This is an automated email from the ASF dual-hosted git repository.
duanzhengqiang pushed a commit to branch master
in repository https://gitbox.apache.org/repos/asf/shardingsphere.git
The following commit(s) were added to refs/heads/master by this push:
new efcc79d19bc readwrite splitting doc (#18558)
efcc79d19bc is described below
commit efcc79d19bce4098ab427cce7aa81d9698ab9da7
Author: Chuxin Chen <[email protected]>
AuthorDate: Fri Jun 24 10:41:17 2022 +0800
readwrite splitting doc (#18558)
---
.../features/readwrite-splitting/concept.cn.md | 40 +++++++++++++-----
.../features/readwrite-splitting/concept.en.md | 47 +++++++++++++++++-----
.../features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.cn.md | 17 --------
.../features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.en.md | 18 ---------
4 files changed, 68 insertions(+), 54 deletions(-)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.cn.md
b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.cn.md
index 3b09a58ff52..7a81cd5bc1e 100644
--- a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.cn.md
+++ b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.cn.md
@@ -1,21 +1,43 @@
+++
-title = "核心概念"
+title = "核心特性"
weight = 1
+++
-## 主库
+## 定义
-添加、更新以及删除数据操作所使用的数据库,目前仅支持单主库。
+读写分离也就是将数据库拆分为主库和从库,即主库负责处理事务性的增删改操作,从库负责处理查询操作的数据库架构。
+
+## 相关概念
-## 从库
+### 主库
+添加、更新以及删除数据操作所使用的数据库,目前仅支持单主库。
+### 从库
查询数据操作所使用的数据库,可支持多从库。
-## 主从同步
+### 主从同步
+将主库的数据异步的同步到从库的操作。 由于主从同步的异步性,从库与主库的数据会短时间内不一致。
+
+### 负载均衡策略
+通过负载均衡策略将查询请求疏导至不同从库。
+
+## 对系统的影响
+用户的系统中可能存在着复杂的主从关系数据库集群,因此应用程序需要接入多个数据源,这种方式就增加了系统维护的成本和业务开发的难度。ShardingSphere
通过读写分离功能,可以让用户像使用一个数据库一样去使用数据库集群,透明化读写分离带来的影响。
+
+## 使用限制
+* 不处理主库和从库的数据同步
+* 不处理主库和从库的数据同步延迟导致的数据不一致
+* 不支持主库多写
+* 不处理主从库间的事务一致性。主从模型中,事务中的数据读写均用主库。
-将主库的数据异步的同步到从库的操作。
-由于主从同步的异步性,从库与主库的数据会短时间内不一致。
+## 原理介绍
+ShardingSphere 的读写分离主要依赖内核的相关功能。包括解析引擎和路由引擎。解析引擎将用户的 SQL 转化为 ShardingSphere
可以识别的 Statement 信息,路由引擎根据 SQL 的读写类型以及事务的状态来做 SQL 的路由。
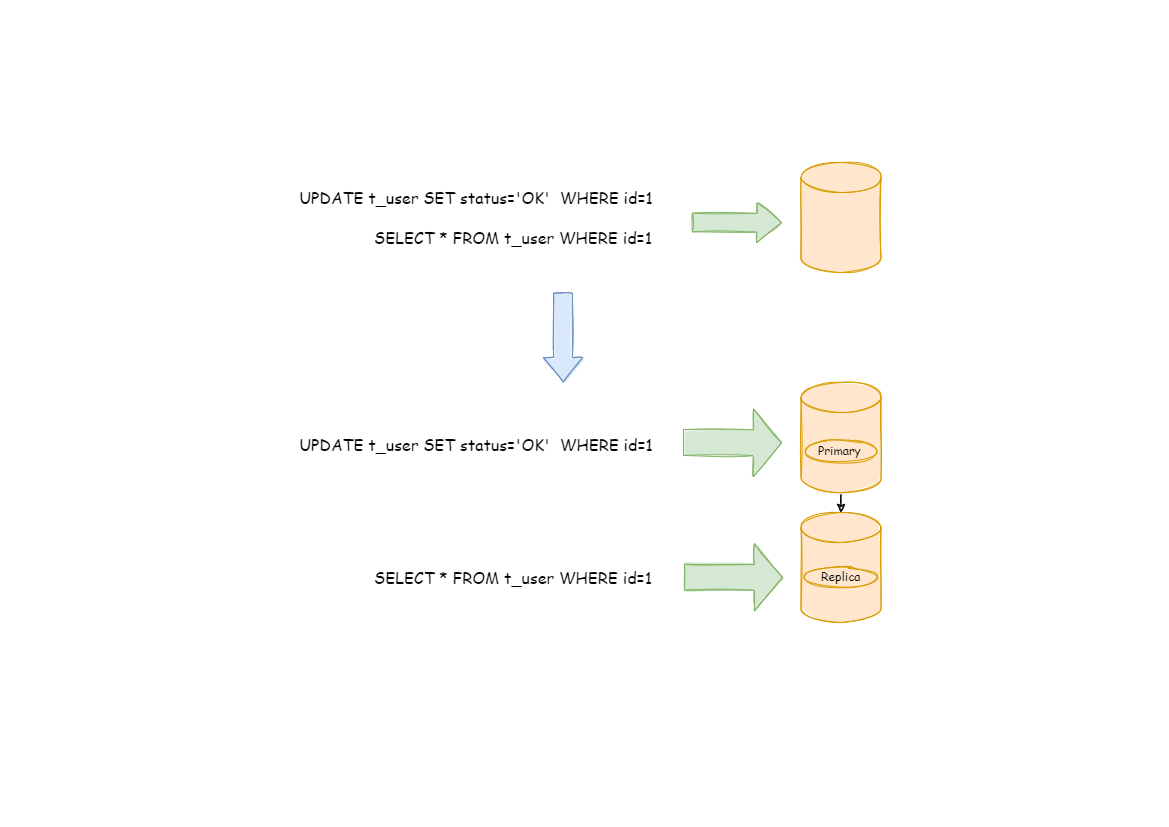
+在从库的路由中支持多种负载均衡算法,包括轮询算法、随机访问算法、权重访问算法等,用户也可以依据 SPI
机制自行扩展所需算法。如下图所示,ShardingSphere 识别到读操作和写操作,分别会路由至不同的数据库实例。
-## 负载均衡策略
+
-通过负载均衡策略将查询请求疏导至不同从库。
\ No newline at end of file
+## 相关参考
+[Java
API](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/java-api/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[YAML
配置](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/yaml-config/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[Spring Boot
Starter](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-boot-starter/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[Spring
命名空间](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-namespace/rules/readwrite-splitting)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.en.md
b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.en.md
index 36e00875a5a..adb979c23f6 100644
--- a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.en.md
+++ b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/concept.en.md
@@ -1,21 +1,48 @@
+++
-title = "Core Concept"
+title = "Core Feature"
weight = 1
+++
-## Primary Database
+## Definition
-It refers to the database used in data insertion, update and deletion. It only
supports single primary database for now.
