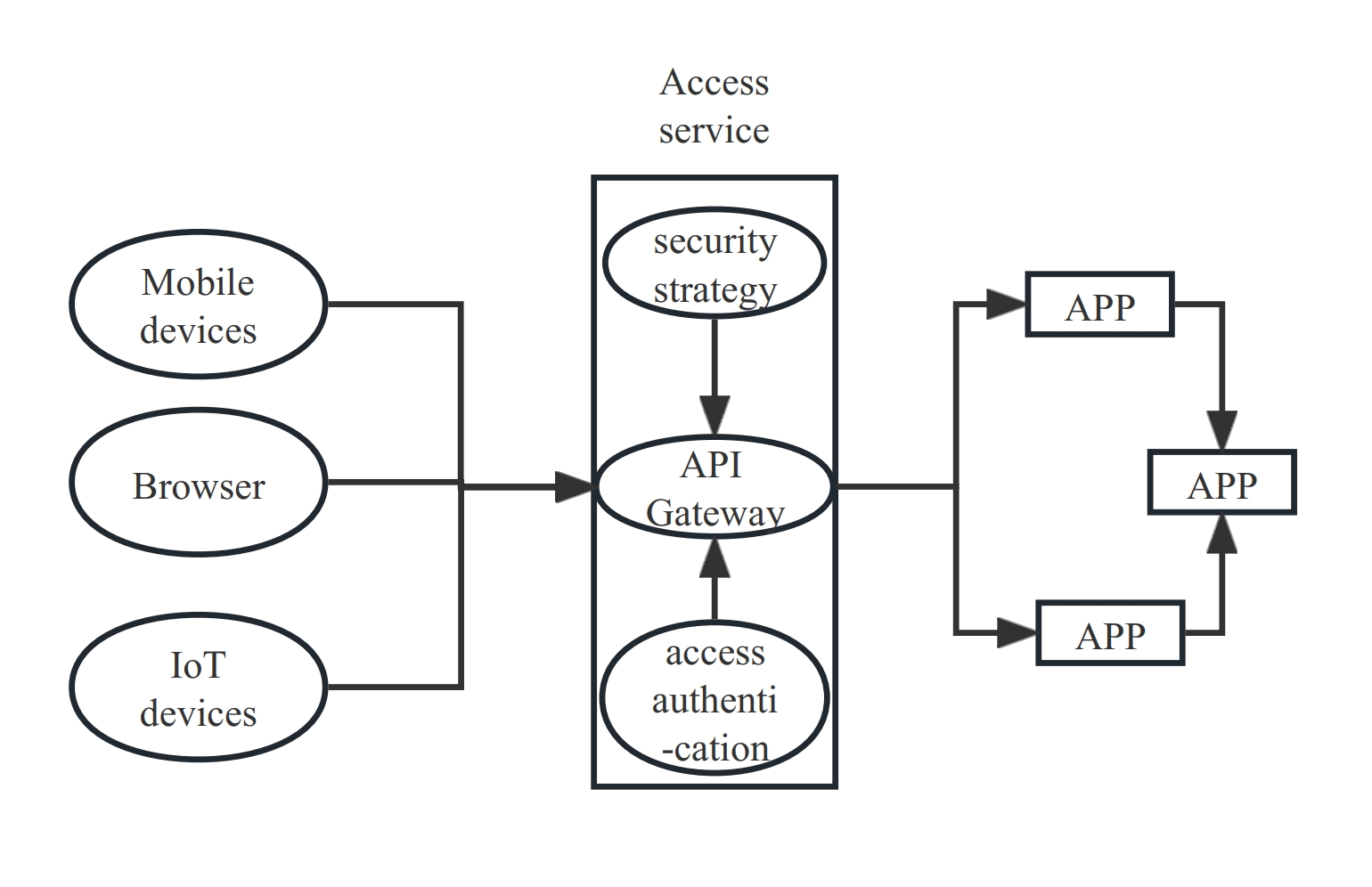
+**Identity authentication**: The following diagram illustrates how
microservices are united with an API gateway for identity authentication, where
all requests go through the gateway, effectively hiding the microservices.
+
+
+
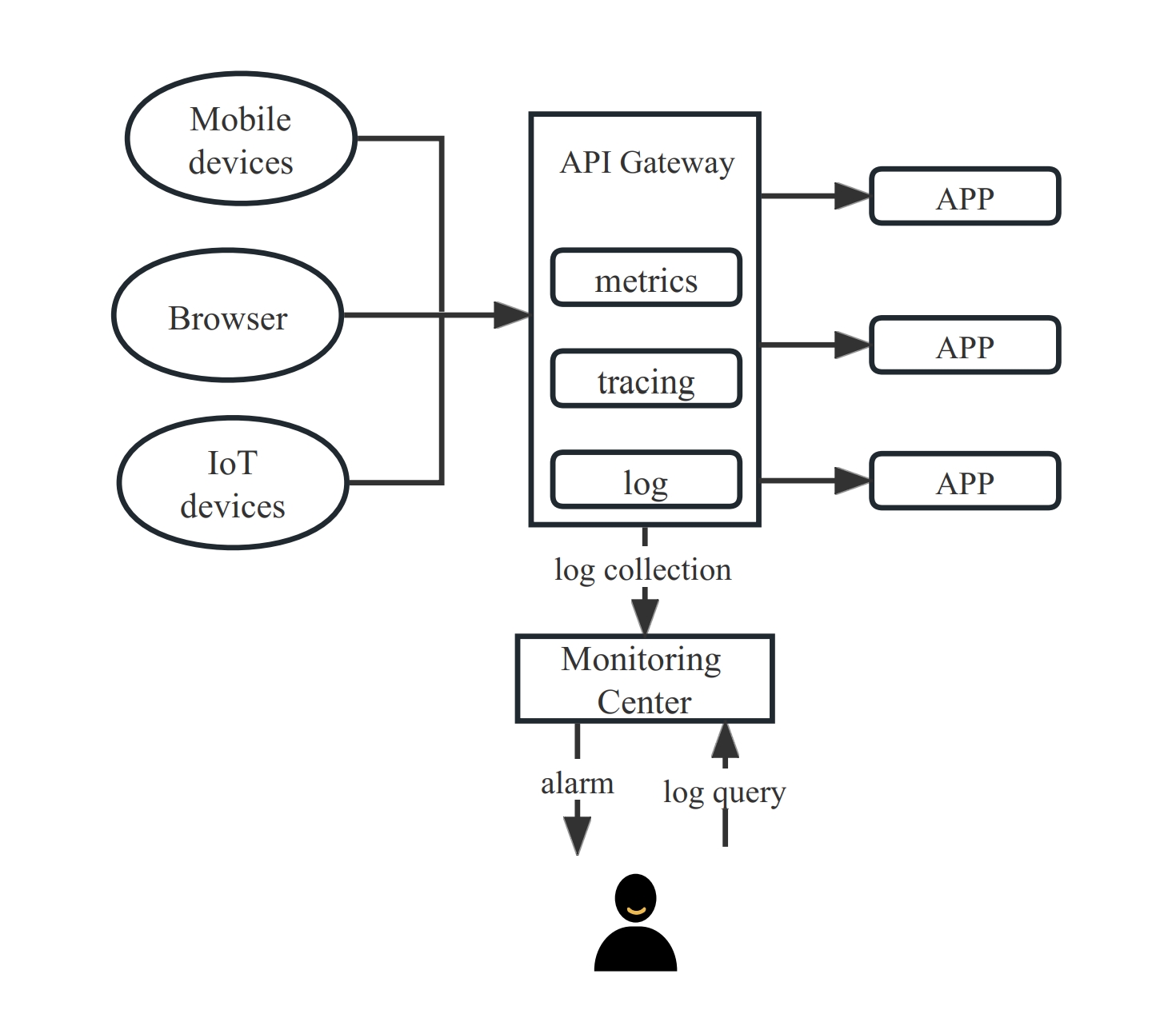
+**Monitoring and Alerting/Tracing Analysis**:
+
+As the intermediary between the client and server, the API gateway is an
excellent carrier for monitoring microservices.
