yzeng25 commented on a change in pull request #895: URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/895#discussion_r811655624
########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] Review comment: ```suggestion tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. Review comment: Remove extra space ```suggestion Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + +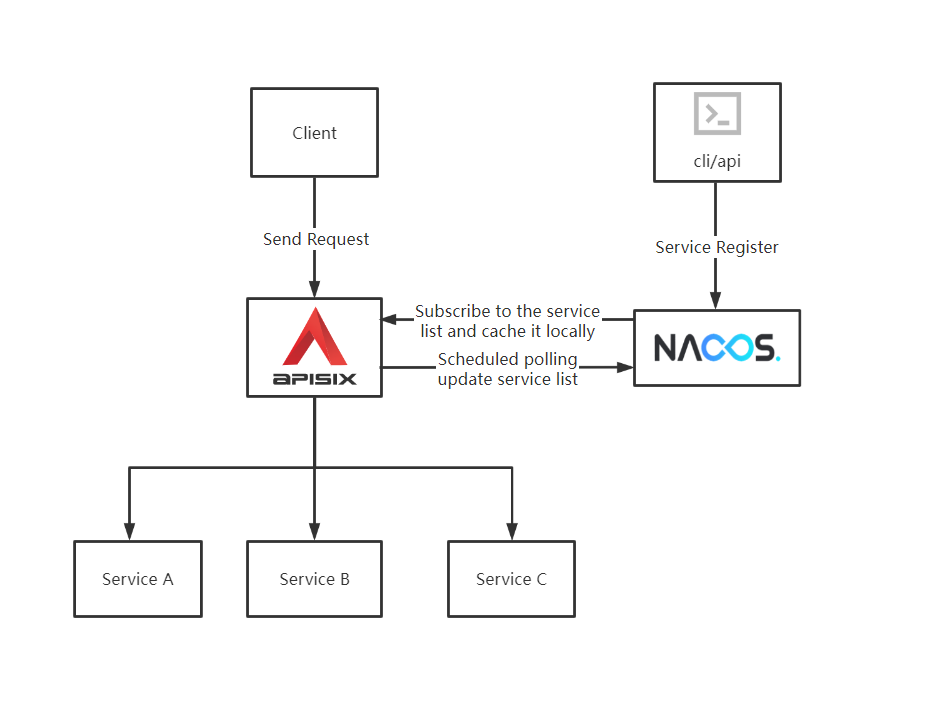 + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` Review comment: This code block belongs to step 1, so you should use `tab` or space to do an indentation. ########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] +--- + +> 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 + +<!--truncate--> + +## 背景信息 + +Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台。它提供了一组简单易用的特性集,可以帮助您快速实现动态服务发现,服务配置,服务元数据及流量管理,让您更敏捷和容易地构建,交付和管理微服务平台。Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构(例如微服务范式、云原生范式)的服务基础设施。 + +## 注册中心 + +注册中心是服务要实现服务化管理的核心组件,类似于目录服务的作用,也是微服务架构中最基础的设施之一,主要用来存储服务信息,譬如服务提供者 URL 、路由信息等。注册中心的实现是通过一种映射的方式,将复杂的服务端信息映射为简单易懂的信息提供给客户端。 + +注册中心的核心功能为以下三点: + +- 服务注册:**服务提供方** 向 **注册中心** 进行注册。 +- 服务发现:**服务消费方** 可以通过注册中心寻找到服务提供方的调用路由信息。 +- 健康检测:确保注册到注册中心的服务节点是可以被正常调用的,避免无效节点导致的调用资源浪费等问题。 + +注册中心本质上是为了 **解耦服务提供者和服务消费者**,在微服务体系中,各个业务服务之间会频繁互相调用,并且需要对各个服务的 IP、port 等路由信息进行统一的管理。但是要如何进行管理呢?我们可以通过注册中心的 **服务注册** 功能将已有服务的相关信息提供到统一的注册中心进行管理。 + +通过上述描述,您可以了解到注册中心可以帮助用户通过映射快速找到服务和服务地址。随着业务更新迭代,服务会频繁发生变化,在服务端中注册了新的服务或者服务宕机后,客户端仍然可以通过注册中心的 **服务发现** 功能拉取服务列表,如果注册中心的服务节点发生变更,注册中心会发送请求通知客户端重新拉取。 + +如果服务端的服务突然宕机,并且没有向注册中心反馈,客户端可以通过注册中心的 **健康检查** 功能,进行固定时间间隔的主动上报心跳方式向服务端表明自己的服务状态。如果服务状态异常,则会通知注册中心,注册中心可以及时把已经宕机的服务节点进行剔除,避免资源的浪费。 + +Apache APISIX + Nacos 可以将各个微服务节点中与业务无关的各项控制,集中在 Apache APISIX 中进行统一管理,即**通过 Apache APISIX 实现接口服务的代理和路由转发的能力**。在 Nacos 上注册各个微服务后,Apache APISIX 可以通过 Nacos 的服务发现功能获取服务列表,查找对应的服务地址从而实现动态代理。 + +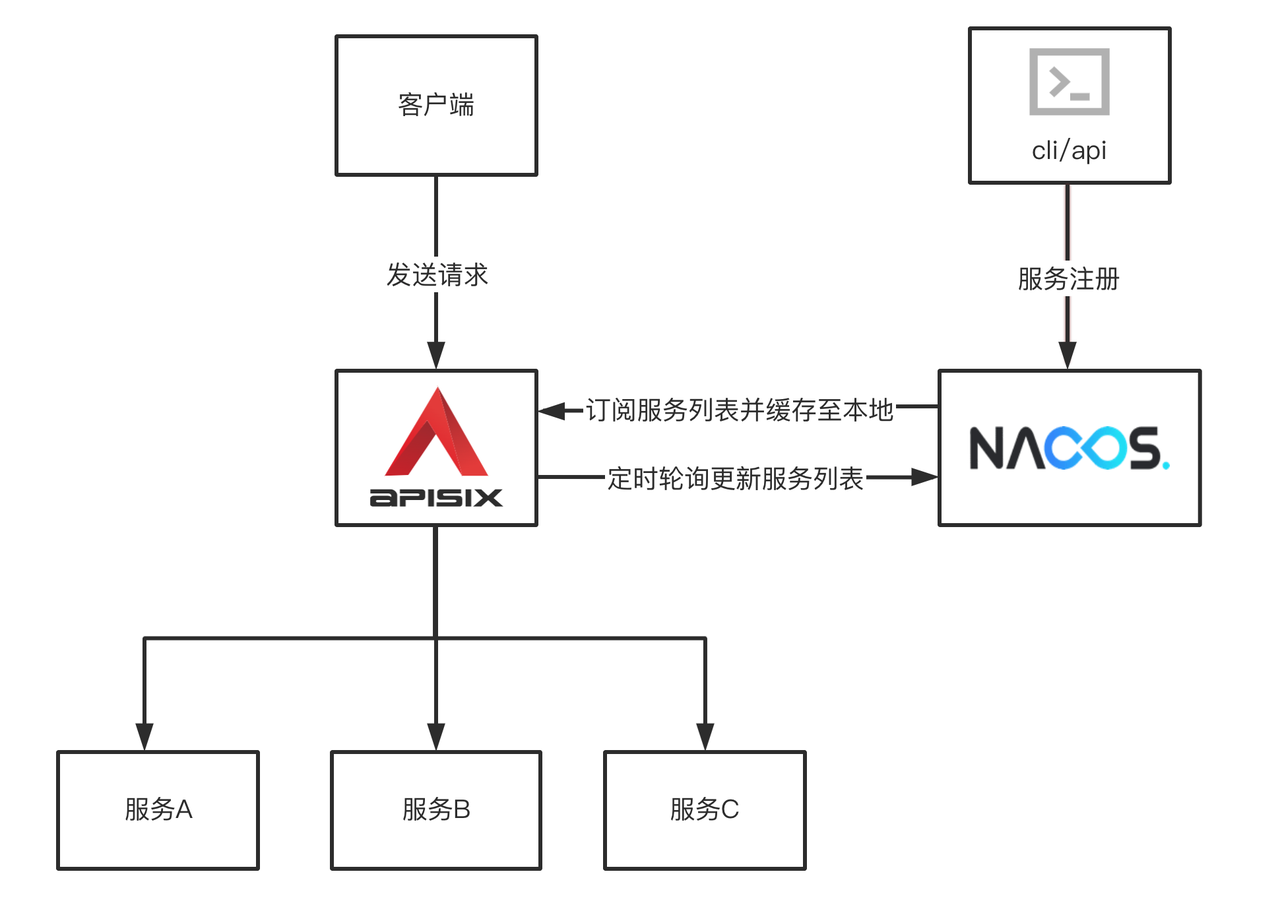 + +## Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现 + +### 前提条件 + +本文操作基于以下环境进行。 + +- 操作系统 Centos 7.9。 +- 已安装 Apache APISIX 12.1.0,详情请参考:[如何构建 Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/how-to-build)。 +- 已安装 Nacos 2.0.4,详情请参考:[Nacos 快速入门](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。 +- 已安装 Node.js,详情请参考:[Node.js 安装指南](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation)。 + +### 步骤一:服务注册 + +1. 使用 Node.js 的 Koa 框架在 `3005` 端口启动一个简单的测试服务作为[上游(Upstream)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/admin-api#upstream)。 + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` Review comment: This code block belongs to step 1, so you should use tab or space to do an indentation. ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` + +### Step 2:Added Nacos Route + +Create a new [route](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/#route) using the Admin API provided by Apache APISIX. APISIX selects the service discovery type to use through the `upstream.discovery_type` field. `upstream.service_name` needs to be associated with the corresponding service name of the registry. Therefore, when creating a route, specify the service discovery type as `nacos`. + +```Shell +curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -i -d ' +{ + "uri": "/nacos/*", + "upstream": { + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS", + "type": "roundrobin", + "discovery_type": "nacos" + } +}' +``` + +In the above command, the request header `X-API-KEY` is the access token of the Admin API, which can be viewed under `apisix.admin_key.key` in the `conf/config.yaml` file. + +After successful addition, examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "action": "set", + "node": { + "key": "\/apisix\/routes\/1", + "value": { + "update_time": 1643191044, + "create_time": 1643176603, + "priority": 0, + "uri": "\/nacos\/*", + "upstream": { + "hash_on": "vars", + "discovery_type": "nacos", + "scheme": "http", + "pass_host": "pass", + "type": "roundrobin", + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS" + }, + "id": "1", + "status": 1 + } + } +} +``` + +In addition, you can also pass other service related parameters in `upstream.discovery_args` to specify the namespace or group where the service is located. For details, please refer to the [official documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos#discovery_args). + +### Step 3: Verify configuration results Review comment: ```suggestion ### Step 3: Verify Configuration Results ``` ########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] +--- + +> 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 + +<!--truncate--> + +## 背景信息 + +Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台。它提供了一组简单易用的特性集,可以帮助您快速实现动态服务发现,服务配置,服务元数据及流量管理,让您更敏捷和容易地构建,交付和管理微服务平台。Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构(例如微服务范式、云原生范式)的服务基础设施。 + +## 注册中心 Review comment: delete these ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information Review comment: ```suggestion ## Background Information ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos Review comment: ```suggestion ## Apache APISIX Integrates Service Discovery Based on Nacos ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos Review comment: ```suggestion ## Apache APISIX Integrates Service Discovery Based on Nacos ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` + +### Step 2:Added Nacos Route + +Create a new [route](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/#route) using the Admin API provided by Apache APISIX. APISIX selects the service discovery type to use through the `upstream.discovery_type` field. `upstream.service_name` needs to be associated with the corresponding service name of the registry. Therefore, when creating a route, specify the service discovery type as `nacos`. + +```Shell +curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -i -d ' +{ + "uri": "/nacos/*", + "upstream": { + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS", + "type": "roundrobin", + "discovery_type": "nacos" + } +}' +``` + +In the above command, the request header `X-API-KEY` is the access token of the Admin API, which can be