nvazquez opened a new pull request #3610: [WIP DO NOT MERGE] KVM: Rolling maintenance URL: https://github.com/apache/cloudstack/pull/3610 ## Description Feature Specification: https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/CLOUDSTACK/%5BKVM%5D+Rolling+Maintenance+of+hosts This feature allows automating the upgrade/patch process of KVM hosts within a zone, pod or cluster by executing custom scripts. In a typical scenario prior this feature, the administrator needed to automate the process of setting hosts in maintenance before performing the upgrade on each host. It is commonly achieved using external automation tools. This feature allows administrators to perform the automation process within CloudStack, providing a flexible framework that allows to define custom scripts to execute on each host. CloudStack executes these scripts within the context of stages. This feature defines 4 stages for a host in the rolling maintenance process: - Pre-flight: Pre-flight script will be run on all hosts as part of the pre-flight checks that are carried out before commencing the rolling maintenance. If pre-flight check scripts return an error from any host, then rolling maintenance will be cancelled with no actions taken, and an error returned. If there are no pre-flight scripts defined, then no checks will be done from the hosts. - Pre-maintenance: Pre-maintenance script runs 'before' a specific host is put into maintenance. If no pre-maintenance script is defined, or if the pre-flight script on a given host determines no pre-maintenance is required on that host, then no pre-maintenance actions will be done, and the management server will move straight to putting the host in maintenance followed by requesting the agent to run the maintenance script. - Maintenance: Maintenance script runs after a host has been put into maintenance. If no maintenance script is defined, or if the pre-flight or pre-maintenance scripts on a given host determine that no maintenance is required on that host, then the host will not be put into maintenance, and the completion of the pre-maintenance scripts will signal the end of all maintenance tasks and the KVM agent will hand the host back to the management server. Once the maintenance scripts have signalled that it have completed, the host agent will signal to the management server that the maintenance tasks have completed, and therefore the host is ready to exit maintenance mode and any 'information' which was collected (such as processing times) will be returned to the management server. - Post maintenance: Post-maintenance script is expected to perform validations after the host exits maintenance. These scripts will help to detect any problem during the maintenance process, including reboots or restarts within scripts. The administrator will be responsible for the maintenance and copying of the hook scripts across all KVM hosts. On all the KVM hosts to undergo rolling maintenance, a maintenance hooks directory will be defined in the ‘agent.properties’. Administrators must define only one script per stage. In case a stage does not contain a script, it is skipped, continuing with the next stage. Administrators are responsible for defining and copying scripts into the hosts. On all the KVM hosts to undergo rolling maintenance, there are two type of scripts execution approaches: - Systemd service executor: This approach uses a systemd service to invoke a script execution. Once a script finishes its execution, it will write content to a file, which the agent reads and sends back the result to the management server. - Agent executor: The CloudStack agent invokes a script execution within the JVM. In case the agent is stopped or restarted, the management server will assume the stage was completed when the agent reconnects. This approach does not keep the state in a file. The API command to commence rolling maintenance will allow for multiple hosts or clusters or pods or zones to be specified (though each type is mutually exclusive). Before commencing any rolling maintenance actions, pre-flight checks will be run. These fall into two categories: - State and capacity and checks on the hosts and clusters to check that a successful run should be possible 'at this time'. - The pre-flight scripts on the hosts. Which are created by the admin to check that a successful run should be possible 'at the time' from the context of the specific actions of the scripts. (i.e. checking that each host can access the yum repo) If maintenance scripts have been defined, prior to running any scripts on a host, capacity within the cluster to put the given host into maintenance will be re-checked. If it is found there is not enough capacity in the cluster for that host to successfully go into maintenance, rolling maintenance will immediately stop and an error be output to the logs Given, that compute demands on any cluster are dynamic (i.e. the virtual machines can be started stopped or created at any time), a cluster will be disabled once the prefight checks have been successfully completed, and re-enabled upon the completion of the rolling maintenance on the cluster OR upon a failure during the maintenance of a host to minimise the impact on end users. ### Management server A new API method is created to start the automated rolling maintenance process on hosts, ‘startRollingMaintenance’, with the following parameters: - ‘hostid’, ‘clusterid’, ‘podid’ and ‘zoneid’ are mutually exclusive, and only one of them must be passed. - ‘forced’: false by default. When enabled, does not stop iterating through hosts in case of any error in the rolling maintenance process. - ‘timeout’: defines a timeout in seconds for a stage to be completed in a host - 'payload': extra parameters to be passed as parameters on scripts ### KVM hosts Two new properties must be set in the agent.properties file: - ‘rolling.maintenance.hooks.dir’: Pointing to the directory in which the custom scripts are defined - ‘rolling.maintenance.service.mode.disabled’: false by default. When enabled, the service execution is disabled, using the CloudStack agent as the scripts’ executor. A new systemctl service is defined to handle scipts’ execution. This service is started by the CloudStack agent when executing a script, allowing to be executed outside of the JVM in which the CloudStack agent runs. With this approach, a script execution is not terminated if the CloudStack agent is terminated, as both processes are not related. This service invokes an executor script which simply invokes the custom script in a given path. ## Types of changes - [ ] Breaking change (fix or feature that would cause existing functionality to change) - [x] New feature (non-breaking change which adds functionality) - [ ] Bug fix (non-breaking change which fixes an issue) - [ ] Enhancement (improves an existing feature and functionality) - [ ] Cleanup (Code refactoring and cleanup, that may add test cases) ## Screenshots (if appropriate): 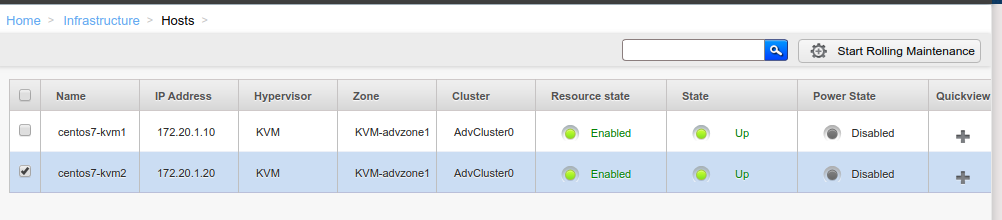 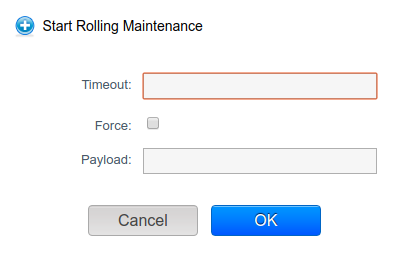 ## How Has This Been Tested?
---------------------------------------------------------------- This is an automated message from the Apache Git Service. To respond to the message, please log on to GitHub and use the URL above to go to the specific comment. For queries about this service, please contact Infrastructure at: [email protected] With regards, Apache Git Services