+
+The primary responsibility of the API gateway's monitoring function is to
detect connection anomalies between the gateway and the backend servers in a
timely manner. Users can view log information, monitoring information, tracing,
etc. on the monitoring platform for the API. Furthermore, any anomalies that
arise on the host will be automatically reported to the control panel. Specific
gateways can issue dual alerts to both the client and server.
+
+
+
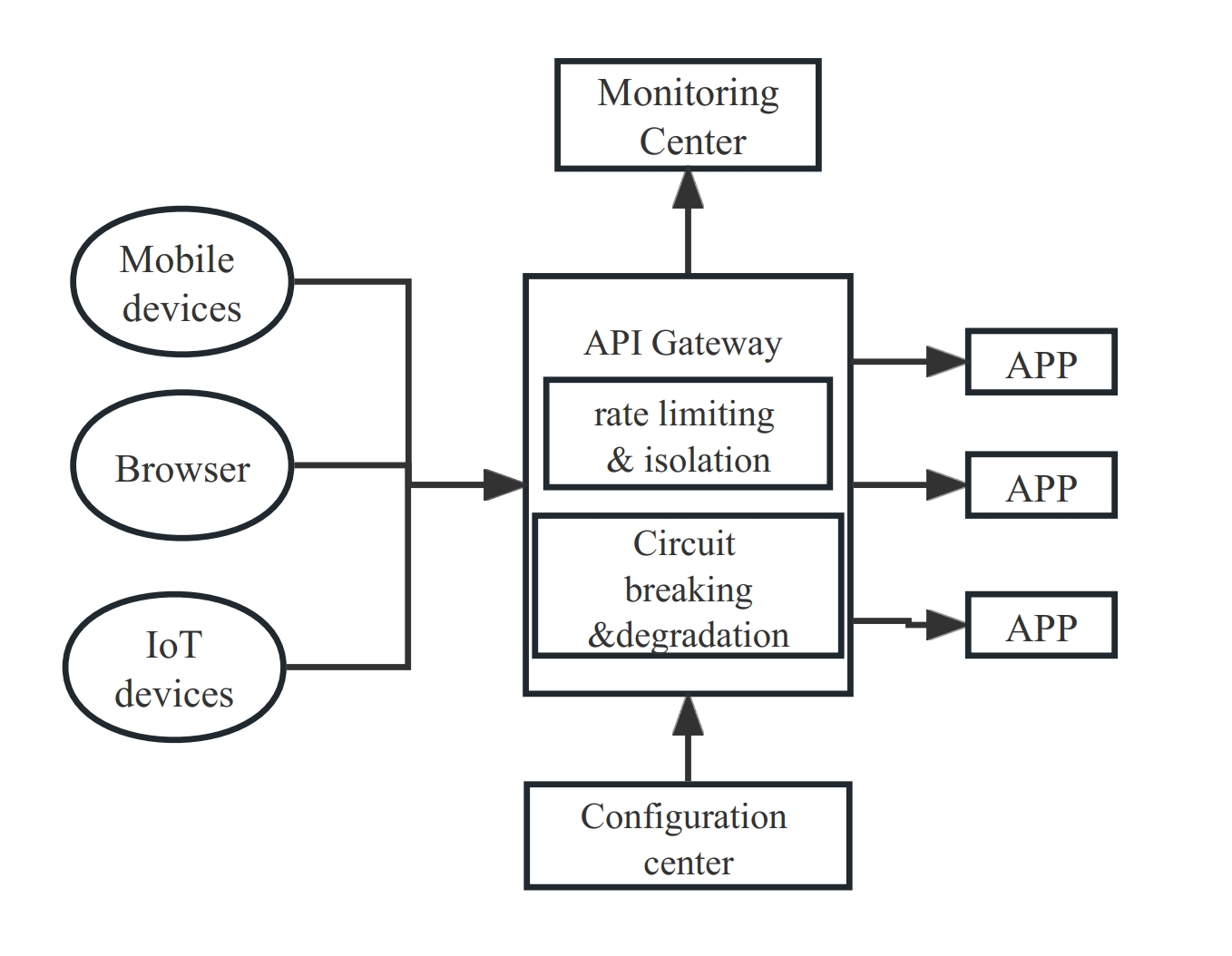
+**Rate limiting, isolation, and circuit breaking**:
+
+As the scale of internet businesses continues to increase, so does the
concurrency of systems. Multiple services are often called by each other, and a
core link may call up to ten services. If the RT (response time) of a certain
service rises sharply and upstream services continue to request, a vicious
cycle will occur. The more upstream waiting for results, the more upstream
services will be blocked, and the entire process will eventually become
unusable, leading to a service avalanche.
+
+Therefore, it is necessary to regulate and manage the incoming traffic. The
following diagram shows how microservice systems combine API gateways to
perform rate limiting, isolation, and circuit breaking.
+
+
+
+### Selection of Mainstream Gateways
+
+Many open-source gateway implementations are available in microservices,
including NGINX, Kong, Apache APISIX, and Envoy. For the Java technology stack,
there are options such as Netflix Zuul, Spring Cloud Gateway, Soul, etc. But
you may wonder, "[Why would you choose Apache APISIX instead of NGINX and
Kong](https://api7.ai/blog/why-choose-apisix-instead-of-nginx-or-kong)?"
+
+Here's a brief comparison.
+
+| Gateway | Painpoints
| Advantages
|
+|---|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
+| [NGINX](https://www.nginx.com/) | 1. Reloading is required for changes to
take effect in the configuration, which can't keep pace with the progress of
cloud-native technologies.
| 1. old-style applications;<br/>
2. Stable, reliable, and time-tested; <br/> 3. High Performance
|
+| [Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/) | 1. The documentation is not
rich or clear enough and needs improvement.
| 1.
Apache Foundation Top-Level Project;<br/> 2. The technical architecture is more
in line with cloud-native principles;<br/> 3. Excellent performance;<br/> 4.
Rich ecosystem;<br/> 5. In addition to supporting Lua development plugins, it
also supports languag [...]
+| [Kong](https://konghq.com/) | 1. The default use of PostgreSQL or Cassandra
databases makes the entire architecture very bloated and can bring about high
availability issues;<br/> 2. The routing uses a traversal search algorithm,
which can lead to a significant decrease in performance when there are more
than thousands of routes in the gateway;<br/> 3. Some important features
require payment; | 1. The pioneer of open-source API gateways with a large user
base;<br/> 2. Performance meets [...]
+| [Envoy](https://envoy.com/) | 1. It is developed in C++, which makes it
difficult for secondary development;<br/> 2. In addition to developing filters
with C++, it also supports WASM and Lua.
| 1. The CNCF graduated project is more suitable for
service mesh scenarios and supports the deployment of multi-language
architectures;
|
+| [Spring Cloud
Gateway](https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-gateway/reference/html/) |
1. Although the Spring community is mature, there is a lack of resources for
Gateway.
| 1. The gateway provides a wealth of out-of-the-box
features, which can be used through SpringBoot configuration or hand-coded
calls; <br/> 2. Spring framework is highly extensible with strong scalability,
easy [...]
+
+## Summary
+
+As the internet world continues to develop, enterprises rapidly evolve,
leading to constant changes in system architecture. The microservices
architecture has been widely adopted by many companies.
+
+As the data and API quantity of microservices increases, it is crucial to
choose an excellent API gateway for high-traffic governance.
+
+This article compares common API gateways, highlighting their respective
advantages and disadvantages. Suppose you are in the process of selecting an
API gateway technology, encountering performance issues in your microservice
system, or looking to build an efficient and stable microservice system. In
that case, this article aims to provide you with some helpful insights.
diff --git a/blog/en/blog/2023/06/12/how-is-apisix-fast.md
b/blog/en/blog/2023/06/12/how-is-apisix-fast.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..ff5aced2709
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2023/06/12/how-is-apisix-fast.md
@@ -0,0 +1,195 @@
+---
+title: How Is Apache APISIX Fast?
+authors:
+ - name: API7.ai
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/api7
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/61078451?s=200&v=4
+keywords:
+ - Apache APISIX
+ - performance
+ - API gateway
+ - radix tree
+description: Taking a look under Apache APISIX's hood to understand how it
achieves ultimate performance.
