yzeng25 commented on a change in pull request #895: URL: https://github.com/apache/apisix-website/pull/895#discussion_r811770736
########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,196 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background Information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. Review comment: Need to add bold to some phrases  ```suggestion - Service registration: **Service providers** register with the **Service Registration Center**. - Service discovery: **Service consumers** can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. ``` ########## File path: website/blog/2022/02/21/nacos.md ########## @@ -0,0 +1,196 @@ +--- +title: "How to Use Apache APISIX Realizes Service Discovery Based on Nacos" +authors: + - name: "Zhihuang Lin" + title: "Author" + url: "https://github.com/oil-oil"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/57465570?v=4"; + - name: "Fei Han" + title: "Technical Writer" + url: "https://github.com/hf400159"; + image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/97138894?v=4"; +keywords: +- Apache APISIX +- Nacos +- Service Discovery +- Service Registry +- Ecosystem +description: This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. +tags: [Technology,Ecosystem,Service Discovery] +--- + +> This article introduces the basic concepts of Apache APISIX and Nacos and Service Registry, and shows you the specific operation of Apache APISIX to realize service discovery based on Nacos. + +<!--truncate--> + +## Background Information + +Nacos is an easy-to-use, open source platform for dynamic service discovery, service configuration and service management. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management. Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach. + +Service Registry is the core component of service management, similar to the role of directory service, and one of the most basic facilities in the microservices architecture. It is mainly used to store service information, such as service provider URL, routing information, and so on. The service registry is implemented by mapping complex service-side information to simple and understandable information for the client. + +The core functions of the Service Registry are as follows: + +- Service registration: Service providers register with the Service Registration Center. +- Service discovery: Service consumers can find the call routing information of service providers through the registry. +- Health check: Ensure that service nodes registered with the service registry can be invoked normally, and avoid the waste of call resources caused by invalid nodes. + +The registry is essentially to decouple service providers and service consumers. In the microservice system, each business service will call each other frequently, and the IP, port and other routing information of each service need to be managed uniformly. But how do you manage it? You can provide information about existing services to a unified service registry for management through the Service Registration function of the Service Registry. + +From the above description, you can know that the registry can help users quickly find services and service addresses through mapping. As business updates iterate, services change frequently. Clients can still pull a list of services through the service discovery function of the registry after registering new services or service downtime on the service side. If the service node of the registry changes, the registry sends a request to notify the client to pull again. + +If the service on the server side suddenly goes down and there is no feedback to the service registry, the client can show the service side its service status by actively reporting the heartbeat at regular intervals through the health check function of the service registry. If the service status is abnormal, the service registry will be notified, and the service registry can remove the down service nodes in time to avoid waste of resources. + +Apache APISIX + Nacos can centralize business-independent control of each microservice node into Apache APISIX for unified management, that is, **the ability to implement proxy and routing forwarding of interface services through Apache APISIX**. After registering various microservices on Nacos, Apache APISIX can get the list of services through the service discovery function of Nacos, and find corresponding service addresses to achieve dynamic proxy. + +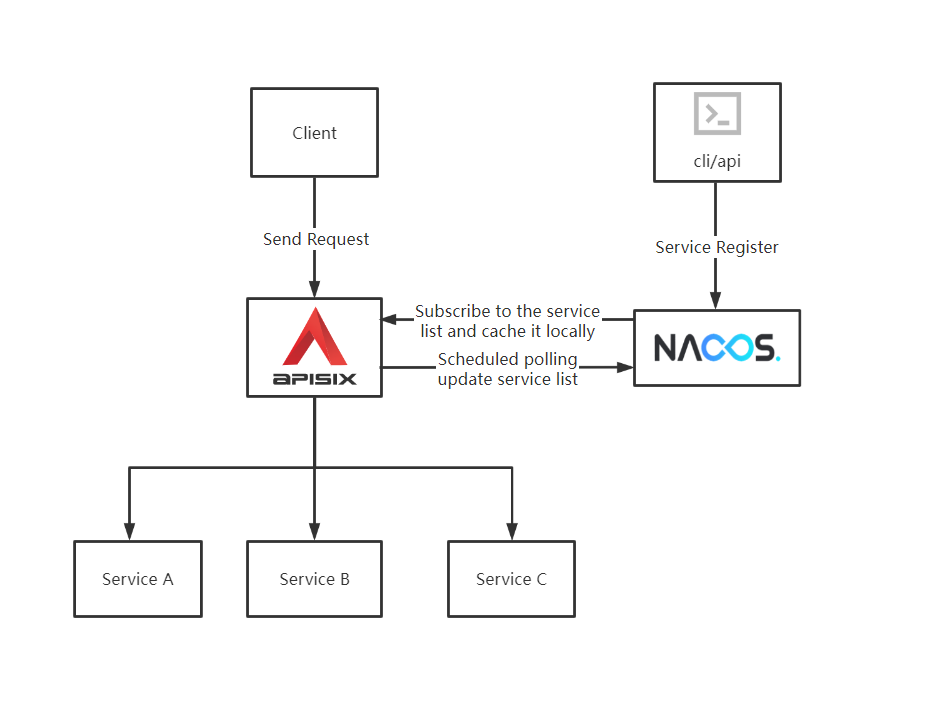 + +## Apache APISIX Integrates Service Discovery Based on Nacos + +### Prerequisites + +This article is based on the following environments. + +- OS: Centos 7.9. +- Apache APISIX 2.12.1, please refer to: [How-to-Bulid Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build). +- Nacos 2.0.4, please refer to: [Nacos Quick Start](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html). +- Node.js, please refer to: [Node.js Installation](https://github.com/nodejs/help/wiki/Installation). + +### Step 1: Service Register + +1. Use Node.js's Koa framework starts a simple test service on port `3005` as [upstream](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/admin-api/). + + ```JavaScript + const Koa = require('koa'); + const app = new Koa(); + + app.use(async ctx => { + ctx.body = 'Hello World'; + }); + + app.listen(3005); + ``` + +2. Register the service on the command line by requesting the Nacos Open API. + + ```Shell + curl -X POST 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS&ip=127.0.0.1&port=3005&ephemeral=false' + ``` + +3. After service registration, use the following command to query the current service. + + ```Shell + curl -X GET 'http://127.0.0.1:8848/nacos/v1/ns/instance/list?serviceName=APISIX-NACOS' + ``` + +Examples of correct returned results are as follows: + + ```JSON + { + "name": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "groupName": "DEFAULT_GROUP", + "clusters": "", + "cacheMillis": 10000, + "hosts": [ + { + "instanceId": "127.0.0.1#3005#DEFAULT#DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "ip": "127.0.0.1", + "port": 3005, + "weight": 1.0, + "healthy": true, + "enabled": true, + "ephemeral": true, + "clusterName": "DEFAULT", + "serviceName": "DEFAULT_GROUP@@APISIX-NACOS", + "metadata": {}, + "instanceHeartBeatInterval": 5000, + "instanceHeartBeatTimeOut": 15000, + "ipDeleteTimeout": 30000, + "instanceIdGenerator": "simple" + } + ], + "lastRefTime": 1643191399694, + "checksum": "", + "allIPs": false, + "reachProtectionThreshold": false, + "valid": true + } + ``` + +### Step 2:Add Nacos Route Review comment: ```suggestion ### Step 2: Add Nacos Route ``` -- This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service. To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the URL above to go to the specific comment. To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected] For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at: [email protected]
