This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
sylviasu pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/apisix-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new df973c16a3b docs: add a new article to the 'blog' module (#1046)
df973c16a3b is described below
commit df973c16a3b6c91e7bf1e09fb03f025cac557baf
Author: 韩振方 <99874763+hanzhenf...@users.noreply.github.com>
AuthorDate: Mon Apr 25 16:09:10 2022 +0800
docs: add a new article to the 'blog' module (#1046)
* addNewBlog:api-observability.md
---
website/blog/2022/04/17/api-observability.md | 235 +++++++++++++++++++++++++++
1 file changed, 235 insertions(+)
diff --git a/website/blog/2022/04/17/api-observability.md
b/website/blog/2022/04/17/api-observability.md
new file mode 100644
index 00000000000..aeecd583f2b
--- /dev/null
+++ b/website/blog/2022/04/17/api-observability.md
@@ -0,0 +1,235 @@
+---
+title: "API Observability with Apache APISIX Plugins"
+keywords:
+- Apache APISIX
+- API Gateway
+- Observability
+authors:
+ - name: "Boburmirzo"
+ title: "Author"
+ url: "https://github.com/Boburmirzo";
+ image_url: "https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/14247607?v=4";
+description: In this blog post, we can leverage the power of some Apache
APISIX Observability Plugins and take a look at how to set up these plugins,
how to use them to understand API behavior, and later solve problems that
impact our users.
+---
+
+> In this blog post, we can leverage the power of some Apache APISIX
Observability Plugins and take a look at how to set up these plugins, how to
use them to understand API behavior, and later solve problems that impact
APISIX's users.
+
+<!--truncate-->
+
+
+
+## APIs are everywhere
+
+APIs — by now, we're all familiar with the term. Every service we use today
either uses an API or is an API itself. APIs are central in building and
delivering your services. Also, you know that the success of your services
depends on the integrity, availability, and performance of your APIs.
+
+Nowadays **API Observability** is already a part of every API development as
it addresses many problems related to API consistency, reliability, and the
ability to quickly iterate on new API features. When you design for full-stack
observability, you get everything you need to find issues and catch breaking
changes.
+
+API observability can help every team in your organization:
+
+* Sales and growth teams to monitor your API usage, free trials, observe
expansion opportunities and ensure that API serves the correct data.
+
+* Engineering teams to monitor and troubleshoot API issues.
+
+* Product teams to understand API usage and business value.
+
+* Security teams to detect and protect from API threats.
+
+## A central point for observation
+
+We know that an API gateway offers a central control point for incoming
traffic to a variety of destinations but it can also be a central point for
observation as well since it is uniquely qualified to know about all the
traffic moving between clients and our service networks. Instead of spending
time integrating your services with other many APIs and technologies to improve
observability, you can easily manage all work with [Apache APISIX
Plugins](https://apisix.apache.org/plugins).
+
+
+
+Most observability platforms like (Prometheus, SkyWalking, and Opentelemetry)
provide pre-built connectors that you can easily integrate with Apache APISIX.
You can leverage these connectors to ingest log data from your API gateways to
further derive useful metrics and gain complete visibility into the usage,
management performance, and security of your APIs in your environment.
+
+The core of observability breaks down into **three key areas**: structured
logs, metrics, and traces. Let’s break down each pillar of API observability
and learn how with Apache APISIX Plugins we can simplify these tasks and
provides a solution that you can use to better understand API usage.
+
+
+
+## Prerequisites
+
+Before enabling our plugins we need to install Apache APISIX, create a route,
an upstream, and map the route to the upstream. You can simply follow [getting
started guide](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/getting-started) provided
on the website.
+
+## Logs
+
+**Logs** are also easy to instrument and trivial steps of API observability,
they can be used to inspect API calls in real-time for debugging, auditing, and
recording time-stamped events that happened over time. There are several logger
plugins Apache APISIX provides such as:
+
+* [http-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/http-logger/)
+
+*
[skywalking-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/skywalking-logger/)
+
+* [tcp-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/tcp-logger)
+
+* [kafka-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/kafka-logger)
+
+*
[rocketmq-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/rocketmq-logger)
+
+* [udp-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/udp-logger)
+
+*
[clickhouse-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/clickhouse-logger)
+
+*
[error-logger](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/error-log-logger)
+
+*
[google-cloud-logging](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/google-cloud-logging)
+
+And you can see the [full
list](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/zipkin) on the official
website of Apache APISIX. Now for demo purposes, let's choose a simple but
mostly used _http-logger_ plugin that is capable of sending API Log data
requests to HTTP/HTTPS servers or sends as JSON objects to Monitoring tools. We
can assume that a route and an upstream are created. You can learn how to set
up them in the **[Getting started with Apache
APISIX](https://youtu.be/dUOjJkb61so)* [...]