viewed under `apisix.admin_key.key` in the `conf/config.yaml` file. + +After successful addition, examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "action": "set", + "node": { + "key": "\/apisix\/routes\/1", + "value": { + "update_time": 1643191044, + "create_time": 1643176603, + "priority": 0, + "uri": "\/nacos\/*", + "upstream": { + "hash_on": "vars", + "discovery_type": "nacos", + "scheme": "http", + "pass_host": "pass", + "type": "roundrobin", + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS" + }, + "id": "1", + "status": 1 + } + } +} +``` + +In addition, you can also pass other service related parameters in `upstream.discovery_args` to specify the namespace or group where the service is located. For details, please refer to the [official documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos#discovery_args). + +### Step 3: Verify configuration results + +Use the following command to send the request to the route to be configured. + +```Shell +curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/nacos/ +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```Apache +HTTP/1.1 200 OK +Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 +Content-Length: 11 +Connection: keep-alive +Date: Thu, 27 Jan 2022 00:48:26 GMT +Server: APISIX/2.12.0 + +Hello World +``` + +It can be seen from the example that the new route in Apache APISIX can find the correct service address through Nacos service discovery and respond normally. + +## Summary + +This article introduces the concept of registry and how Apache APISIX cooperates with Nacos to implement routing proxy based on service discovery.Users can use Apache APISIX and Nacos according to their business requirements and past technology architecture to realize the proxy and routing and forwarding capabilities of interface services. Review comment: ```suggestion This article introduces the concept of registry center and how Apache APISIX cooperates with Nacos to implement routing proxy based on service discovery. Users can use Apache APISIX and Nacos according to their business requirements and past technology architecture to realize the proxy and routing and forwarding capabilities of interface services. ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` + +### Step 2:Added Nacos Route Review comment: ```suggestion ### Step 2:Add Nacos Route ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` Review comment: ditto ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` + +### Step 2:Added Nacos Route + +Create a new [route](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/#route) using the Admin API provided by Apache APISIX. APISIX selects the service discovery type to use through the `upstream.discovery_type` field. `upstream.service_name` needs to be associated with the corresponding service name of the registry. Therefore, when creating a route, specify the service discovery type as `nacos`. + +```Shell +curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -i -d ' +{ + "uri": "/nacos/*", + "upstream": { + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS", + "type": "roundrobin", + "discovery_type": "nacos" + } +}' +``` + +In the above command, the request header `X-API-KEY` is the access token of the Admin API, which can be viewed under `apisix.admin_key.key` in the `conf/config.yaml` file. + +After successful addition, examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "action": "set", + "node": { + "key": "\/apisix\/routes\/1", + "value": { + "update_time": 1643191044, + "create_time": 1643176603, + "priority": 0, + "uri": "\/nacos\/*", + "upstream": { + "hash_on": "vars", + "discovery_type": "nacos", + "scheme": "http", + "pass_host": "pass", + "type": "roundrobin", + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS" + }, + "id": "1", + "status": 1 + } + } +} +``` + +In addition, you can also pass other service related parameters in `upstream.discovery_args` to specify the namespace or group where the service is located. For details, please refer to the [official documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos#discovery_args). + +### Step 3: Verify configuration results + +Use the following command to send the request to the route to be configured. + +```Shell +curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/nacos/ +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```Apache +HTTP/1.1 200 OK +Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 +Content-Length: 11 +Connection: keep-alive +Date: Thu, 27 Jan 2022 00:48:26 GMT +Server: APISIX/2.12.0 + +Hello World +``` + +It can be seen from the example that the new route in Apache APISIX can find the correct service address through Nacos service discovery and respond normally. + +## Summary + +This article introduces the concept of registry and how Apache APISIX cooperates with Nacos to implement routing proxy based on service discovery.Users can use Apache APISIX and Nacos according to their business requirements and past technology architecture to realize the proxy and routing and forwarding capabilities of interface services. + +To get more information about the nacos plugin description and full configuration list, you can refer to the [official documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos/). Review comment: ```suggestion To get more information about the `nacos` plugin description and full configuration list, you can refer to the [Apache APISIX's official documentation](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos/). ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,198 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Service Registry +- Nacos +- Developer +- Guide +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +## Service Registry + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + + + +## Apache APISIX realizes service discovery based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 12.1.0, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` Review comment: ditto ########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] +--- + +> 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 + +<!