This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
liuqiufeng pushed a commit to branch docusaurus
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/incubator-seata-website.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/docusaurus by this push:
new fed370216f optimize: optimize raft blog img links (#857)
fed370216f is described below
commit fed370216fc886addd2f387741ca19075923c6ca
Author: funkye <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Fri Mar 29 10:06:30 2024 +0800
optimize: optimize raft blog img links (#857)
---
.../seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md | 10 +++++-----
.../seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md | 12 ++++++------
static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105203431.jpg | Bin 0 -> 60447 bytes
static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105204423.jpg | Bin 0 -> 87956 bytes
static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105211035.jpg | Bin 0 -> 88989 bytes
static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106230931.jpg | Bin 0 -> 102740 bytes
static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106231817.jpg | Bin 0 -> 57666 bytes
7 files changed, 11 insertions(+), 11 deletions(-)
diff --git
a/i18n/en/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
b/i18n/en/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
index 9e47424745..b1d4a0c4ea 100644
--- a/i18n/en/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
+++ b/i18n/en/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
@@ -66,14 +66,14 @@ However, the prerequisite is that computation and storage
must be separated. Why
The design philosophy of Seata-Raft mode is to encapsulate the File mode,
which is unable to achieve high availability, and use the Raft algorithm to
synchronize data between multiple TCs. This mode ensures data consistency among
multiple TCs when using the File mode and replaces asynchronous flushing
operations with Raft logs and snapshots for data recovery.
-
+
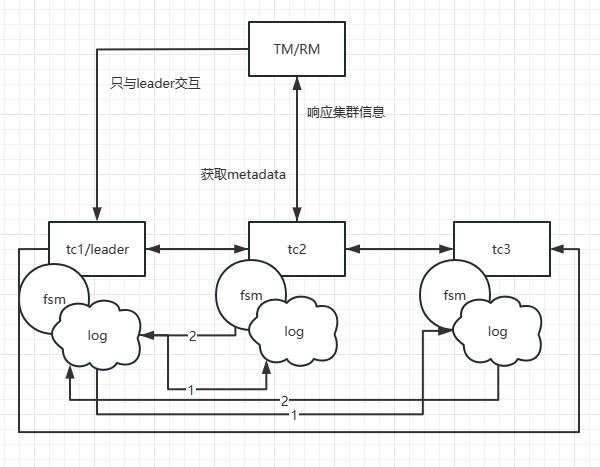
In the Seata-Raft mode, the client-side, upon startup, retrieves its
transaction group (e.g., default) and the IP addresses of relevant Raft cluster
nodes from the configuration center. By sending a request to the control port
of Seata-Server, the client can obtain metadata for the Raft cluster
corresponding to the default group, including leader, follower, and learner
member nodes. Subsequently, the client monitors (watches) any member nodes of
non-leader nodes.
Assuming that TM initiates a transaction, and the leader node in the local
metadata points to the address of TC1, TM will only interact with TC1. When TC1
adds global transaction information, through the Raft protocol, denoted as step
1 in the diagram, TC1 sends the log to other nodes. Step 2 represents the
response of follower nodes to log reception. When more than half of the nodes
(such as TC2) accept and respond successfully, the state machine (FSM) on TC1
will execute the action of [...]