+
+You can generate a mock HTTP server at [mockbin.com](https://mockbin.org/) to
record and view the logs. Note that we also bind the route to an upstream (You
can refer to this documentation to learn about more [core concepts of Apache
APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/architecture-design/apisix)).
+
+The following is an example of how to enable the http-logger for a specific
route.
+
+```
+curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 \-H 'X-API-KEY:
edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "plugins": {
+ "http-logger": {
+ "uri":
"http://mockbin.org/bin/5451b7cd-af27-41b8-8df1-282ffea13a61";
+ }
+ },
+ "upstream_id": "1",
+ "uri": "/get"
+}'
+```
+
+> To http-logger plugin settings, your can just put your mock server URI
address like below:
+
+```
+{"uri": "http://mockbin.org/bin/5451b7cd-af27-41b8-8df1-282ffea13a61"}
+```
+
+Once we get a successful response from APISIX server, we can send a request to
this _get_ endpoint to generate logs.
+
+```
+curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/get
+```
+
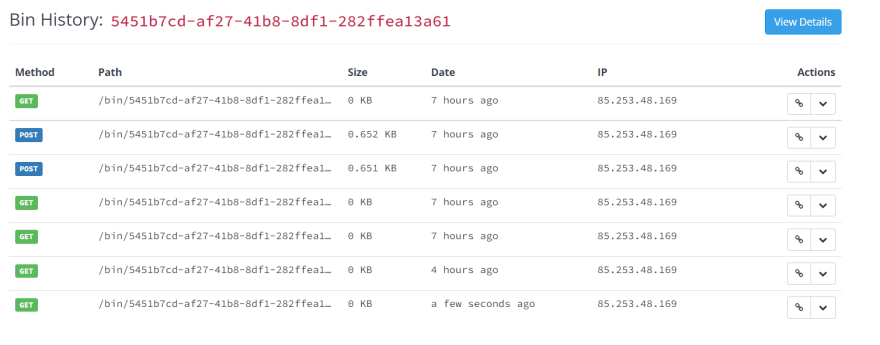
+Then if you click and navigate to the following [mock server
link](http://mockbin.org/bin/5451b7cd-af27-41b8-8df1-282ffea13a61/log) some
recent logs are sent and we can see them:
+
+
+
+## Metrics
+
+**Metrics** are a numeric representation of data measured over intervals of
time. You can also aggregate this data into daily or weekly frequency and run
queries against a distributed system like
[Elasticsearch](https://www.elastic.co/). Or sometimes based on metrics you
trigger alerts to take any action later. Once API metrics are collected, you
can track them with metrics tracking tools such as
[Prometheus](https://prometheus.io/).
+
+Apache APISIX API Gateway also offers
[prometheus-plugin](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/prometheus/)
to fetch your API metrics and expose them in Prometheus. Behind the scene,
Apache APISIX downloads the Grafana dashboard meta, imports it to
[Grafana](https://grafana.com/), and fetches real-time metrics from the
Prometheus plugin.
+
+Let’s enable prometheus-plugin for our route:
+
+```
+ curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 -H 'X-API-KEY:
edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "uri": "/get",
+ "plugins": {
+ "prometheus":{}
+ },
+ "upstream_id": "1"
+}
+```
+
+We fetch the metric data from the specified URL `/apisix/prometheus/`metrics.
+
+```
+curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9091/apisix/prometheus/metrics
+```
+
+You will get a response with Prometheus metrics something like below:
+
+```
+HTTP/1.1 200 OK
+Server: openresty
+Date: Fri, 25 Mar 2022 11:13:14 GMT
+Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8
+Transfer-Encoding: chunked
+Connection: keep-alive
+# HELP apisix_batch_process_entries batch process remaining entries
+# TYPE apisix_batch_process_entries gauge
+apisix_batch_process_entries{name="http
logger",route_id="1",server_addr="172.19.0.8"} 0
+# HELP apisix_etcd_modify_indexes Etcd modify index for APISIX keys
+# TYPE apisix_etcd_modify_indexes gauge
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="consumers"} 17819
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="global_rules"} 17832
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="max_modify_index"} 20028
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="prev_index"} 18963
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="protos"} 0
+apisix_etcd_modify_indexes{key="routes"} 20028
+...