+tags: [Ecosystem]
+image:
https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/06/08/3LuvBVWL_apisix-fast-cover.png
+---
+
+>In this article, we will look under the hood of APISIX and see what these are
and how all of these work together to keep APISIX maintaining peak performance
while handling significant traffic.
+<!--truncate-->
+
+"High speed," "minimum latency," and "ultimate performance" are often used to
characterize [Apache APISIX](https://api7.ai/apisix). Even when someone asks me
about APISIX, my answer always includes "high-performance cloud native API
gateway."
+
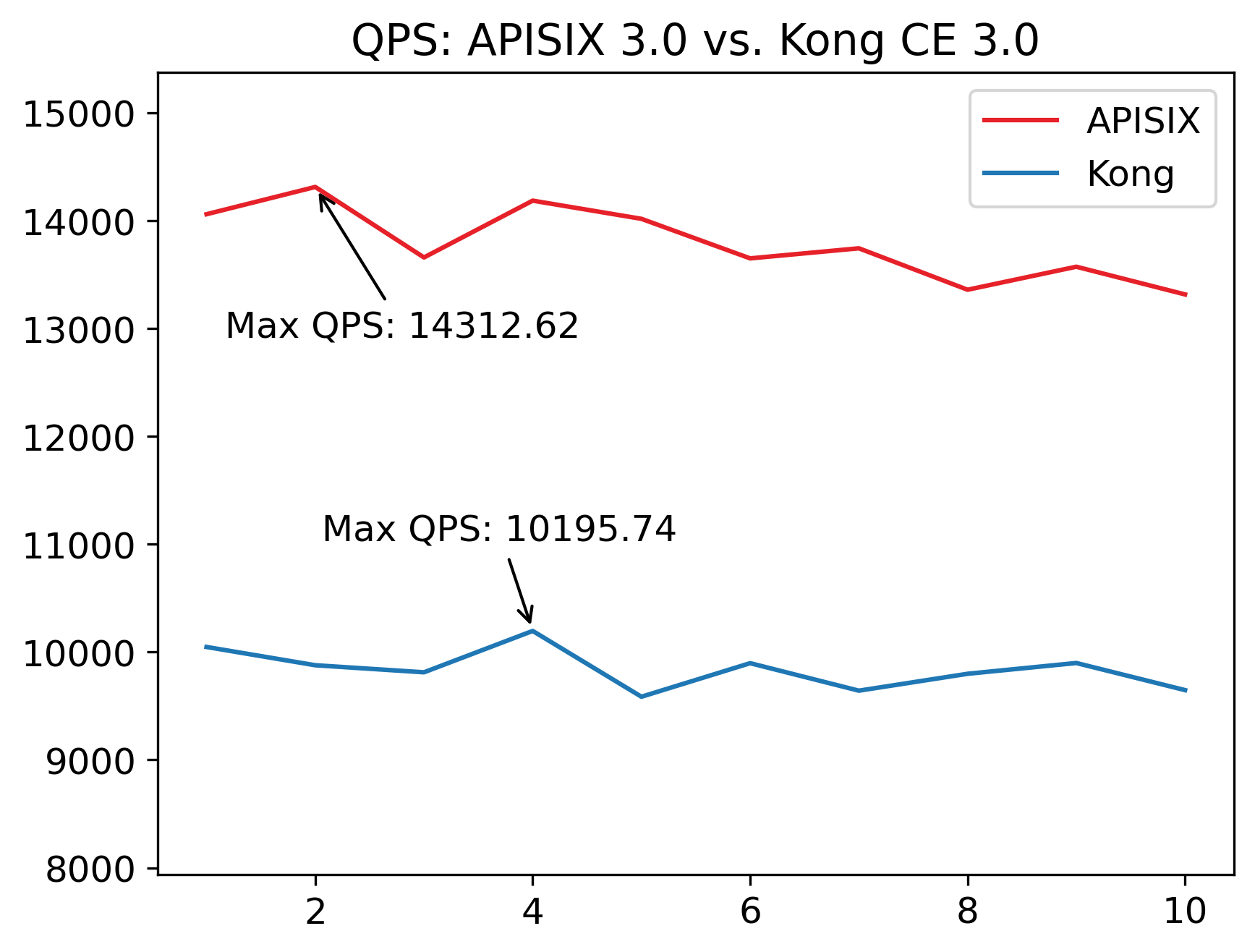
+Performance benchmarks (vs.
[Kong](https://api7.ai/blog/apisix-kong-3-0-performance-comparison),
[Envoy](https://apisix.apache.org/blog/2021/06/10/apache-apisix-and-envoy-performance-comparison/))
confirm these characteristics are indeed accurate ([test
yourself](https://github.com/api7/apisix-benchmark)).
+
+
+
+_[Tests run](https://github.com/api7/apisix-benchmark) for 10 rounds with 5000
unique routes on Standard D8s v3 (8 vCPUs, 32 GiB memory)._
+
+But how does APISIX achieve this?
+
+To answer that question, we must look at three things: etcd, hash tables, and
radix trees.
+
+In this article, we will look under the hood of APISIX and see what these are
and how all of these work together to keep APISIX maintaining peak performance
while handling significant traffic.
+
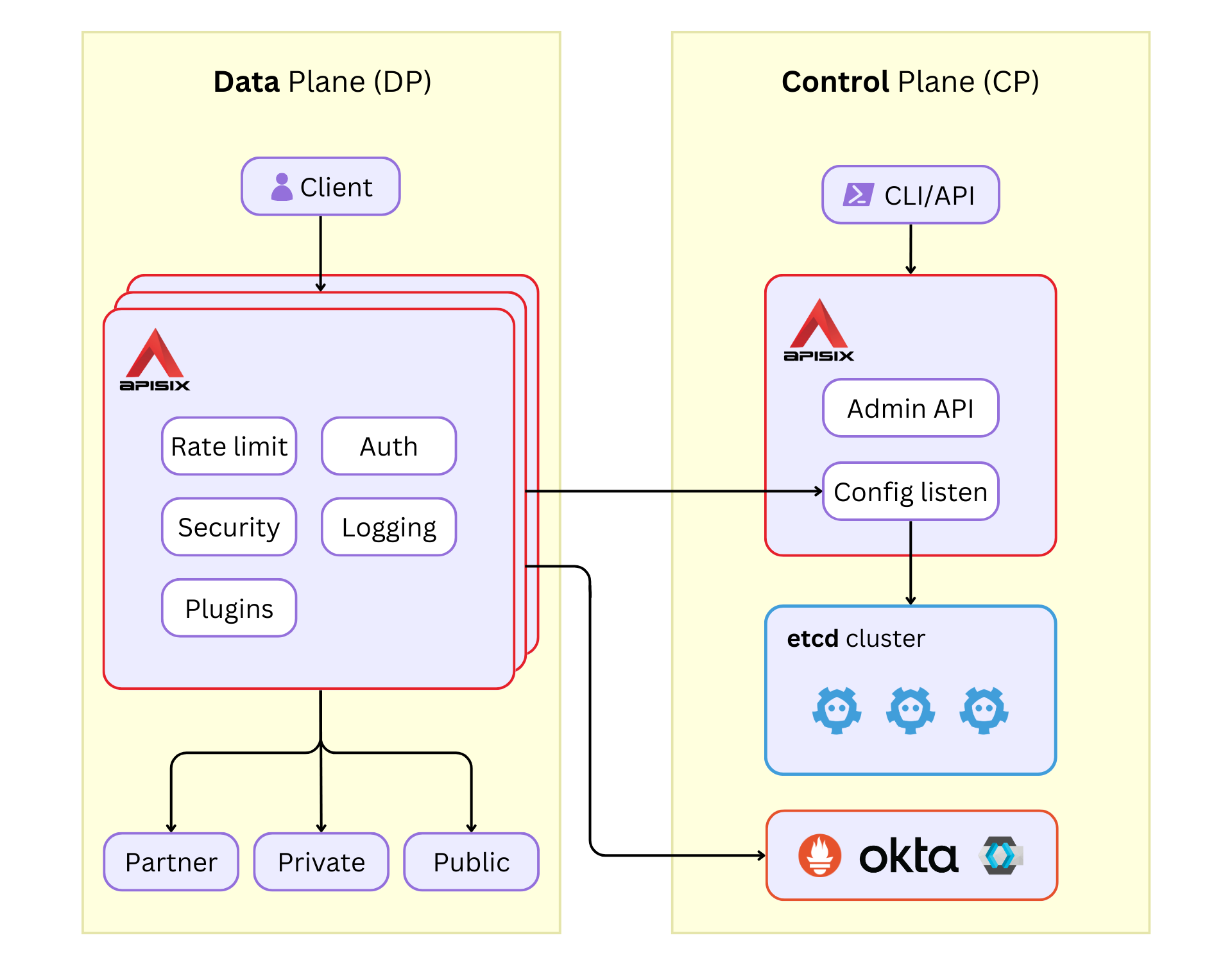
+## etcd as the Configuration Center
+
+APISIX uses [etcd](https://etcd.io/) to store and synchronize configurations.
