hailin0 commented on code in PR #321: URL: https://github.com/apache/skywalking-banyandb/pull/321#discussion_r1311028221
########## docs/concept/clustering.md: ########## @@ -1,17 +1,17 @@ # BanyanDB Clustering -BanyanDB Clustering introduces a robust and scalable architecture that comprises "Query Nodes", "Liaison Nodes", "Data Nodes", and "Meta Nodes". This structure allows for effectively distributing and managing time-series data within the system. +BanyanDB Clustering introduces a robust and scalable architecture that comprises "Liaison Nodes", "Data Nodes", and "Meta Nodes". This structure allows for effectively distributing and managing time-series data within the system. ## 1. Architectural Overview -A BanyanDB installation includes four distinct types of nodes: Data Nodes, Meta Nodes, Query Nodes, and Liaison Nodes. - -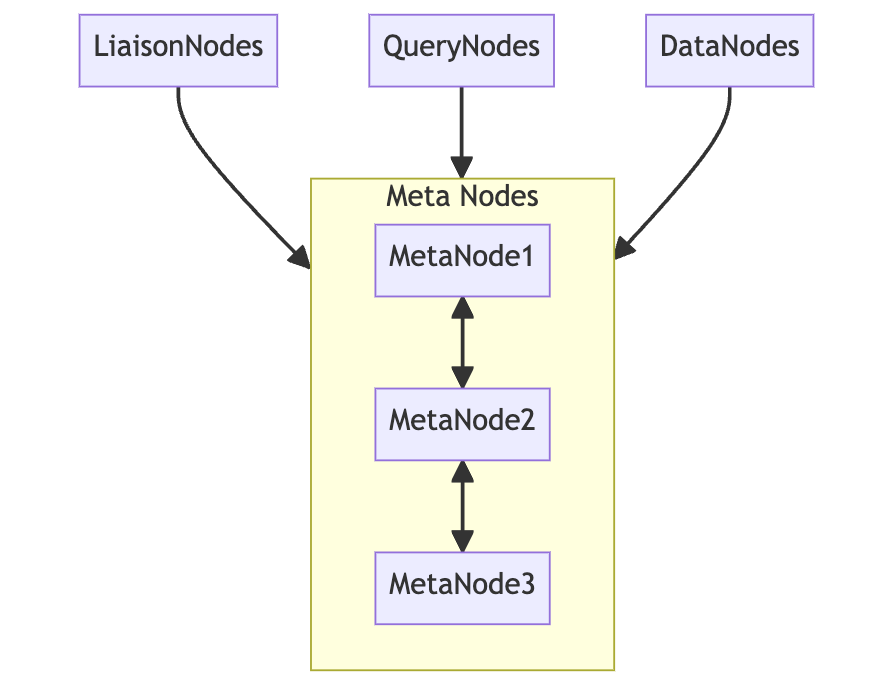 +A BanyanDB installation includes four distinct types of nodes: Data Nodes, Meta Nodes, and Liaison Nodes. Review Comment: `four distinct`? ########## docs/concept/clustering.md: ########## @@ -70,17 +59,17 @@ By storing shard allocation information, Meta Nodes help ensure that data is rou Data Nodes store all raw time series data, metadata, and indexed data. On disk, the data is organized by `<group>/shard-<shard_id>/<segment_id>/`. The segment is designed to support retention policy. -### 3.3 Query Nodes - -Query Nodes do not store data. They handle the computational tasks associated with data queries, interacting directly with Data Nodes to execute queries and return results. - -### 3.4 Liaison Nodes +### 3.3 Liaison Nodes Liaison Nodes do not store data but manage the routing of incoming requests to the appropriate Query or Data Nodes. They also provide authentication, TTL, and other security services. +They also handle the computational tasks associated with data queries, interacting directly with Data Nodes to execute queries and return results. + ## 4. **Determining Optimal Node Counts** -When creating a BanyanDB cluster, choosing the appropriate number of each node type to configure and connect is crucial. The number of Meta Nodes should always be odd, for instance, “3”. The number of Data Nodes scales based on your storage and query needs. The number of Query Nodes and Liaison Nodes depends on the expected query load and routing complexity. +When creating a BanyanDB cluster, choosing the appropriate number of each node type to configure and connect is crucial. The number of Meta Nodes should always be odd, for instance, “3”. The number of Data Nodes scales based on your storage and query needs. The number of Liaison Nodes depends on the expected query load and routing complexity. + +If the write and read load is from different sources, it is recommended to separate the Liaison Nodes for write and read. This allows for more efficient routing of requests and better performance. Review Comment: need further explanation why -- This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service. To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the URL above to go to the specific comment. To unsubscribe, e-mail: [email protected] For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at: [email protected]