+```
+
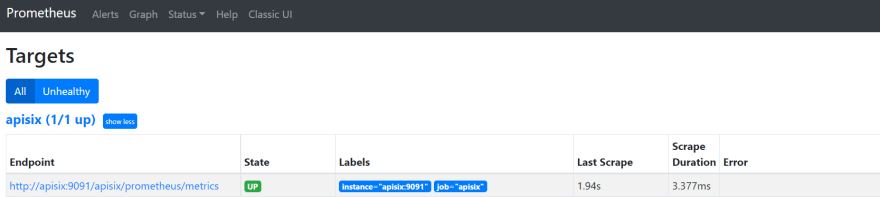
+And we can also check the status of our endpoint at the Prometheus dashboard
by pointing to this URL `http://localhost:9090/targets`.
+
+
+
+As you can see, Apache APISIX exposed metrics endpoint is upon and running.
+
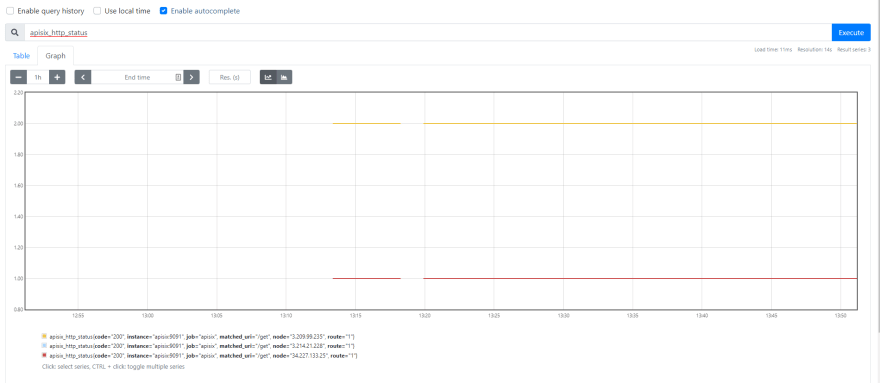
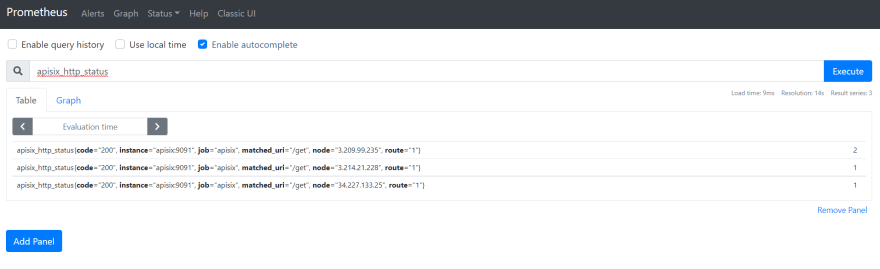
+Now you can query metrics for `apisix_http_status` to see what HTTP requests
are handled by API Gateway and what was the outcome.
+
+
+
+
+
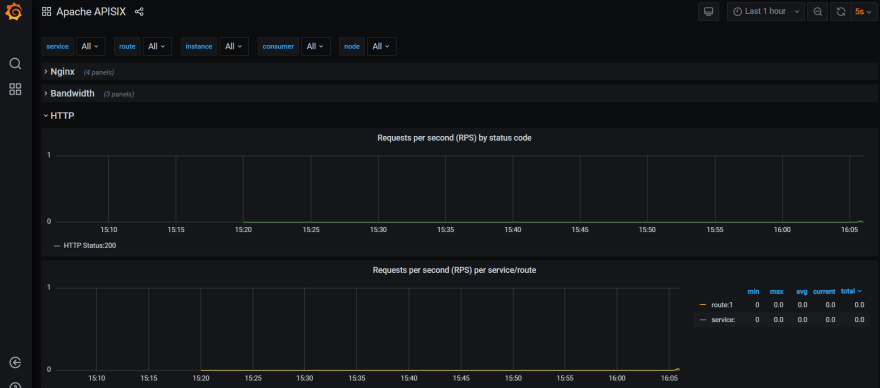
+In addition to this, you can view the Grafana dashboard running in your local
instance. Go to `http://localhost:3000/`
+
+
+
+## Tracing
+
+The third is **tracing** or distributed tracing allows you to understand the
life of a request as it traverses your service network and allows you to answer
questions like what service has this request touched and how much latency was
introduced. Traces enable you to further explore which logs to look at for a
particular session or related set of API calls.
+
+[Zipkin](https://zipkin.io/), an open-source distributed tracing system.