+
+etcd is designed to work as a key-value store for configurations of
large-scale distributed systems. APISIX is intended to be distributed and
highly scalable from the ground up, and using etcd over traditional databases
facilitates that.
+
+
+
+Another key indispensable feature for API gateways is to be highly available,
avoiding downtime and data loss. You can efficiently achieve this by deploying
multiple instances of etcd to ensure a fault-tolerant, cloud native
architecture.
+
+APISIX can read/write configurations from/to etcd with minimum latency.
Changes to the configuration files are notified instantly, allowing APISIX to
monitor only the etcd updates instead of polling a database frequently, which
can add performance overhead.
+
+This [chart](https://etcd.io/docs/v3.5/learning/why/#comparison-chart)
summarizes how etcd compares with other databases.
+
+## Hash Tables for IP Addresses
+
+IP address-based allowlists/denylists are a common use case for API gateways.
+
+To achieve high performance, APISIX stores the list of IP addresses in a hash
table and uses it for matching (O(1)) than iterating through the list (O(N)).
+
+As the number of IP addresses in the list increases, the performance impact of
using hash tables for storage and matching becomes apparent.
+
+Under the hood, APISIX uses the
[lua-resty-ipmatcher](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-ipmatcher) library to
implement this functionality. The example below shows how the library is used:
+
+```lua
+local ipmatcher = require("resty.ipmatcher")
+local ip = ipmatcher.new({
+ "162.168.46.72",
+ "17.172.224.47",
+ "216.58.32.170",
+})
+
+ngx.say(ip:match("17.172.224.47")) -- true
+ngx.say(ip:match("176.24.76.126")) -- false
+```
+
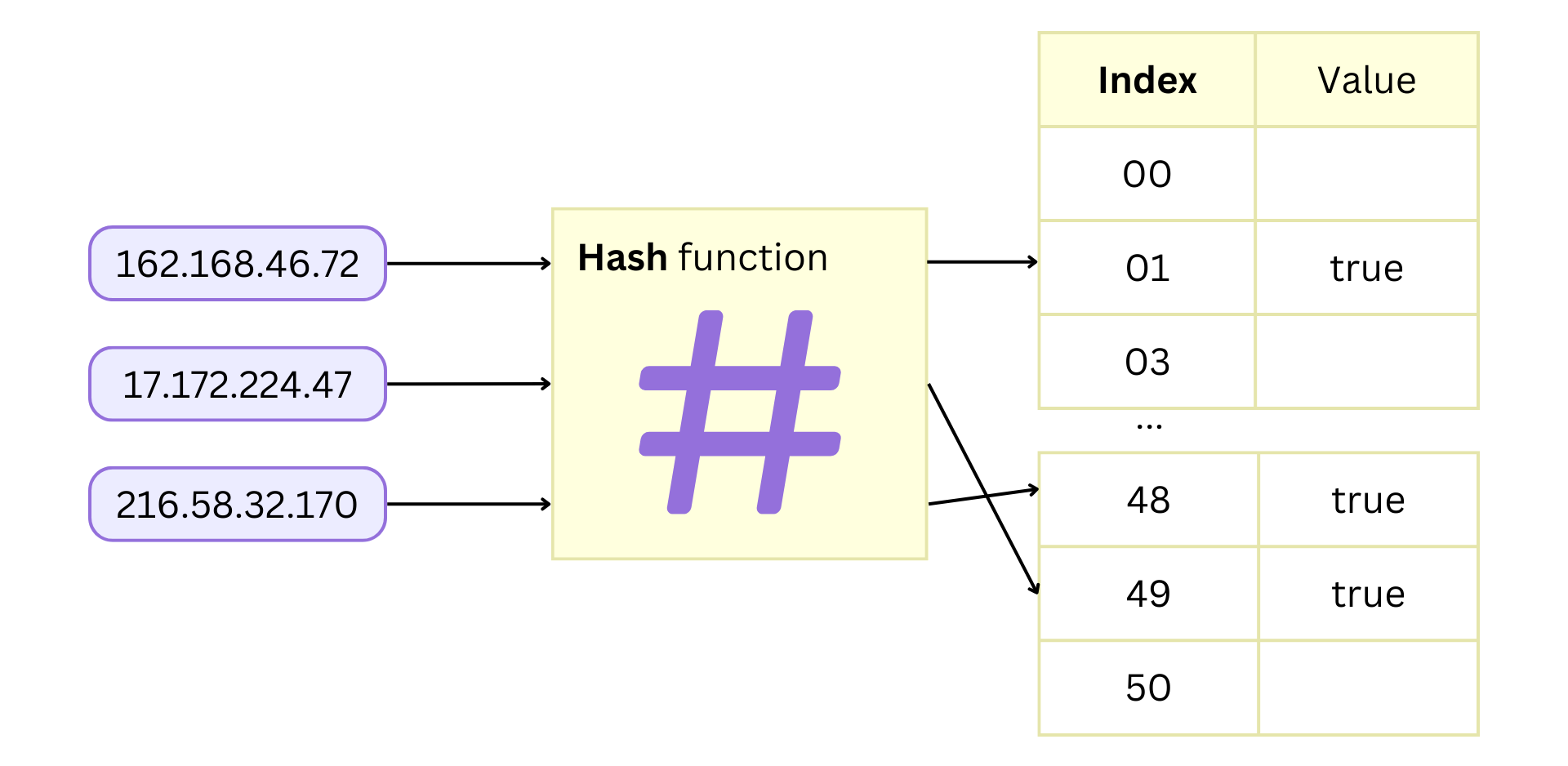
+The library uses Lua tables which are hash tables. The IP addresses are hashed
and stored as indices in a table, and to search for a given IP address, you
just have to index the table and test whether it is nil or not.
+
+
+
+_To search for an IP address, it first computes the hash (index) and checks
its value. If it is non-empty, we have a match. This is done in constant time
O(1)._
+
+## Radix Trees for Routing
+
+Please forgive me for tricking you into a data structures lesson! But hear me
out; this is where it gets interesting.
+
+A key area where APISIX optimizes performance is route matching.
+
+APISIX matches a route with a request from its URI, HTTP methods, host, and
other information (see
[router](https://github.com/apache/apisix/blob/98e56716fdf76b97c90531cac24de811d841c296/conf/config-default.yaml#L77)).
And this needs to be efficient.
+
+If you have read the previous section, an obvious answer would be to use a
hash algorithm. But route matching is tricky because multiple requests can
match the same route.
+
+For example, if we have a route `/api/*`, then both `/api/create` and
`/api/destroy` must match the route. But this is not possible with a hash
algorithm.
+
+Regular expressions can be an alternate solution. Routes can be configured in
a regex, and it can match multiple requests without the need to hardcode each
request.
+
+If we take our previous example, we can use the regex `/api/[A-Za-z0-9]+` to
match both `/api/create` and `/api/destroy`. More complex regexes could match
more complex routes.
+
+But regex is slow! And we know APISIX is fast. So instead, APISIX uses radix
trees which are compressed prefix trees (trie) that work really well for fast
lookups.