+Read/write splitting is to split the database into primary and secondary
databases. The primary database is responsible for handling transactional
operations including additions, deletions and changes.
+And the secondary database is responsible for the query operation of database
architecture.
-## Replica Database
+## Related Concepts
-It refers to the database used in data query. It supports multiple replica
databases.
+### Primary database
+The primary database is used to add, update, and delete data operations.
Currently, only single primary database is supported.
-## Primary Replica Replication
+### Secondary database
+The secondary database is used to query data operations and multi-secondary
databases are supported.
-It refers to the operation to asynchronously replicate data from the primary
database to the replica database.
-Because of the asynchrony of primary-replica synchronization, there may be
short-time data inconsistency between them.
+### Primary-Secondary synchronization
+It refers to the operation of asynchronously synchronizing data from a primary
database to a secondary database. Due to the asynchronism of primary-secondary
synchronization,
+data from the primary and secondary databases may be inconsistent for a short
time.
-## Load Balance Strategy
+### Load balancer policy
+Channel query requests to different secondary databases through load balancer
policy.
-Through this strategy, queries separated to different replica databases.
+## Impact on the System
+There may be complex primary-secondary relational database clusters in users'
systems, so applications need to access multiple data sources, which increases
the cost of system maintenance and the
+difficulty of business development. ShardingSphere enables users to use
database clusters like a database through read/write splitting function, and
the impact of read/write splitting will be transparent to users.
+
+## Limitations
+* Data synchronization of primary and secondary databases is not supported.
+* Data inconsistency resulting from data synchronization delays between
primary and secondary databases is not supported.
+* Multi-write of primary database is not supported.
+* Transactional consistency between primary and secondary databases is not
supported. In the primary-secondary model, both data reads and writes in
transactions use the primary database.
+
+## How it works
+ShardingSphere's read/write splitting mainly relies on the related functions
of its kernel, including a parsing engine and a routing engine.
+The parsing engine converts the user's SQL into Statement information that can
be identified by ShardingSphere, and the routing engine performs SQL routing
according to the read/write type of SQL and transactional status.
+The routing from the secondary database supports a variety of load balancing
algorithms, including polling algorithm, random access algorithm, weight access
algorithm, etc.
+Users can also expand the required algorithm according to the SPI mechanism.
As shown in the figure below, ShardingSphere identifies read and write
operations and routes them to different database instances respectively.
+
+
+
+## 相关参考
+[Java
API](/en/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/java-api/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[YAML
Configuration](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/yaml-config/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[Spring Boot
Starter](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-boot-starter/rules/readwrite-splitting)\
+[Spring
Namespace](/cn/user-manual/shardingsphere-jdbc/spring-namespace/rules/readwrite-splitting)
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.cn.md
b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.cn.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 799535d7e3a..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.cn.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "使用规范"
-weight = 2
-+++
-
-## 支持项
-
-* 提供一主多从的读写分离配置,可独立使用,也可配合数据分片使用;
-* 事务中的数据读写均用主库;
-* 基于 Hint 的强制主库路由。
-
-## 不支持项
-
-* 主库和从库的数据同步;
-* 主库和从库的数据同步延迟导致的数据不一致;
-* 主库多写;
-* 主从库间的事务一致性。主从模型中,事务中的数据读写均用主库。
diff --git a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.en.md
b/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.en.md
deleted file mode 100644
index 63e16ef2efa..00000000000
--- a/docs/document/content/features/readwrite-splitting/use-norms.en.md
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
-+++
-title = "Use Norms"
-weight = 2
-+++
-
-## Supported
-
-* Provide the readwrite-splitting configuration of one primary database with
multiple replica databases, which can be used alone or with sharding table and
database;
-* Primary nodes need to be used for both reading and writing in the
transaction;
-* Forcible primary database route based on SQL Hint;
-
-## Unsupported
-
-* Data replication between the primary and the replica databases;
-* Data inconsistency caused by replication delay between databases;
-* Double or multiple primary databases to provide write operation;
-* The data for transaction across primary and replica nodes are inconsistent;
-In the readwrite-splitting model, primary nodes need to be used for both
reading and writing in the transaction.