--truncate--> + +## 背景信息 + +Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台。它提供了一组简单易用的特性集,可以帮助您快速实现动态服务发现,服务配置,服务元数据及流量管理,让您更敏捷和容易地构建,交付和管理微服务平台。Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构(例如微服务范式、云原生范式)的服务基础设施。 + +## 注册中心 + +注册中心是服务要实现服务化管理的核心组件,类似于目录服务的作用,也是微服务架构中最基础的设施之一,主要用来存储服务信息,譬如服务提供者 URL 、路由信息等。注册中心的实现是通过一种映射的方式,将复杂的服务端信息映射为简单易懂的信息提供给客户端。 + +注册中心的核心功能为以下三点: + +- 服务注册:**服务提供方** 向 **注册中心** 进行注册。 +- 服务发现:**服务消费方** 可以通过注册中心寻找到服务提供方的调用路由信息。 +- 健康检测:确保注册到注册中心的服务节点是可以被正常调用的,避免无效节点导致的调用资源浪费等问题。 + +注册中心本质上是为了 **解耦服务提供者和服务消费者**,在微服务体系中,各个业务服务之间会频繁互相调用,并且需要对各个服务的 IP、port 等路由信息进行统一的管理。但是要如何进行管理呢?我们可以通过注册中心的 **服务注册** 功能将已有服务的相关信息提供到统一的注册中心进行管理。 + +通过上述描述,您可以了解到注册中心可以帮助用户通过映射快速找到服务和服务地址。随着业务更新迭代,服务会频繁发生变化,在服务端中注册了新的服务或者服务宕机后,客户端仍然可以通过注册中心的 **服务发现** 功能拉取服务列表,如果注册中心的服务节点发生变更,注册中心会发送请求通知客户端重新拉取。 + +如果服务端的服务突然宕机,并且没有向注册中心反馈,客户端可以通过注册中心的 **健康检查** 功能,进行固定时间间隔的主动上报心跳方式向服务端表明自己的服务状态。如果服务状态异常,则会通知注册中心,注册中心可以及时把已经宕机的服务节点进行剔除,避免资源的浪费。 + +Apache APISIX + Nacos 可以将各个微服务节点中与业务无关的各项控制,集中在 Apache APISIX 中进行统一管理,即**通过 Apache APISIX 实现接口服务的代理和路由转发的能力**。在 Nacos 上注册各个微服务后,Apache APISIX 可以通过 Nacos 的服务发现功能获取服务列表,查找对应的服务地址从而实现动态代理。 + + + +## Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现 + +### 前提条件 + +本文操作基于以下环境进行。 + +- 操作系统 Centos 7.9。 +- 已安装 Apache APISIX 12.1.0,详情请参考:[如何构建 Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/how-to-build)。 +- 已安装 Nacos 2.0.4,详情请参考:[Nacos 快速入门](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。 +- 已安装 Node.js,详情请参考:[Node.js 安装指南](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation)。 + +### 步骤一:服务注册 + +1. 使用 Node.js 的 Koa 框架在 `3005` 端口启动一个简单的测试服务作为[上游(Upstream)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/admin-api#upstream)。 + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. 在命令行中通过请求 Nacos Open API 的方式进行服务注册。 + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` Review comment: This code block belongs to step 2, so you should use tab or space to do an indentation. ########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] +--- + +> 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 + +<!--truncate--> + +## 背景信息 + +Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台。它提供了一组简单易用的特性集,可以帮助您快速实现动态服务发现,服务配置,服务元数据及流量管理,让您更敏捷和容易地构建,交付和管理微服务平台。Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构(例如微服务范式、云原生范式)的服务基础设施。 + +## 注册中心 + +注册中心是服务要实现服务化管理的核心组件,类似于目录服务的作用,也是微服务架构中最基础的设施之一,主要用来存储服务信息,譬如服务提供者 URL 、路由信息等。注册中心的实现是通过一种映射的方式,将复杂的服务端信息映射为简单易懂的信息提供给客户端。 + +注册中心的核心功能为以下三点: + +- 服务注册:**服务提供方** 向 **注册中心** 进行注册。 +- 服务发现:**服务消费方** 可以通过注册中心寻找到服务提供方的调用路由信息。 +- 健康检测:确保注册到注册中心的服务节点是可以被正常调用的,避免无效节点导致的调用资源浪费等问题。 + +注册中心本质上是为了 **解耦服务提供者和服务消费者**,在微服务体系中,各个业务服务之间会频繁互相调用,并且需要对各个服务的 IP、port 等路由信息进行统一的管理。但是要如何进行管理呢?我们可以通过注册中心的 **服务注册** 功能将已有服务的相关信息提供到统一的注册中心进行管理。 + +通过上述描述,您可以了解到注册中心可以帮助用户通过映射快速找到服务和服务地址。随着业务更新迭代,服务会频繁发生变化,在服务端中注册了新的服务或者服务宕机后,客户端仍然可以通过注册中心的 **服务发现** 功能拉取服务列表,如果注册中心的服务节点发生变更,注册中心会发送请求通知客户端重新拉取。 + +如果服务端的服务突然宕机,并且没有向注册中心反馈,客户端可以通过注册中心的 **健康检查** 功能,进行固定时间间隔的主动上报心跳方式向服务端表明自己的服务状态。