+
+Let's look at a simple example. Suppose we have the following words:
+
+- romane
+- romanus
+- romulus
+- rubens
+- ruber
+- rubicon
+- rubicundus
+
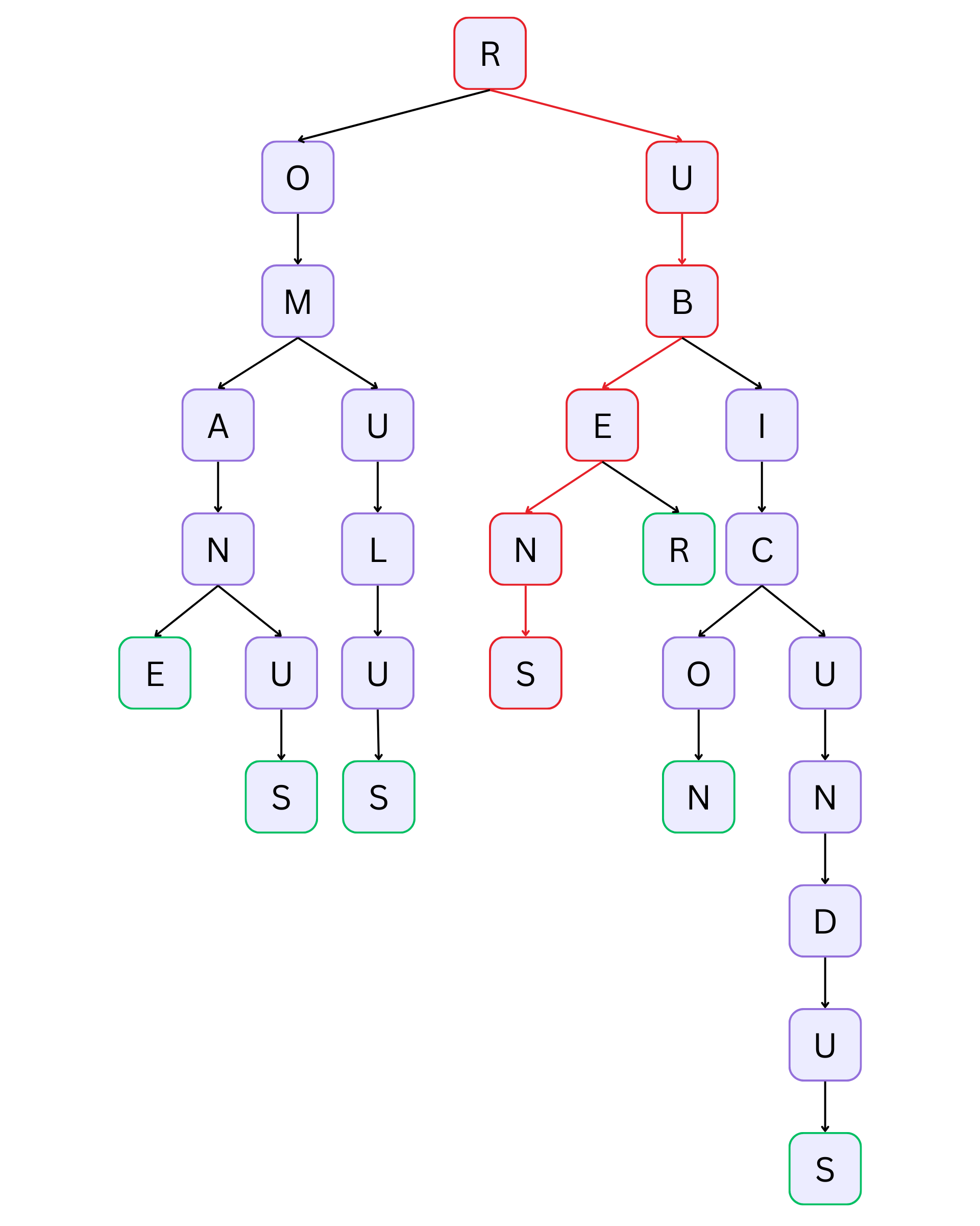
+A prefix tree would store it like this:
+
+
+
+_The highlighted traversal shows the word "rubens."_
+
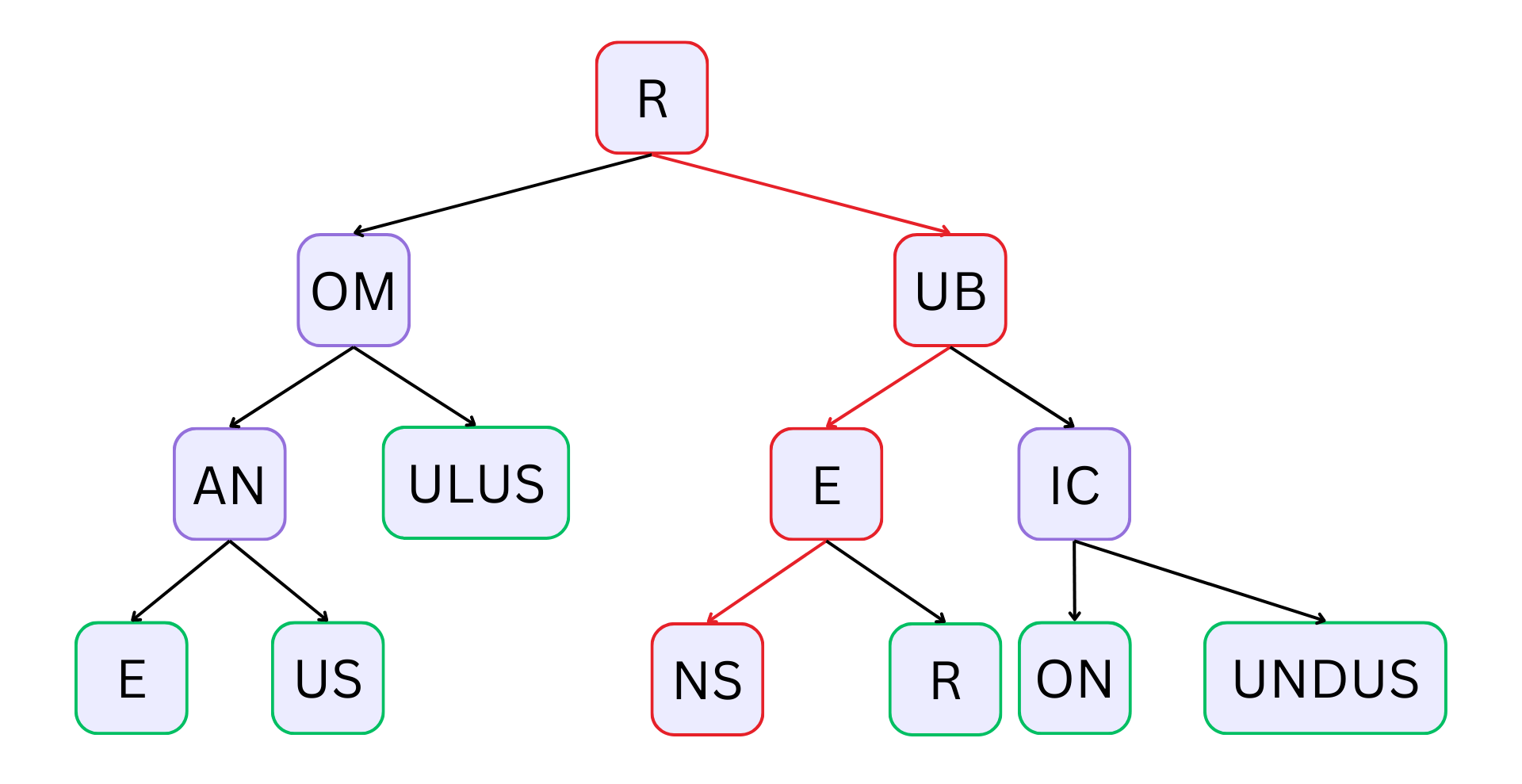
+A radix tree optimizes a prefix tree by merging child nodes if a node only has
one child node. Our example trie would look like this as a radix tree:
+
+
+
+_The highlighted traversal still shows the word "rubens." But the tree looks
much smaller!_
+
+When you [create routes in
APISIX](https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/configure-routes), APISIX
stores them in these trees.