-
-
+
+
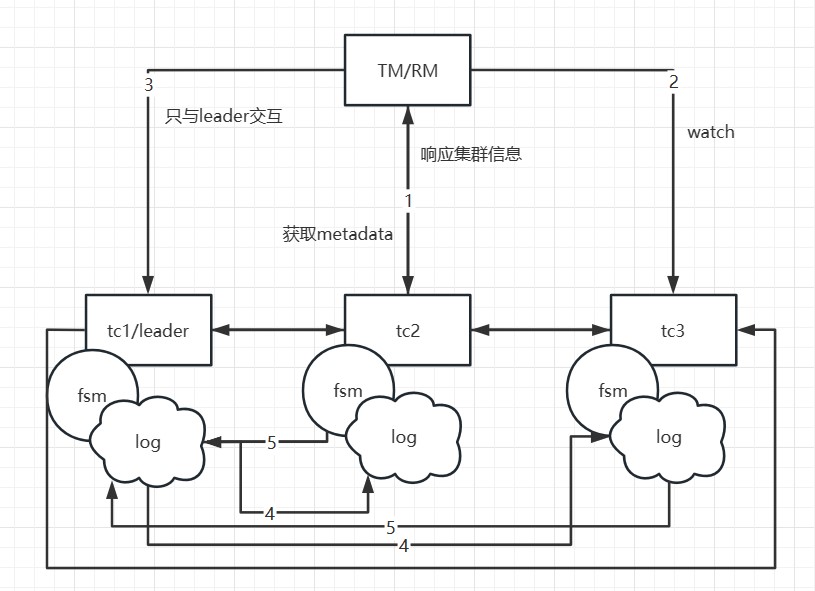
If TC1 crashes or a reelection occurs, what happens? Since the metadata has
been obtained during the initial startup, the client will execute the watch
follower node's interface to update the local metadata information. Therefore,
subsequent transaction requests will be sent to the new leader (e.g., TC2).
Meanwhile, TC1's data has already been synchronized to TC2 and TC3, ensuring
data consistency. Only at the moment of the election, if a transaction happens
to be sent to the old leader, [...]
@@ -83,7 +83,7 @@ It is important to note that in this mode, if a transaction