如果服务状态异常,则会通知注册中心,注册中心可以及时把已经宕机的服务节点进行剔除,避免资源的浪费。 + +Apache APISIX + Nacos 可以将各个微服务节点中与业务无关的各项控制,集中在 Apache APISIX 中进行统一管理,即**通过 Apache APISIX 实现接口服务的代理和路由转发的能力**。在 Nacos 上注册各个微服务后,Apache APISIX 可以通过 Nacos 的服务发现功能获取服务列表,查找对应的服务地址从而实现动态代理。 + + + +## Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现 + +### 前提条件 + +本文操作基于以下环境进行。 + +- 操作系统 Centos 7.9。 +- 已安装 Apache APISIX 12.1.0,详情请参考:[如何构建 Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/how-to-build)。 +- 已安装 Nacos 2.0.4,详情请参考:[Nacos 快速入门](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。 +- 已安装 Node.js,详情请参考:[Node.js 安装指南](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation)。 + +### 步骤一:服务注册 + +1. 使用 Node.js 的 Koa 框架在 `3005` 端口启动一个简单的测试服务作为[上游(Upstream)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/admin-api#upstream)。 + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. 在命令行中通过请求 Nacos Open API 的方式进行服务注册。 + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. 执行服务注册后使用以下命令查询当前服务情况。 + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +正确返回结果示例如下: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` + +### 步骤二:新增 Nacos 路由 + +使用 Apache APISIX 提供的 Admin API 创建一个新的[路由(Route)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/admin-api#route),APISIX 通过 `upstream.discovery_type` 字段选择使用的服务发现类型,`upstream.service_name` 需要与注册中心的对应服务名进行关联,因此创建路由时指定服务发现类型为 `nacos`。 + +```Shell +curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -i -d ' +{ + "uri": "/nacos/*", + "upstream": { + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS", + "type": "roundrobin", + "discovery_type": "nacos" + } +}' +``` + +在上述命令中,请求头 `X-API-KEY` 是 Admin API 的访问 token,可以在 `conf/config.yaml` 文件中的 `apisix.admin_key.key` 查看。 + +添加成功后,正确返回结果示例如下: + +```JSON +{ + "action": "set", + "node": { + "key": "\/apisix\/routes\/1", + "value": { + "update_time": 1643191044, + "create_time": 1643176603, + "priority": 0, + "uri": "\/nacos\/*", + "upstream": { + "hash_on": "vars", + "discovery_type": "nacos", + "scheme": "http", + "pass_host": "pass", + "type": "roundrobin", + "service_name": "APISIX-NACOS" + }, + "id": "1", + "status": 1 + } + } +} +``` + +除此之外,您还可以在 upstream.discovery_args 中传递其他服务相关参数用于指定服务所在的命名空间或组别,具体内容可参考[官方文档](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/next/discovery/nacos/#%E5%8F%82%E6%95%B0)。 + +### 步骤三:验证配置结果 + +使用以下命令发送请求至需要配置的路由。 + +```Shell +curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/nacos/ +``` + +正常返回结果示例如下: + +```Apache +HTTP/1.1 200 OK +Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 +Content-Length: 11 +Connection: keep-alive +Date: Thu, 27 Jan 2022 00:48:26 GMT +Server: APISIX/2.12.0 + +Hello World +``` + +通过示例看到,Apache APISIX 中新增的路由已经可以通过 Nacos 服务发现找到正确的服务地址,并正常响应。 + +## 总结 + +本文为大家介绍了注册中心的概念以及 Apache APISIX 如何配合 Nacos 实现基于服务发现的路由代理。用户可以根据自身的业务需求和过往技术架构使用 Apache APISIX 与 Nacos,以实现接口服务的代理和路由转发的能力。 +关于 `nacos` 插件的更多说明和完整配置信息,可参考官网文档:[nacos](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos)。 Review comment: ```suggestion 关于 `nacos` 插件的更多说明和完整配置信息,可参考[Apache APISIX 官方文档](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/discovery/nacos)。 ``` ########## File path: website/i18n/zh/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,197 @@ +--- +title: "如何使用 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现" +authors: + - name: "林志煌" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "韩飞" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 +tags: [Technology,Ecosyste,Service Discovery] +--- + +> 本文为您介绍 Apache APISIX、Nacos 基本概念以及注册中心的作用,并为您展示了 Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现的具体操作。 + +<!--truncate--> + +## 背景信息 + +Nacos 是阿里巴巴开源的一个易于使用的动态服务发现、配置和服务管理平台。它提供了一组简单易用的特性集,可以帮助您快速实现动态服务发现,服务配置,服务元数据及流量管理,让您更敏捷和容易地构建,交付和管理微服务平台。Nacos 是构建以“服务”为中心的现代应用架构(例如微服务范式、云原生范式)的服务基础设施。 + +## 注册中心 + +注册中心是服务要实现服务化管理的核心组件,类似于目录服务的作用,也是微服务架构中最基础的设施之一,主要用来存储服务信息,譬如服务提供者 URL 、路由信息等。注册中心的实现是通过一种映射的方式,将复杂的服务端信息映射为简单易懂的信息提供给客户端。 + +注册中心的核心功能为以下三点: + +- 服务注册:**服务提供方** 向 **注册中心** 进行注册。 +- 服务发现:**服务消费方** 可以通过注册中心寻找到服务提供方的调用路由信息。 +- 健康检测:确保注册到注册中心的服务节点是可以被正常调用的,避免无效节点导致的调用资源浪费等问题。 + +注册中心本质上是为了 **解耦服务提供者和服务消费者**,在微服务体系中,各个业务服务之间会频繁互相调用,并且需要对各个服务的 IP、port 等路由信息进行统一的管理。但是要如何进行管理呢?我们可以通过注册中心的 **服务注册** 功能将已有服务的相关信息提供到统一的注册中心进行管理。 + +通过上述描述,您可以了解到注册中心可以帮助用户通过映射快速找到服务和服务地址。随着业务更新迭代,服务会频繁发生变化,在服务端中注册了新的服务或者服务宕机后,客户端仍然可以通过注册中心的 **服务发现** 功能拉取服务列表,如果注册中心的服务节点发生变更,注册中心会发送请求通知客户端重新拉取。 + +如果服务端的服务突然宕机,并且没有向注册中心反馈,客户端可以通过注册中心的 **健康检查** 功能,进行固定时间间隔的主动上报心跳方式向服务端表明自己的服务状态。如果服务状态异常,则会通知注册中心,注册中心可以及时把已经宕机的服务节点进行剔除,避免资源的浪费。 + +Apache APISIX + Nacos 可以将各个微服务节点中与业务无关的各项控制,集中在 Apache APISIX 中进行统一管理,即**通过 Apache APISIX 实现接口服务的代理和路由转发的能力**。在 Nacos 上注册各个微服务后,Apache APISIX 可以通过 Nacos 的服务发现功能获取服务列表,查找对应的服务地址从而实现动态代理。 + + + +## Apache APISIX 基于 Nacos 实现服务发现 + +### 前提条件 + +本文操作基于以下环境进行。 + +- 操作系统 Centos 7.9。 +- 已安装 Apache APISIX 12.1.0,详情请参考:[如何构建 Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/how-to-build)。 +- 已安装 Nacos 2.0.4,详情请参考:[Nacos 快速入门](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。 +- 已安装 Node.js,详情请参考:[Node.js 安装指南](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation)。 + +### 步骤一:服务注册 + +1. 使用 Node.js 的 Koa 框架在 `3005` 端口启动一个简单的测试服务作为[上游(Upstream)](https://apisix.apache.org/zh/docs/apisix/admin-api#upstream)。 + +```JavaScript +const Koa = require('koa'); +const app = new Koa(); + +app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; +}); + +app.listen(3005); +``` + +2. 在命令行中通过请求 Nacos Open API 的方式进行服务注册。 + +```Shell +curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' +``` + +3. 执行服务注册后使用以下命令查询当前服务情况。 + +```Shell +curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' +``` + +正确返回结果示例如下: + +```JSON +{ + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true +} +``` Review comment: This code block belongs to step 3, so you should use tab or space to do an indentation. -- This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service. To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the URL above to go to the specific comment. To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected] For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at: [email protected]