+
+APISIX can then work flawlessly because the time it takes to match a route
only depends on the length of the URI in the request and is independent of the
number of routes (O(K), K is the length of the key/URI).
+
+So APISIX will be as quick as it is when matching 10 routes when you first
start out and 5000 routes when you scale.
+
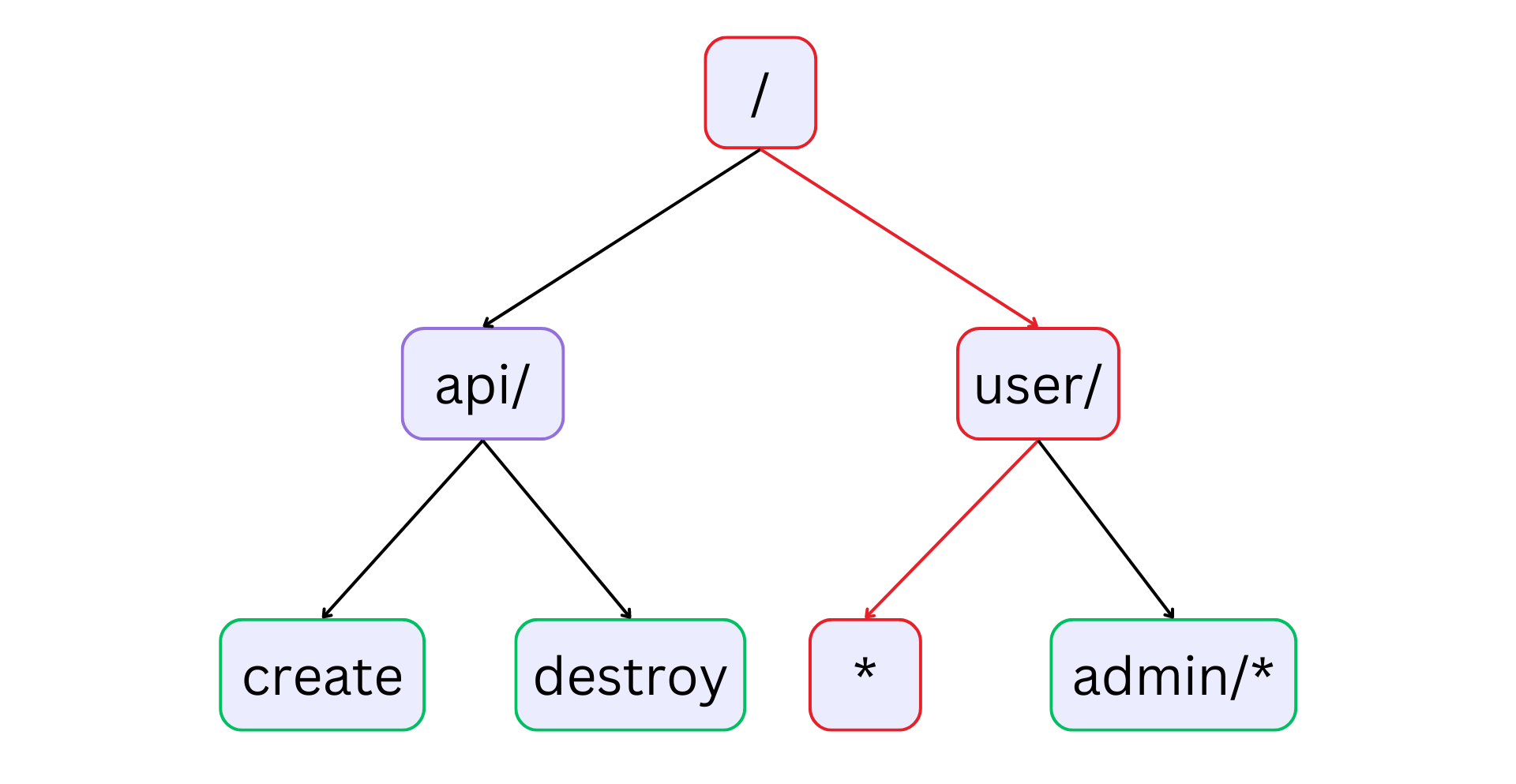
+This crude example shows how APISIX can store and match routes using radix
trees:
+
+
+
+_The highlighted traversal shows the route `/user/*` where the `*` represents
a prefix. So a URI like `/user/navendu` will match this route. The example code
below should give more clarity to these ideas._
+
+APISIX uses the
[lua-resty-radixtree](https://github.com/api7/lua-resty-radixtree) library,
which wraps around [rax](https://github.com/antirez/rax), a radix tree
implementation in C. This improves the performance compared to implementing the
library in pure Lua.
+
+The example below shows how the library is used:
+
+```lua
+local radix = require("resty.radixtree")
+local rx = radix.new({
+ {
+ paths = { "/api/*action" },
+ metadata = { "metadata /api/action" }
+ },
+ {
+ paths = { "/user/:name" },
+ metadata = { "metadata /user/name" },
+ methods = { "GET" },
+ },
+ {
+ paths = { "/admin/:name" },
+ metadata = { "metadata /admin/name" },
+ methods = { "GET", "POST", "PUT" },
+ filter_fun = function(vars, opts)
+ return vars["arg_access"] == "admin"
+ end
+ }
+})
+
+local opts = {
+ matched = {}
+}
+
+-- matches the first route
+ngx.say(rx:match("/api/create", opts)) -- metadata /api/action
+ngx.say("action: ", opts.matched.action) -- action: create
+
+ngx.say(rx:match("/api/destroy", opts)) -- metadata /api/action
+ngx.say("action: ", opts.matched.action) -- action: destroy
+
+local opts = {
+ method = "GET",
+ matched = {}
+}
+
+-- matches the second route
+ngx.say(rx:match("/user/bobur", opts)) -- metadata /user/name
+ngx.say("name: ", opts.matched.name) -- name: bobur
+
+local opts = {
+ method = "POST",
+ var = ngx.var,
+ matched = {}
+}
+
+-- matches the third route
+-- the value for `arg_access` is obtained from `ngx.var`
+ngx.say(rx:match("/admin/nicolas", opts)) -- metadata /admin/name
+ngx.say("admin name: ", opts.matched.name) -- admin name: nicolas
+```
+
+The ability to manage a large number of routes efficiently has made APISIX the
API gateway of choice for [many large-scale
projects](https://api7.ai/category/usercase).
+
+## Look under the Hood
+
+There is only so much I can explain about the inner workings of APISIX in one
article.
+
+But the best part is that the libraries mentioned here and Apache APISIX are
[entirely open source](https://github.com/apache/apisix/), meaning you can look
under the hood and modify things yourself.
+
+And if you can improve APISIX to get that final bit of performance, you can
[contribute the
changes](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/general/contributor-guide/) back to the
project and let everyone benefit from your work.
diff --git a/blog/en/blog/2023/07/09/apisix-integrates-with-vault.md
b/blog/en/blog/2023/07/09/apisix-integrates-with-vault.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..78cd811c7fc
--- /dev/null
+++ b/blog/en/blog/2023/07/09/apisix-integrates-with-vault.md
@@ -0,0 +1,246 @@
+---
+title: How to Use Vault to Manage Certificates in APISIX
+authors:
+ - name: API7.ai
+ title: Author
+ url: https://github.com/api7
+ image_url: https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/61078451?s=200&v=4
+keywords:
+ - Apache APISIX
+ - HashiCorp Vault
+ - Certificate management
+description: APISIX can integrate Vault to realize SSL certificate management,
allowing for secure storage and management of SSL certificates.
+tags: [Ecosystem]
+image:
https://static.apiseven.com/uploads/2023/06/07/isIAWmKT_How%20to%20Use%20Vault%20to%20Manage%20Certificates%20in%20APISIX.png
+---
+
+>This article takes configuring HTTPS communication between the downstream
client and APISIX as an example to introduce how APISIX integrates Vault to
implement SSL certificate management.
+<!--truncate-->
+
+API gateway is a key basic component in API lifecycle management. It is the
entrance of all traffic and is responsible for routing API requests from
downstream clients to the correct upstream service for processing. Therefore,
the API gateway works for the network communication between the upstream
services and the downstream clients.