[APISIX plugin](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/plugins/zipkin) is
supported to collect tracing and report to Zipkin Collector based on [Zipkin
API specification](https://zipkin.io/pages/instrumenting.html).
+
+Here’s an example to enable the _zipkin plugin_ on the specified route:
+
+```shell
+curl http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/admin/routes/1 \
+-H 'X-API-KEY: edd1c9f034335f136f87ad84b625c8f1' -X PUT -d '
+{
+ "methods": ["GET"],
+ "uri": "/get",
+ "plugins": {
+ "zipkin": {
+ "endpoint": "http://127.0.0.1:9411/api/v2/spans";,
+ "sample_ratio": 1
+ }
+ },
+ "upstream_id": "1"
+}'
+```
+
+We can test our example by simply running the following curl command:
+
+`curl -i http://127.0.0.1:9080/get`
+
+As you can see, there are some additional trace identifiers (like traceId,
spanId, parentId) were appended to the headers:
+
+```
+"X-B3-Parentspanid": "61bd3f4046a800e7",
+"X-B3-Sampled": "1",
+"X-B3-Spanid": "855cd5465957f414",
+"X-B3-Traceid": "e18985df47dab632d62083fd96626692",
+```
+
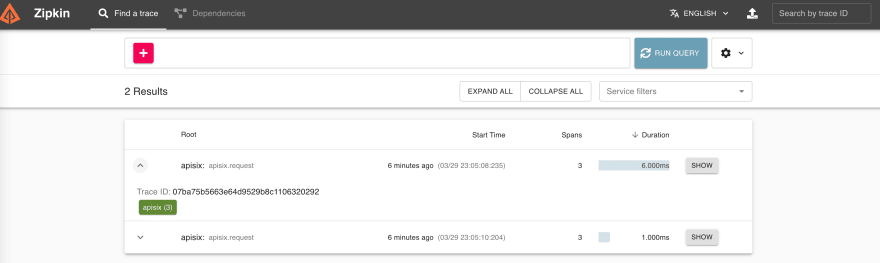
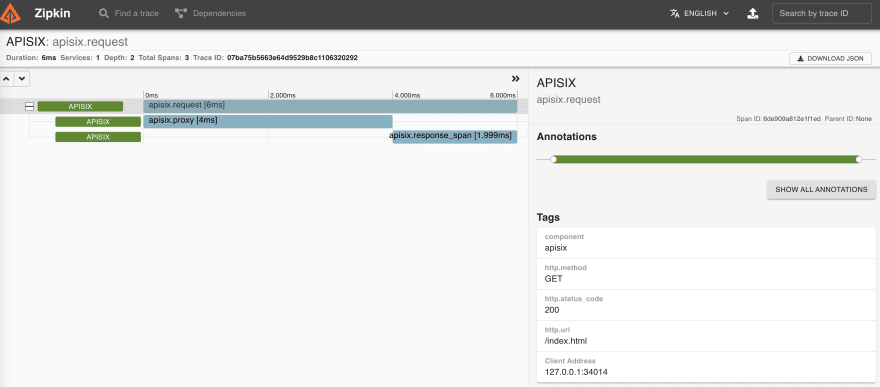
+Then you can use a browser to access `http://127.0.0.1:9411/zipkin`, see
traces on the Web UI of Zipkin.
+
+> Note that you need to run the Zipkin instance in order to install Zipkin Web
UI. For example, by using docker you can simply run it:
+> `docker run -d -p 9411:9411 openzipkin/zipkin`
+
+
+
+
+
+As you noticed, the recent traces were exposed in the above pictures.
+
+## Summary
+
+As we learned, API Observability is a sort of framework for managing your
applications in an API world and Apache APISIX API Gateway plugins can help
when observing modern API-driven applications by integrating to several
observability platforms. So, you can make your development work focused on core
business features instead of building a custom integration for observability
tools.
+
+You can also click below to get more details:
+
+* [Download Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/downloads)
+* [Getting Started with Apache APISIX](https://youtu.be/dUOjJkb61so)
+* [Getting Started with Apache APISIX Dashboard](https://youtu.be/-9-HZKK2ccI)
+* [Overview of Apache APISIX Plugins](https://youtu.be/ixSZA4ILBKQ)
+* [Install Apache APISIX](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/apisix/how-to-build)
+* [Watch the Video version of the blog post](https://youtu.be/XK0xcui5BQU)
+
+If you have any questions, feel free to mail [Apache APISIX
Community](https://apisix.apache.org/docs/general/join/)