is in the phase of s
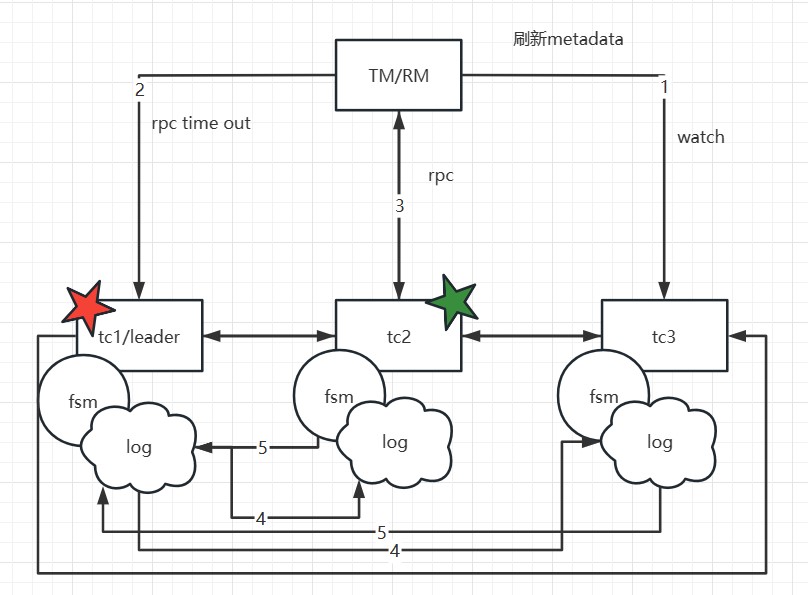
In Seata, when a TC experiences a failure, the data recovery process is as
follows:
-
+
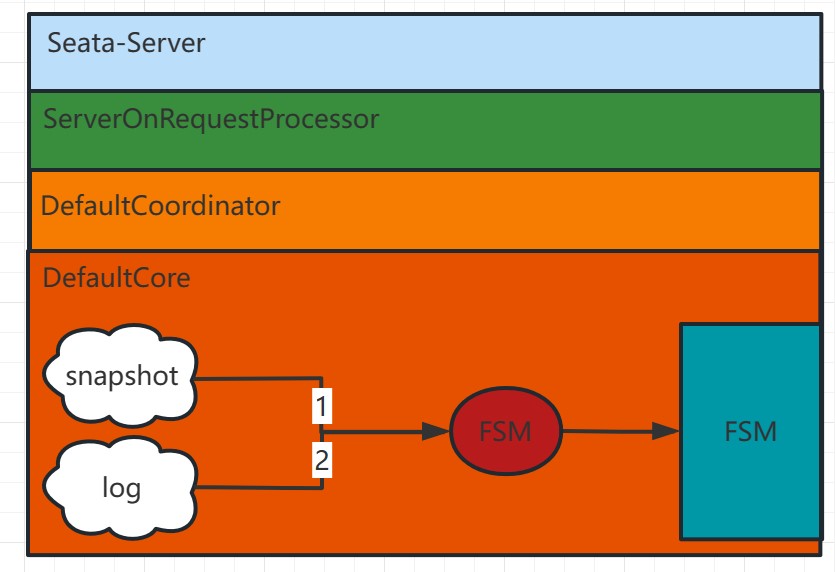
As shown in the above diagram:
@@ -97,7 +97,7 @@ Through these steps, Seata can achieve data recovery after a
failure. It first a
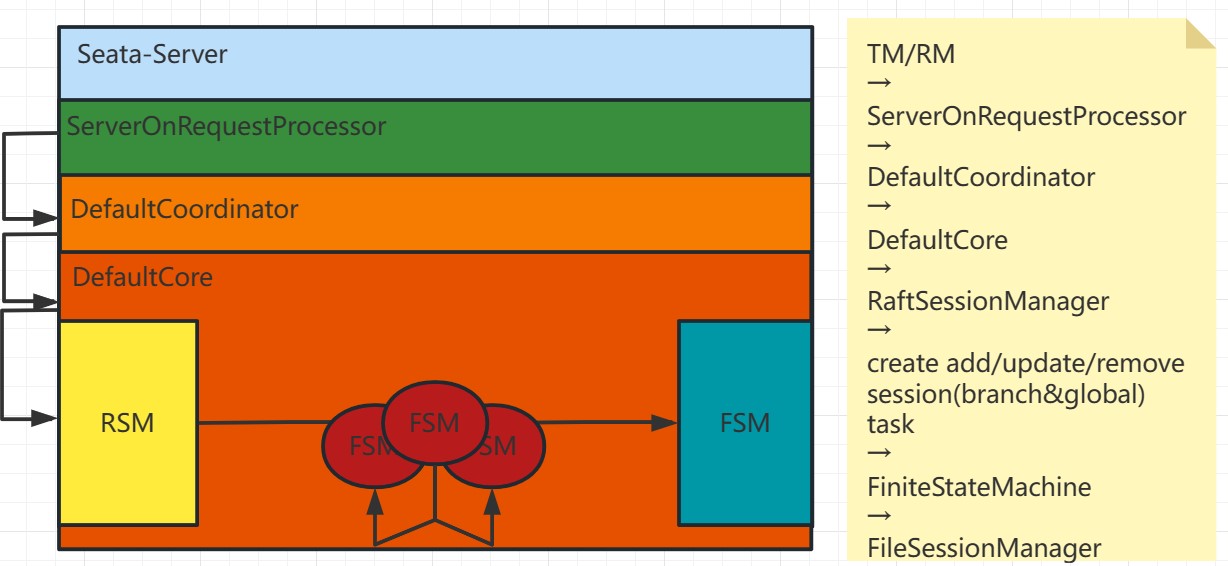
### 2.3.3 Business Processing Synchronization Process
-
+
For the case where the client side is obtaining the latest metadata while a
business thread is executing operations such as begin, commit, or registry,
Seata adopts the following handling:
- On the client side:
diff --git
a/i18n/zh-cn/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
b/i18n/zh-cn/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
index 0fb9dd978a..0a52afc359 100644
---
a/i18n/zh-cn/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
+++
b/i18n/zh-cn/docusaurus-plugin-content-blog/seata-raft-detailed-explanation.md
@@ -52,14 +52,14 @@ RAFT 是一种新型易于理解的分布式一致性复制协议,由斯坦福
## 2.3 Seata-Raft是如何设计的呢?
### 2.3.1 设计原理
Seata-Raft模式的设计思路是通过封装无法高可用的file模式,利用Raft算法实现多个TC之间数据的同步。该模式保证了使用file模式时多个TC的数据一致性,同时将异步刷盘操作改为使用Raft日志和快照进行数据恢复。
-
+
在Seata-Raft模式中,client端在启动时会从配置中心获取当前client的事务分组(例如default)以及相关Raft集群节点的IP地址。通过向Seata-Server的控制端口发送请求,client可以获取到default分组对应的Raft集群的元数据,包括leader、follower和learner成员节点。然后,client会监视(watch)非leader节点的任意成员节点。
假设TM开始一个事务,并且本地的metadata中的leader节点指向了TC1的地址,那么TM只会与TC1进行交互。当TC1添加一个全局事务信息时,通过Raft协议,即图中标注为步骤1的日志发送,TC1会将日志发送给其他节点,步骤2是follower节点响应日志接收情况。当超过半数的节点(如TC2)接受并响应成功时,TC1上的状态机(FSM)将执行添加全局事务的动作。
-
-
+
+
如果TC1宕机或发生重选举,会发生什么呢?由于首次启动时已经获取到了元数据,client会执行watch
follower节点的接口来更新本地的metadata信息。因此,后续的事务请求将发送到新的leader(例如TC2)。同时,TC1的数据已经被同步到了TC2和TC3,因此数据一致性不会受到影响。只在选举发生的瞬间,如果某个事务正好发送给了旧的leader,该事务会被主动回滚,以确保数据的正确性。
@@ -67,18 +67,18 @@ Seata-Raft模式的设计思路是通过封装无法高可用的file模式,利
### 2.3.2 故障恢复
在Seata中,当TC发生故障时,数据恢复的过程如下:
-
+
如上图所示
-
检查是否存在最新的数据快照:首先,系统会检查是否存在最新的数据快照文件。数据快照是基于内存的数据状态的一次全量拷贝,如果有最新的数据快照,则系统将直接加载该快照到内存中。
-
根据快照后的Raft日志进行回放:如果存在最新的快照或者没有快照文件,系统将根据之前记录的Raft日志进行数据回放。每个Seata-Server中的请求最终会经过ServerOnRequestProcessor进行处理,然后转移到具体的协调者类(DefaultCoordinator或RaftCoordinator)中,再转向具体的业务代码(DefaultCore)进行相应的事务处理(如begin、commit、rollback等)。
-- 当日志回放完成后,便会由leader发起日志的同步,并继续执行相关事务的增删改动作。
+- 当日志回放完成后,便会由leader发起日志的同步,并继续执行相关事务的增删改动作。f
通过以上步骤,Seata能够实现在故障发生后的数据恢复。首先尝试加载最新的快照,如果有的话可以减少回放的时间;然后根据Raft日志进行回放,保证数据操作的一致性;最后通过日志同步机制,确保数据在多节点之间的一致性。
### 2.3.3 业务处理同步过程
-
+
对于client侧获取最新metadata时恰好有业务线程在执行begin、commit或registry等操作的情况,Seata采取了以下处理方式:
- client侧:
diff --git a/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105203431.jpg
b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105203431.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ae15271a2c
Binary files /dev/null and b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105203431.jpg differ
diff --git a/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105204423.jpg
b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105204423.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..abf8e7f144
Binary files /dev/null and b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105204423.jpg differ
diff --git a/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105211035.jpg
b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105211035.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..77e992604b
Binary files /dev/null and b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230105211035.jpg differ
diff --git a/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106230931.jpg
b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106230931.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..87372e6f7e
Binary files /dev/null and b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106230931.jpg differ
diff --git a/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106231817.jpg
b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106231817.jpg
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..a4e1d7f4b7
Binary files /dev/null and b/static/img/blog/Dingtalk_20230106231817.jpg differ
---------------------------------------------------------------------
To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected]
For additional commands, e-mail: [email protected]