+
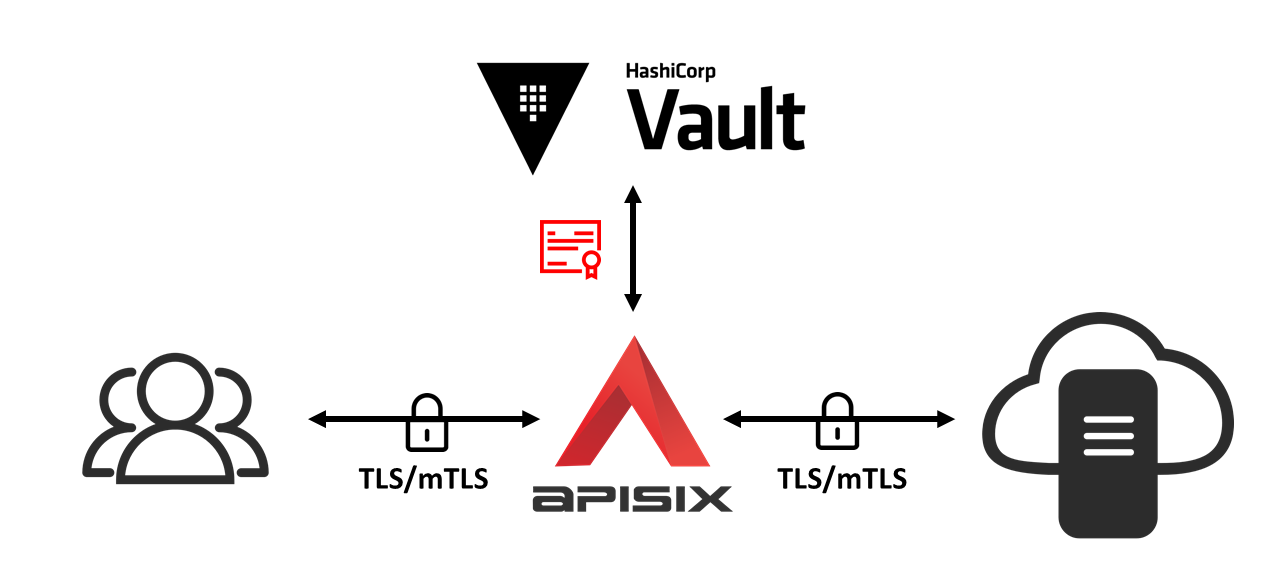
+As a new cloud-native API gateway, Apache APISIX provides the TLS/mTLS
communication mechanism between the downstream clients and APISIX, and that
between APISIX and upstream services, so as to ensure the network security
between them. APISIX saves the SSL certificate as an SSL certificate object,
and realizes the dynamic loading of the SSL certificate through the extension
SNI (Server Name Indication) that supports the TLS protocol.
+
+In order to securely store the SSL certificates in APISIX, APISIX has achieved
integration with HashiCorp Vault, thus realizing the unified management of SSL
certificates by taking advantage of Vault's secret security storage. This
article takes configuring HTTPS communication between the downstream client and
APISIX as an example to introduce how APISIX integrates Vault to implement SSL
certificate management.
+
+
+
+## What Is SSL Certificate
+
+SSL/TLS is a cryptographic protocol that protects the security of network
communication by establishing an encrypted network connection between the two
communicating parties. The SSL/TLS protocol ensures that data is sent to the
correct client and server by authenticating users and servers. In addition, the
SSL/TLS protocol can encrypt communication data, thereby ensuring that data
cannot be stolen, tampered with or forged during transmission.
+
+An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website's
identity and enables an encrypted connection using the SSL/TLS protocol. An SSL
certificate is usually issued by a trusted digital certificate authority (CA),
which mainly includes the following information:
+
+* Domain name
+* Certificate authority
+* Digital signature signed by the certificate authority
+* Associated subdomains
+* Issue date of certificates
+* Expiration date of certificates
+* The public key (while the private key is a secret key)
+
+## What Is HashiCorp Vault
+
+HashiCorp Vault (hereinafter referred to as Vault) is an enterprise-level
Secret management tool that can store and manage sensitive data such as tokens,
passwords, and certificates. Vault can be integrated with technologies in the
entire IT system, provide identity-based security automation and encryption
services, centrally control access to sensitive data and systems, and help
organizations reduce the risk of data leakage and data exposure, thereby
improving cloud and application security.
+
+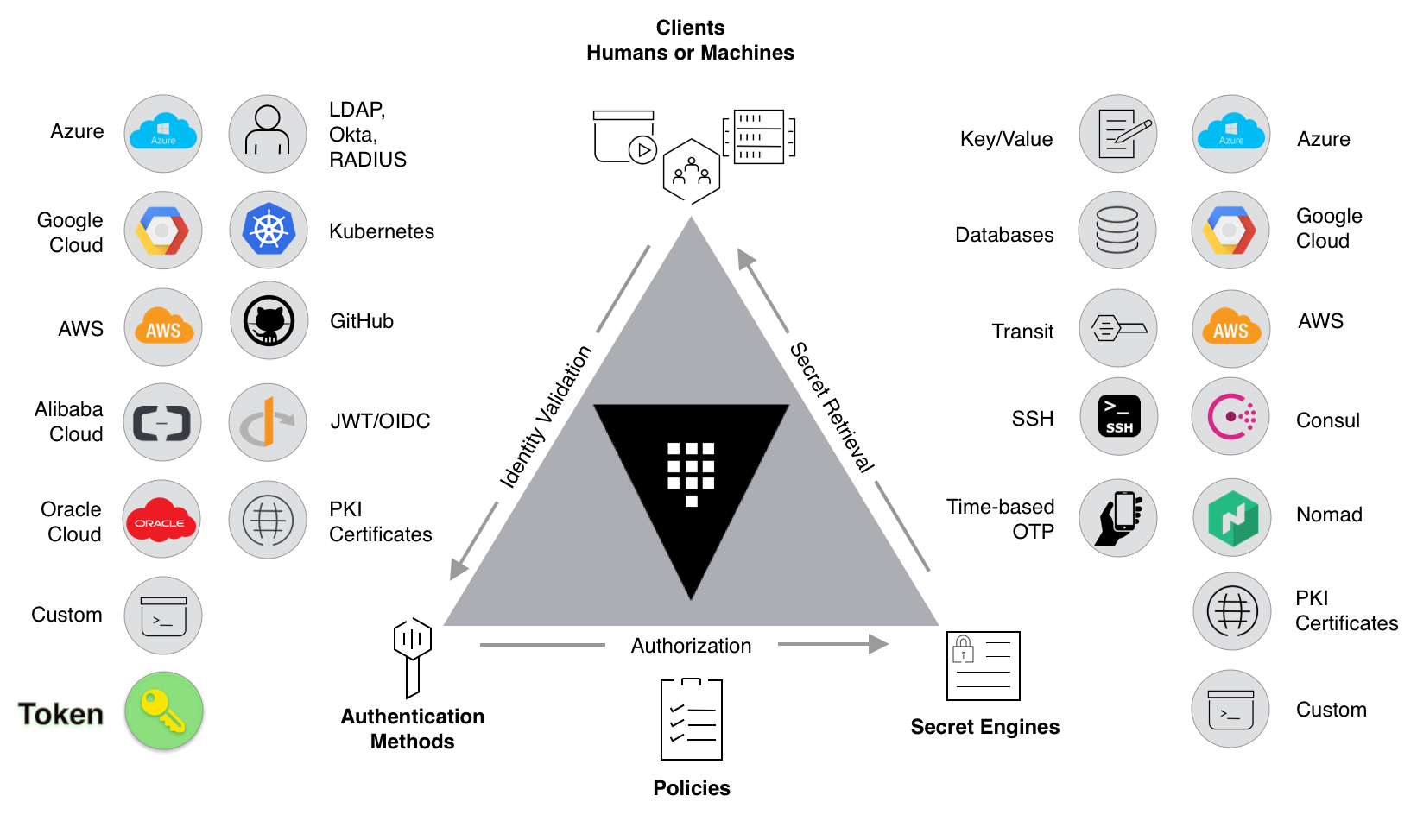
+
+## How to Store APISIX SSL Certificates in Vault
+
+### Environment Preparation
+
+* Install [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/)
+* Install [cURL](https://curl.se/)
+* A running APISIX service, or follow [Getting Started
tutorial](https://docs.api7.ai/apisix/getting-started/) to deploy an APISIX
Docker container
+
+### Deploy and Configure Vault Service
+
+In this section, we will use Docker to deploy a Vault container service. You
can skip this section if you already have a Vault service instance available in
your environment.
+
+Create and deploy a Vault container in Dev mode, named
`apisix-quickstart-vault`. Specify the Vault Token as
`apisix-quickstart-vault-token` and map port `8200` to the host:
+
+```shell
+docker run -d --cap-add=IPC_LOCK \
+ -e 'VAULT_DEV_LISTEN_ADDRESS=0.0.0.0:8200' \
+ -e 'VAULT_ADDR=http://0.0.0.0:8200' \
+ -e 'VAULT_DEV_ROOT_TOKEN_ID=apisix-quickstart-vault-token' \
+ -e 'VAULT_TOKEN=apisix-quickstart-vault-token' \
+ --network=apisix-quickstart-net \
+ --name apisix-quickstart-vault \
+ -p 8200:8200 vault:1.13.0
+```
+
+Select `kv` as the APISIX SSL certificate storage path:
+
+```shell
+docker exec apisix-quickstart-vault vault secrets enable -path=kv -version=1 kv
+```
+
+### Configure APISIX
+
+APISIX needs to read SSL certificates from Vault, so Vault should grant read
permission to APISIX on the specified path.
+
+Create a Vault policy named `apisix-policy.hcl`, granting APISIX read access
to the path `kv/apisix/`:
+
+```shell
+docker exec apisix-quickstart-vault /bin/sh -c "echo '
+path \"kv/apisix/*\" {
+ capabilities = [\"read\"]
+}
+' > /etc/apisix-policy.hcl"
+```
+
+Apply the created policy file `apisix-policy.hcl` to Vault:
+
+```shell
+docker exec apisix-quickstart-vault vault policy write apisix-policy
/etc/apisix-policy.hcl
+```
+
+Create an APISIX secret object with the id `quickstart-secret-id` to save the
Vault connection information and certificate storage path:
+
+```shell
+curl -i
"http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/secrets/vault/quickstart-secret-id"; -X PUT
-d '
+{
+ "uri": "http://apisix-quickstart-vault:8200";,
+ "prefix": "kv/apisix",
+ "token" : "apisix-quickstart-vault-token"
+}'
+```
+
+### Store SSL Certificates in Vault
+
+Create a self-signed CA certificate `ca.crt` and key `ca.key`:
+
+```shell
+openssl genrsa -out ca.key 2048 && \
+ openssl req -new -sha256 -key ca.key -out ca.csr -subj "/CN=ROOTCA" && \
+ openssl x509 -req -days 36500 -sha256 -extensions v3_ca -signkey ca.key -in
ca.csr -out ca.crt
+```
+
+The SSL certificate `server.crt` and the key `server.key` are issued by the
CA, and its common name (CN) is `test.com`:
+
+```shell
+openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048 && \
+ openssl req -new -sha256 -key server.key -out server.csr -subj
"/CN=test.com" && \
+ openssl x509 -req -days 36500 -sha256 -extensions v3_req \
+ -CA ca.crt -CAkey ca.key -CAserial ca.srl -CAcreateserial \
+ -in server.csr -out server.crt
+```
+
+Copy the issued SSL certificate and key to the Vault container:
+
+```shell
+docker cp server.key apisix-quickstart-vault:/root/
+docker cp server.crt apisix-quickstart-vault:/root/
+```
+
+Use the `vault kv put` command to store the SSL certificate and key as a
secret, the key is `ssl`, and the storage path is `kv/apisix`:
+
+```shell
+docker exec apisix-quickstart-vault vault kv put kv/apisix/ssl
test.com.crt=@/root/server.crt test.com.key=@/root/server.key
+```
+
+Through the above command, we have stored a secret named `ssl` in Vault, which
contains 2 key-value pairs: certificate and private key.
+
+## How to Use APISIX SSL Certificate Stored in Vault
+
+APISIX supports TLS/mTLS network encryption between downstream clients and
APISIX, and between APISIX and upstream services, where the SSL certificates
stored in Vault can be used. We will take configuring HTTPS communication
between the client and APISIX as an example to demonstrate how to use the SSL
certificate stored in Vault in APISIX.
+
+### Configure HTTPS Communication Between Client and APISIX
+
+Create an SSL certificate object to hold the SSL certificate:
+
+```shell
+curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/ssls"; -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "id": "quickstart-tls-client-ssl",
+ "sni": "test.com",
+ "cert": "$secret://vault/quickstart-secret-id/ssl/test.com.crt",
+ "key": "$secret://vault/quickstart-secret-id/ssl/test.com.key"
+}'
+```
+
+The `sni` of this object is `test.com`, which is consistent with the CN that
issued the certificate. The `cert` and `key` correspond to the issued
certificate and private key, which are automatically obtained from the Vault
through the established secret resource locator, and the resource locator rules
are:
+
+```text
+$secret://$manager/$id/$secret_name/$key
+```
+
+* manager: key management service Vault
+* id: APISIX secret resource ID
+* secret_name: the secret name in Vault
+* key: the key of the key-value pair in the secret named secret_name
+
+### Verify HTTPS Communication Between Client and APISIX
+
+Create a route to forward all requests sent to `/ip` to upstream `httpbin.org`:
+
+```shell
+curl -i "http://127.0.0.1:9180/apisix/admin/routes"; -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "id": "quickstart-client-ip",
+ "uri": "/ip",
+ "upstream": {
+ "nodes": {
+ "httpbin.org:80":1
+ },
+ "type": "roundrobin"
+ }
+}'
+```
+
+Use cURL to send a request to `https://test.com:9443/ip`, `test.com` resolves
to `127.0.0.1`:
+
+```shell
+curl -ikv --resolve "test.com:9443:127.0.0.1" "https://test.com:9443/ip";
+```
+
+If the configuration is successful, the client and APISIX TLS handshake
process returned by cURL will be the same as the following results:
+
+```text
+* Added test.com:9443:127.0.0.1 to DNS cache
+* Hostname test.com was found in DNS cache
+* Trying 127.0.0.1:9443...
+* Connected to test.com (127.0.0.1) port 9443 (#0)
+* ALPN, offering h2
+* ALPN, offering http/1.1
+* successfully set certificate verify locations:
+* CAfile: /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt
+* CApath: /etc/ssl/certs
+* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Encrypted Extensions (8):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
+* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Change cipher spec (1):
+* TLSv1.3 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
+* SSL connection using TLSv1.3 / TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
+* ALPN, server accepted to use h2
+* Server certificate:
+* subject: CN=test.com
+* start date: Apr 21 07:47:54 2023 GMT
+* expire date: Mar 28 07:47:54 2123 GMT
+* issuer: CN=ROOTCA
+* SSL certificate verify result: unable to get local issuer certificate (20),
continuing anyway.
+* Using HTTP2, server supports multi-use
+* Connection state changed (HTTP/2 confirmed)
+* Copying HTTP/2 data in stream buffer to connection buffer after upgrade:
len=0
+* Using Stream ID: 1 (easy handle 0x556274d632e0)
+> GET /ip HTTP/2
+> Host: test.com:9443
+> user-agent: curl/7.74.0
+> accept: */*
+>
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Newsession Ticket (4):
+* TLSv1.3 (IN), TLS handshake, Newsession Ticket (4):
+* old SSL session ID is stale, removing
+* Connection state changed (MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS == 128)!
+< HTTP/2 200
+HTTP/2 200
+...
+```
+
+## Summary
+
+We introduced how APISIX integrates Vault to implement SSL certificate
management and showed the configuration and integration steps in detail taking
HTTPS communication between downstream clients and APISIX as an example.
